Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Oncol. Jun 24, 2025; 16(6): 105996
Published online Jun 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i6.105996
Published online Jun 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i6.105996
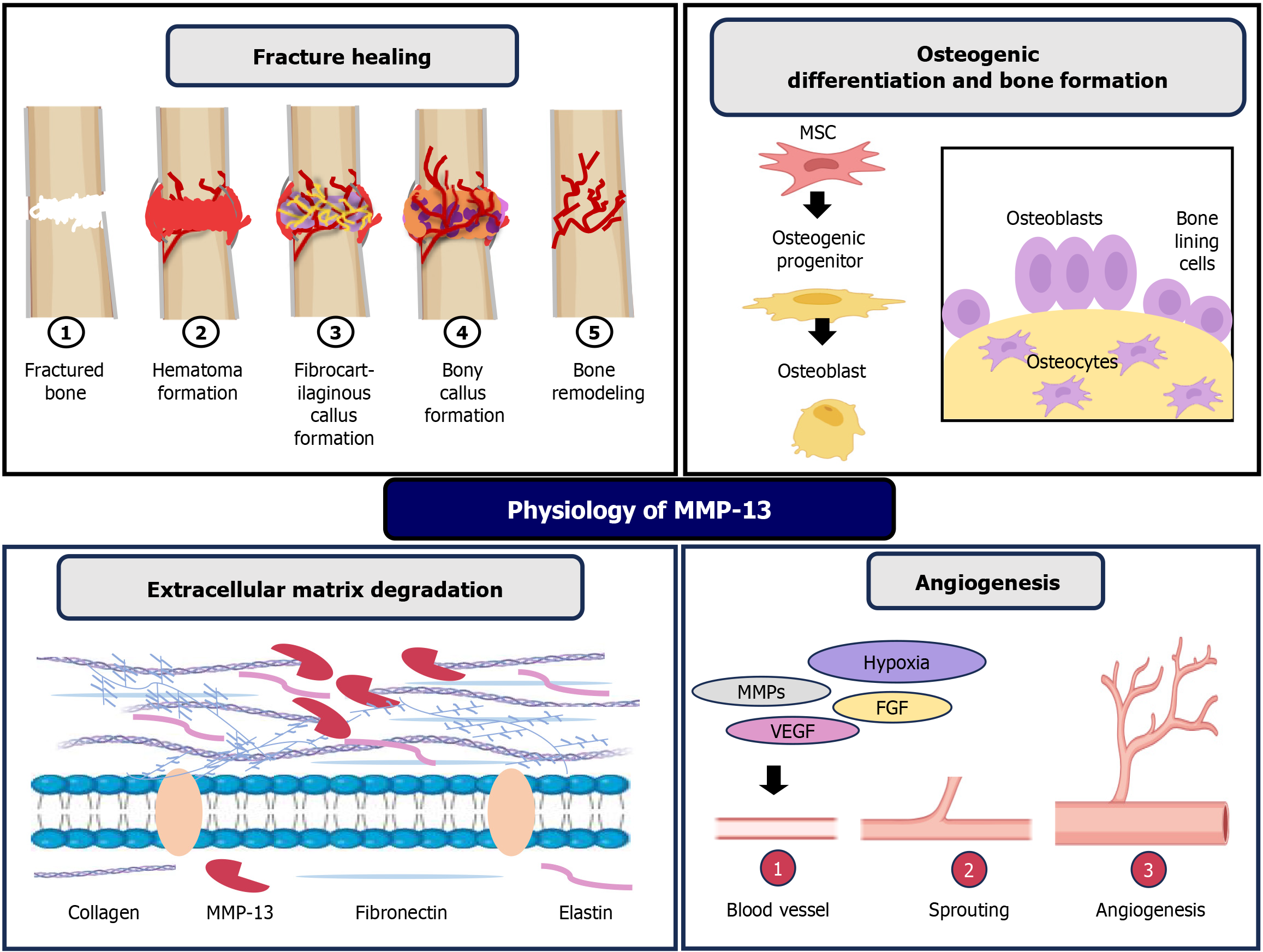
Figure 1 Physiological role of matrix metalloproteinase-13.
A schematic diagram illustrates the diverse functions of matrix metalloproteinase-13 in various physiological processes. MSC: Mesenchymal stem cells; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase; FGF: Fibroblast growth factor; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor.
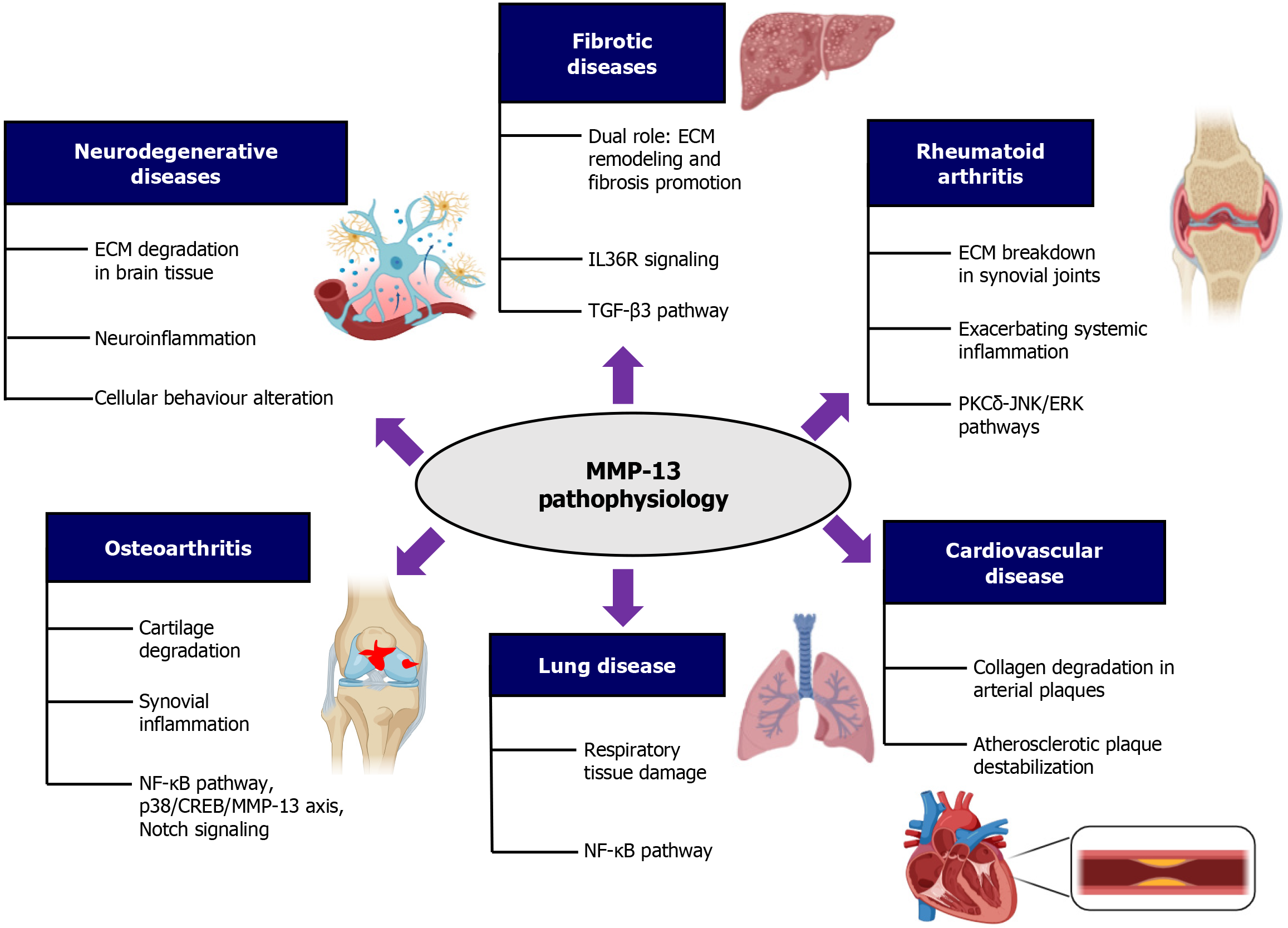
Figure 2 Pathophysiological role of matrix metalloproteinase-13 in various diseases.
A schematic diagram illustrates the involvement of matrix metalloproteinase-13 (MMP-13) in the development and progression of various diseases. ECM: Extracellular matrix; PKC: Protein kinase C delta; JNK: Jun N-terminal kinase; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; CREB: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate-response element binding protein; IL36R: Interleukin 36R; TGF-β3: Transforming growth factor-beta 3; MMP-13: Matrix metalloproteinase-13.
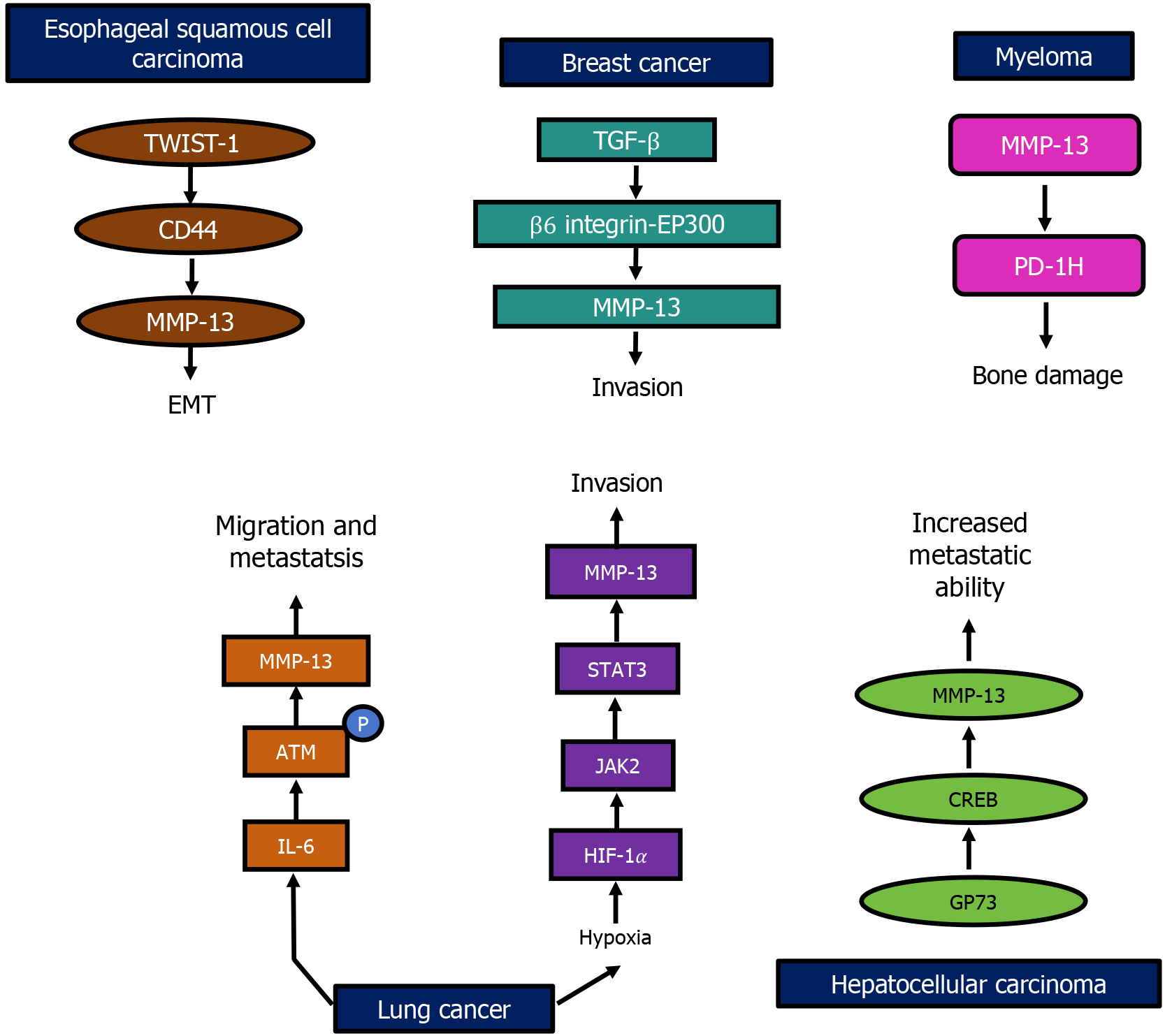
Figure 3 Matrix metalloproteinase-13-mediated cancer progression.
The overexpression of matrix metalloproteinase-13 (MMP-13) has been associated with increased invasion, migration, and metastasis in different types of cancer. In breast cancer, transforming growth factor-β/β6 integrin-histone acetyltransferase p300/MMP-13 axis increases the invasive potential, and in lung cancer, hypoxia-inducible factor 1/ Janus kinase 2/signal transducers and activators of transcription 3/MMP-13 and interleukin 6/ataxia telangiectasia mutated protein/MMP-13 axes are involved in tumor aggressiveness. Then, the Golgi protein 73/cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element-binding protein/MMP-13 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma further accelerates metastasis. TWIST 1: Twist family basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor 1; MMP-13: Matrix metalloproteinase-13; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-β; EP-300: Histone acetyltransferase p300; PD-1H: Programmed death-1 homolog; ATM: Ataxia telangiectasia mutated protein; EMT: Epithelial mesenchymal transition; IL-6: Interleukin 6; HIF-1: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1; JAK2: Janus kinase 2; STAT3: Signal transducers and activators of transcription 3; GP73: Golgi protein 73; CREB: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element-binding protein.
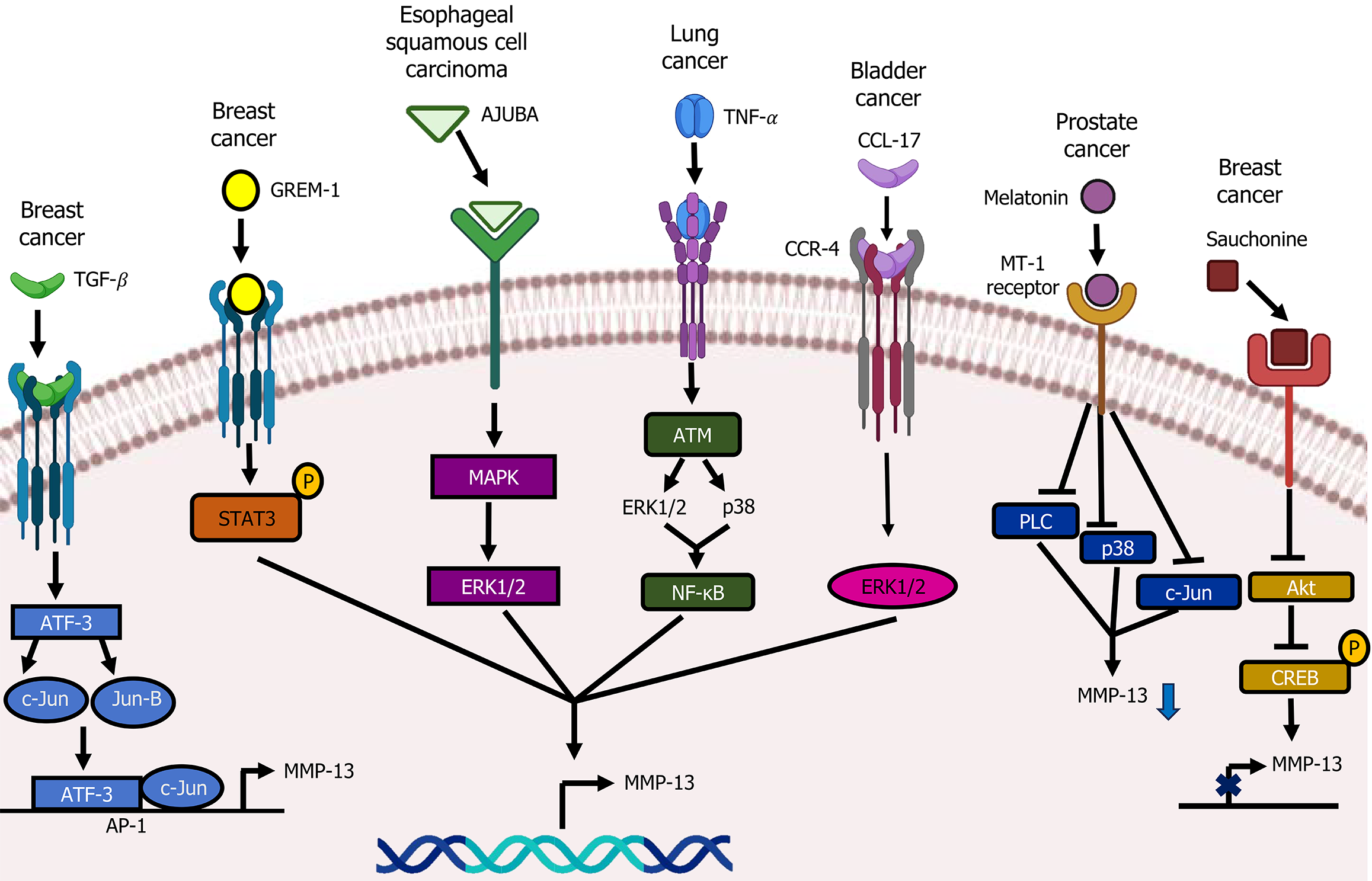
Figure 4 Signaling pathways controlling matrix metalloproteinase-13 in cancer.
This figure shows the most important signaling pathways regulating matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression in various cancers, such as breast cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, lung cancer, bladder cancer, and prostate cancer. MMP-13: Matrix metalloproteinase-13; ATF3: Activating transcription factor 3, STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; AP1: Activating protein 1; GREM1: Gremlin-1, TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor α; ATM: Ataxia telangiectasia mutated protein; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-β; MAPK: Mitogen activated protein kinase; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; PLC: Phospholipase C; Akt: Protein kinase B; CREB: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element-binding protein; c-Jun: Cellular Jun; CCR4: C-C motif chemokine receptor 4; CCL-17: C-C motif chemokine ligand 17.
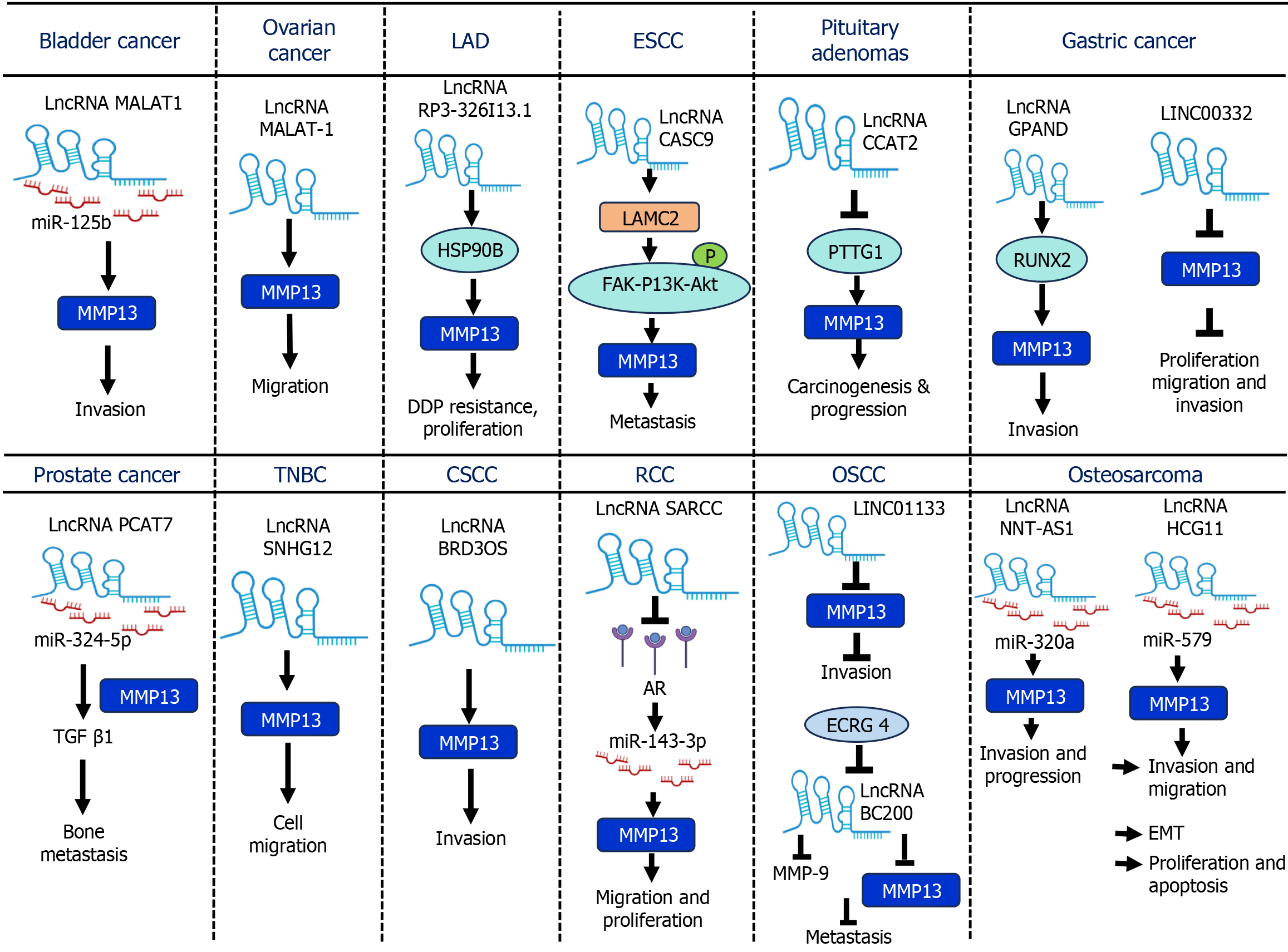
Figure 5 Involvement of long non-coding RNAs in regulating matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression in cancer.
This figure illustrates the role of long non-coding RNAs in regulating matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression across various cancer types. LncRNAs: Long non-coding RNAs; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase; LAD: Lung adenocarcinoma; ESCC: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; TNBC: Triple negative breast cancer; CSCC: Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma; RCC: Renal cell carcinoma; OSCC: Oral squamous cell carcinoma; HSP90B: Heat shock protein-90 beta; LAMC2: Laminin subunit gamma 2; PTTG1: Pituitary tumor transforming gene 1; RUNX2: Runt-related transcription factor 2; TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor beta 1; AR: Androgen receptor; ECRG4: Esophageal cancer related gene 4; EMT: Epithelial mesenchymal transition; MALAT1: Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1; CASC9: Cancer susceptibility candidate 9; CCAT2: Colon cancer associated transcript 2; GPAND: Gastric progression associated non-coding RNA; PCAT7: Prostate cancer-associated transcript 7; SNHG12: Small nucleolar RNA host gene 12; SARCC: Suppressing androgen receptor in renal cell carcinoma; NNT-AS1: Nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase antisense RNA 1; HCG11: Human leukocyte antigen complex group 11; FAK: Focal adhesion kinase; P13K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; Akt: Protein kinase B.
- Citation: Chidambaram D, Subashini V, Nanthanalaxmi M, Saranya I, Selvamurugan N. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-13 in cancer: Signaling pathways and non-coding RNAs in tumor progression and therapeutic targeting. World J Clin Oncol 2025; 16(6): 105996
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v16/i6/105996.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v16.i6.105996