©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Oncol. Jul 24, 2025; 16(7): 107788
Published online Jul 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i7.107788
Published online Jul 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i7.107788
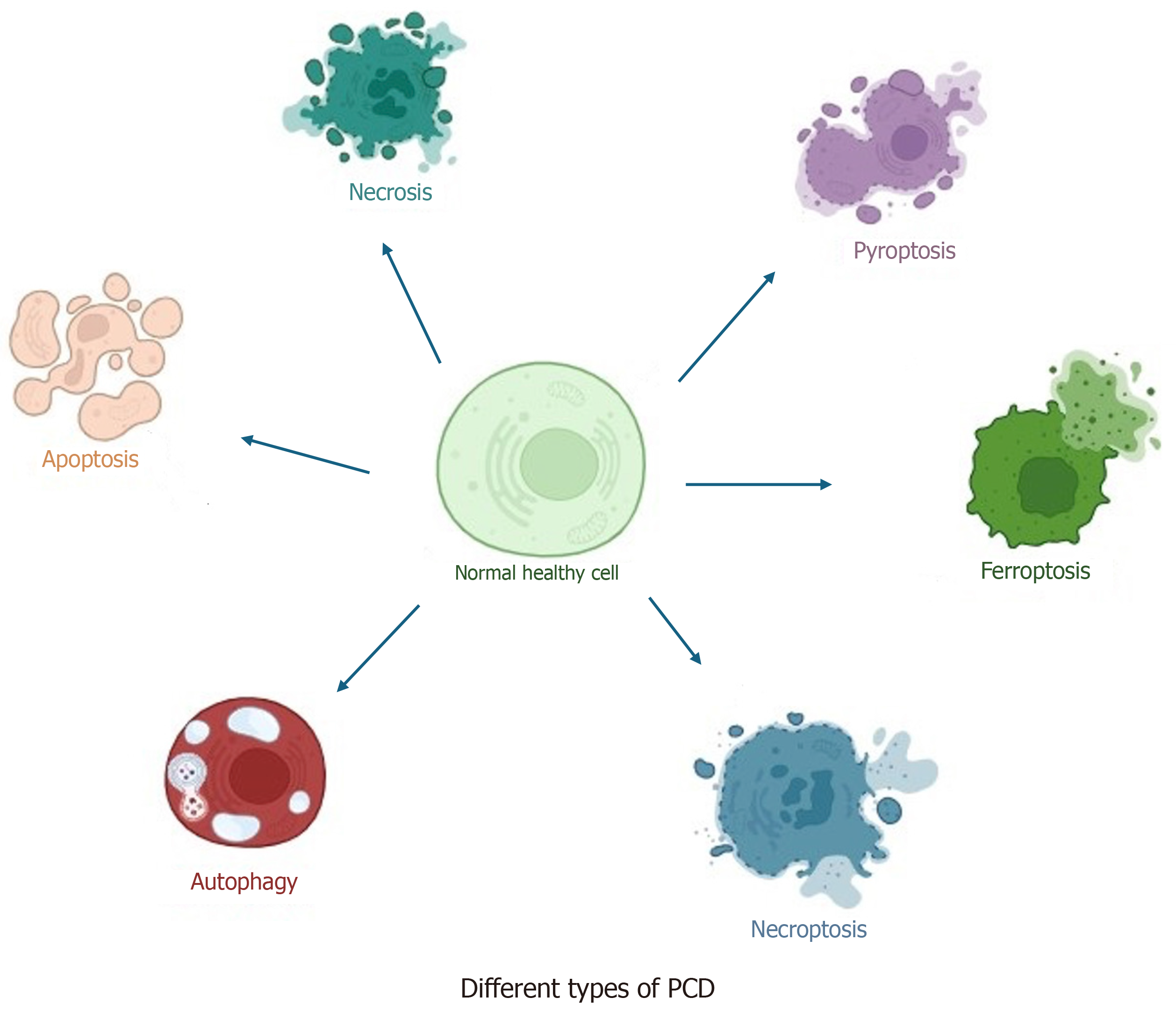
Figure 1 Various forms of programmed cell death.
Programmed cell death is a crucially controlled form of cell death, where different pathways regulate the process. Programmed cell death (PCD) is necessary to maintain cell homeostasis, control growth, and support immunity. PCD primarily occurs in two forms: Apoptotic and non-apoptotic. Non-apoptotic forms of cell death have been studied only in the past decade, including ferroptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis.
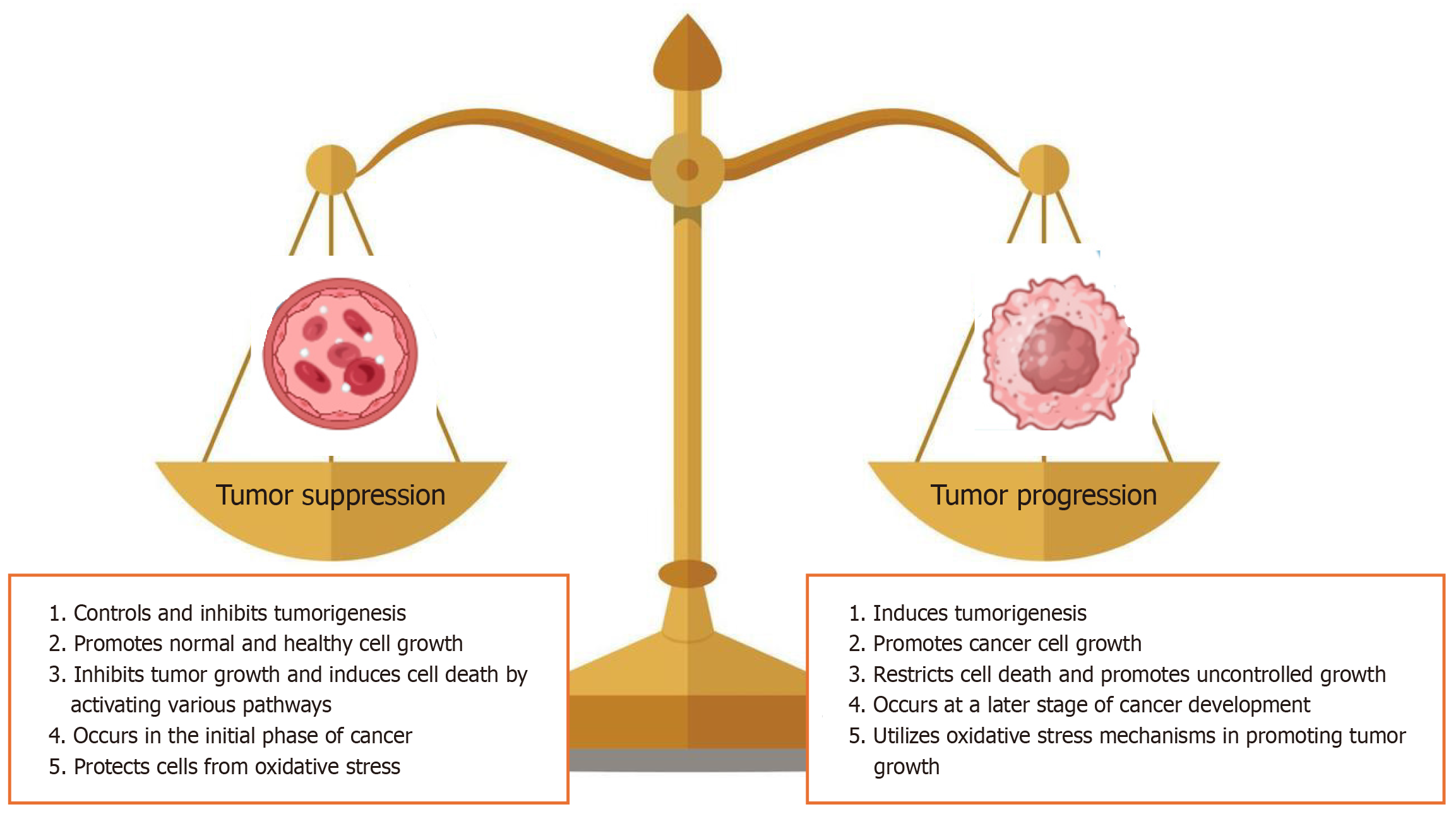
Figure 2 Dual role of autophagy in tumorigenesis.
At an early stage of cancer, autophagy controls the tumor progression and causes cell death. By contrast, autophagy promotes tumor growth under stress conditions where reactive oxygen species and oxidative stress increase.
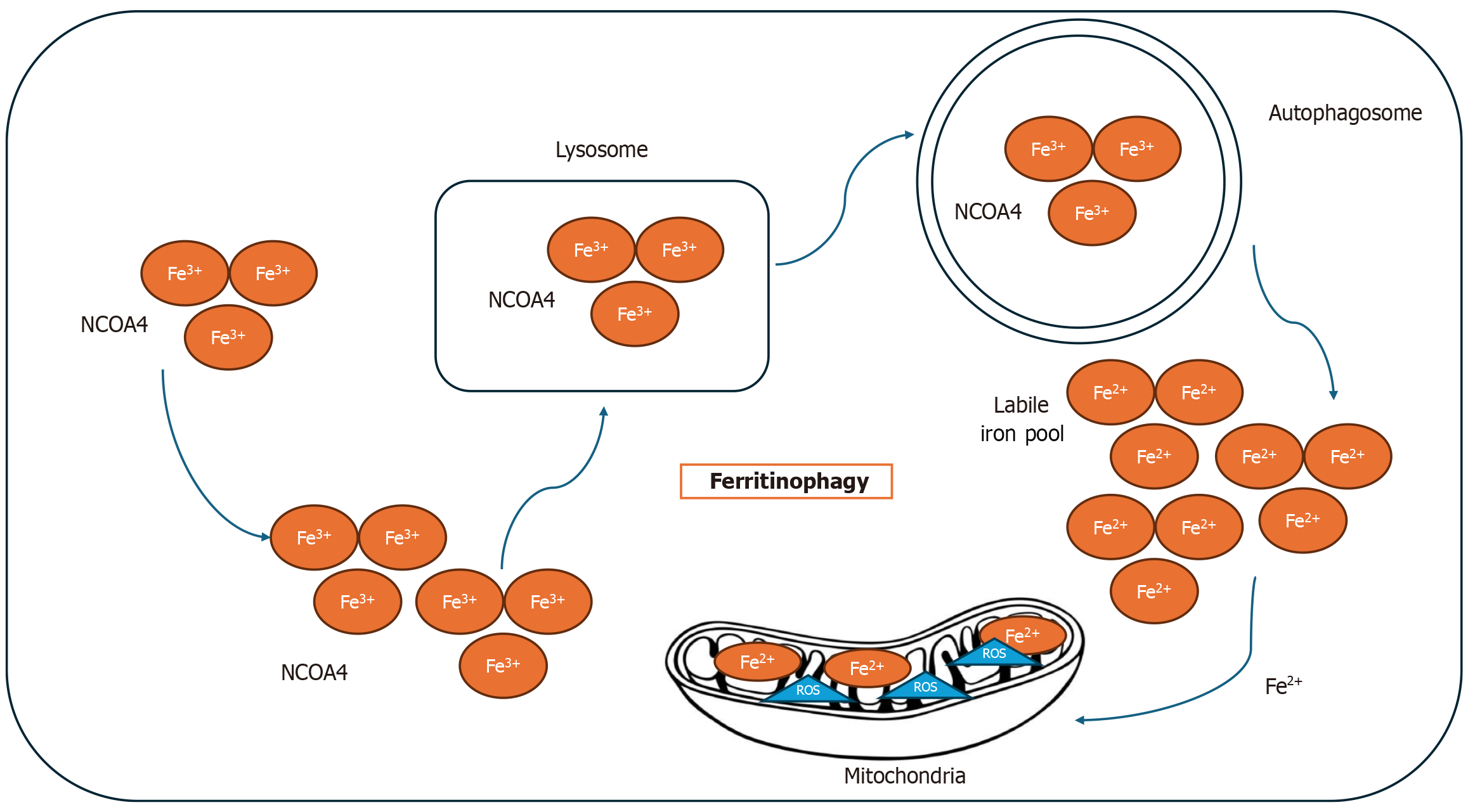
Figure 3 Mechanism of ferritinophagy.
Ferritin is transported to the autophagolysosome with the help of nuclear receptor coactivator 4 (NCOA4), leading to the degradation of ferritin and the release of free iron. The increase of free iron intracellularly leads to the production of reactive oxygen species in labile iron pool. As a result, the cells become sensitive to ferroptosis. Fe2+: Ferrous iron; Fe3+: Ferric iron.
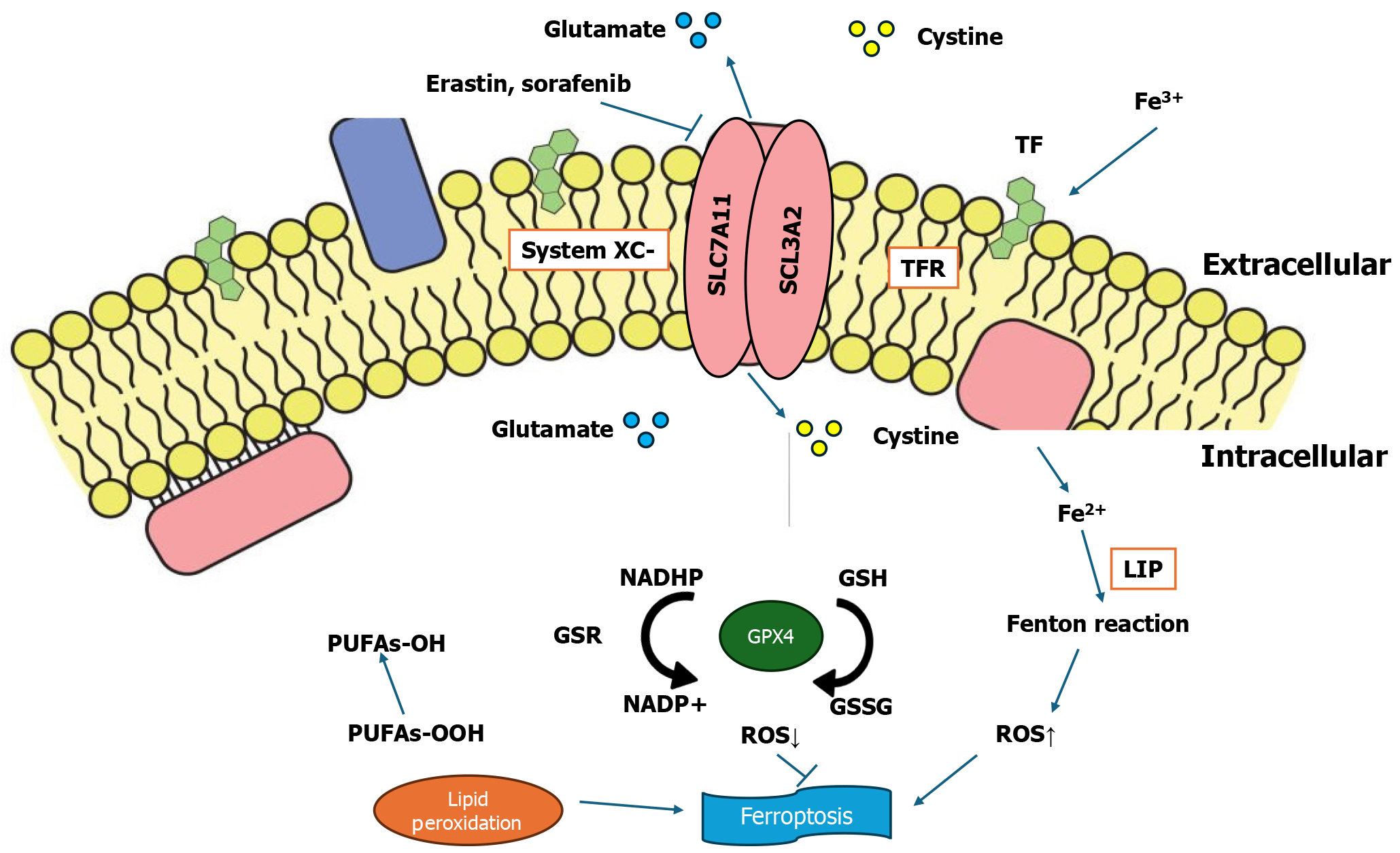
Figure 4 Ferroptosis regulatory pathway, along with the effects of drugs on ferroptosis.
System Xc- is a heterodimer of a light chain and heavy chain subunit, solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11) and SLC3A2, respectively. These function in importing cysteine and exporting glutamate. The accumulation of a labile iron pool, reactive oxygen species, and lipid peroxidation plays a crucial role in causing ferroptosis. Glutathione phosphate (GPX4) is responsible for lipid peroxidation. Drugs such as erastin and sorafenib may inhibit the role of System Xc-. RAS-selective lethal 3 inhibits the activity of GPX4.
- Citation: Rana TA, Prajapati A. Unleashing the potential of ferroptosis, autophagy, and mitochondrial dynamics as emerging modalities in cancer treatment. World J Clin Oncol 2025; 16(7): 107788
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v16/i7/107788.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v16.i7.107788