©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Oncol. May 24, 2025; 16(5): 104138
Published online May 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i5.104138
Published online May 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i5.104138
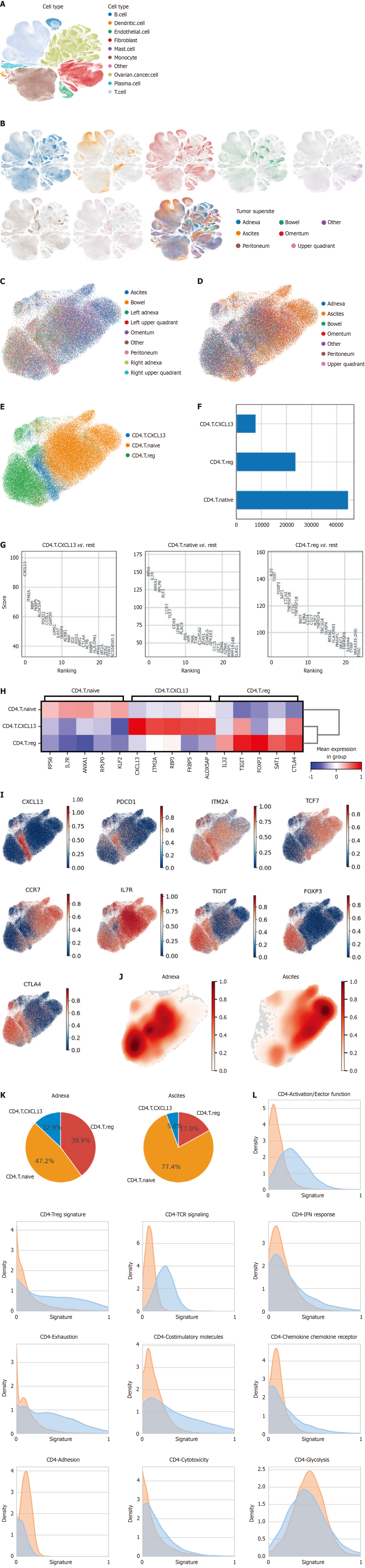
Figure 1 Distinct CD4+ T cell subtypes and functional signatures in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma microenvironments.
A: UMAP visualization showing the distribution of all cell subtypes across samples from 42 high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma patients; B: UMAP visualization demonstrating the anatomical origins of all cells, including samples from ascites and multiple tumor sites; C: UMAP visualization demonstrating distinct transcriptional profiles of CD4+ T cells isolated from adnexal tissues; D: UMAP visualization showing transcriptional profiles of CD4+ T cells isolated from ascites; E: Identification of major CD4+ T cell subtypes: Naive CD4+ T cells, regulatory T cells (Tregs), and CXCL13-expressing CD4+ T cells; F: Distribution of cell counts across the three identified CD4+ T cell subtypes; G: Top-ranked marker genes for each CD4+ T cell subtype identified by differential expression analysis; H: Expression heatmap highlighting key marker genes for distinct CD4+ T cell subtypes, including naive T cells, regulatory T cells (Tregs), and CXCL13-expressing CD4+ T cells. The heatmap reveals subtype-specific transcriptional profiles; I: UMAP feature plots displaying the expression patterns of marker genes for distinct CD4+ T cell subtypes across all sampled tissues; J: Density plots showing the spatial distribution of CD4+ T cells in adnexal tissues (left) and ascites (right) on UMAP projections; K: Pie charts depicting the proportional composition of CD4+ T cell subtypes in adnexal tissues (left) and ascites (right); L: Functional profiling of CD4+ T cell subtypes, comparing signatures for TCR signaling, activation, exhaustion, co-stimulatory molecules, and glycolytic metabolism between adnexa and ascites, highlighting distinct tissue-specific immune profiles.
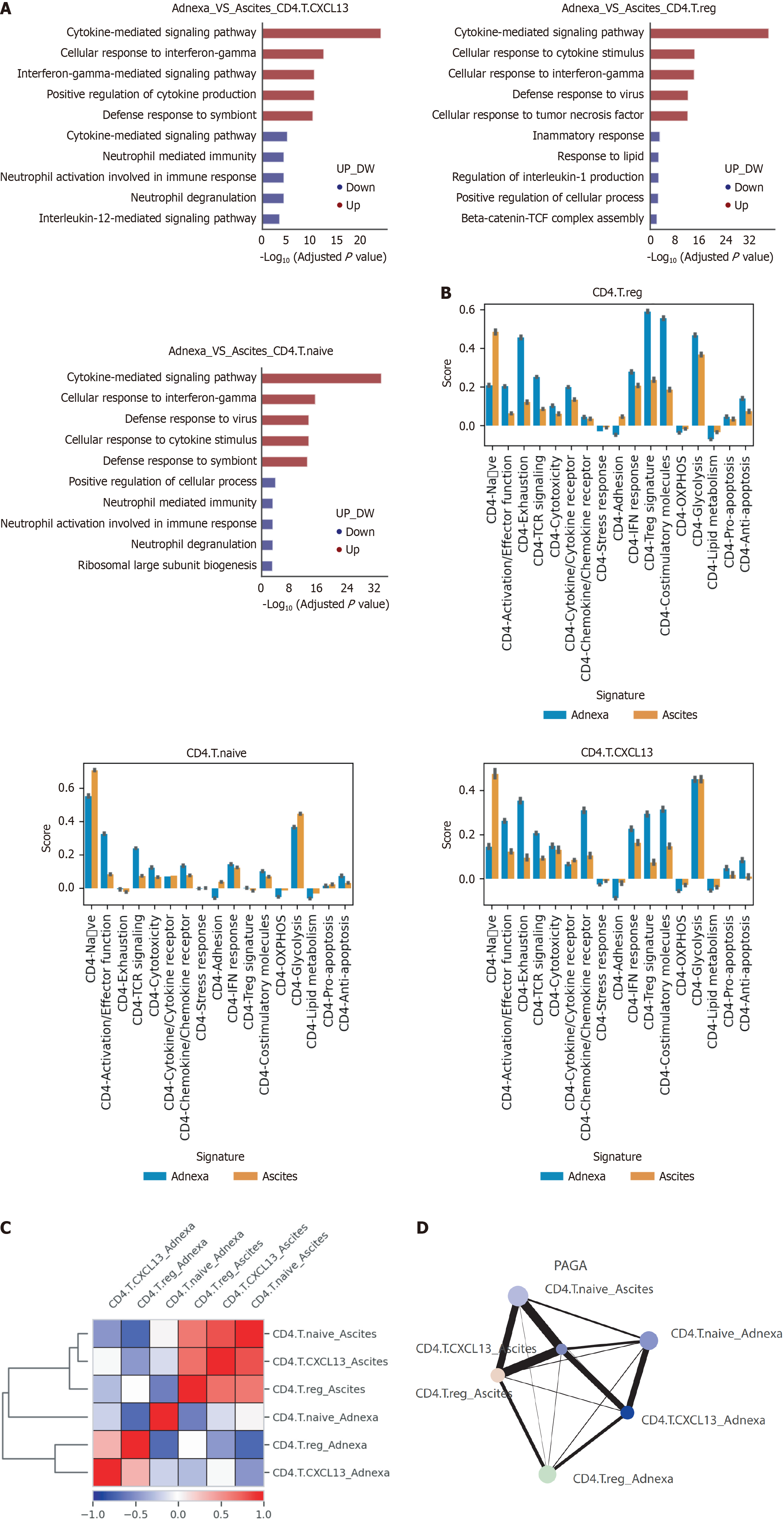
Figure 2 Functional and pathway differences of CD4+ T cell subtypes between adnexal tissues and ascites in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma patients.
Differential pathway analysis highlights the distinct functional roles of CD4+ T cell subtypes in adnexal tissues vs ascites. A: Differential pathway enrichment analysis of CD4+ T cell subtypes in adnexal tissues vs ascites; B: Comparative functional signature scores of CD4+ T cell subtypes in adnexal tissues and ascites; C: Correlation heatmap of CD4+ T cell subtypes between adnexal tissues and ascites; D: Partition-based graph abstraction analysis of CD4+ T cell subtypes across adnexal tissues and ascites.
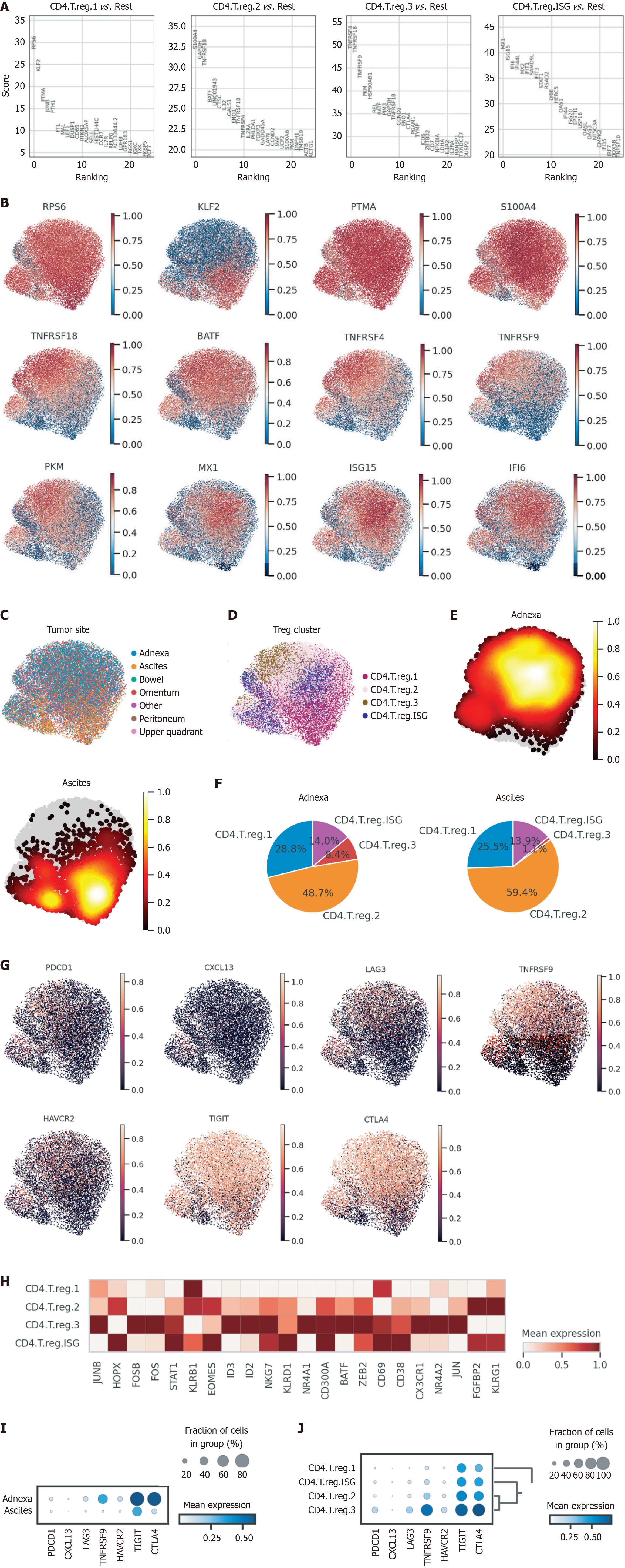
Figure 3 Differential distribution and functional profiling of regulatory T cell subtypes in adnexa and ascites.
A: Marker gene ranking for CD4+ Treg subtypes; B: UMAP plots illustrating the expression of key marker genes across CD4+ Treg subtypes; C: Correlation heatmap of CD4+ T cell subtypes between adnexal tissues and ascites; D: UMAP visualization of CD4+ Treg subtypes; E: Density distribution of Treg cells in adnexa and ascites; F: Proportional distribution of CD4+ Treg subtypes in adnexa and ascites; G: UMAP visualization of exhaustion and activation marker expression in Treg cells; H: Heatmap of key transcriptional regulators and marker expression across Treg subtypes; I: Expression levels and group distribution of exhaustion markers in Treg cells across adnexa and ascites; J: Exhaustion marker expression across Treg subtypes.
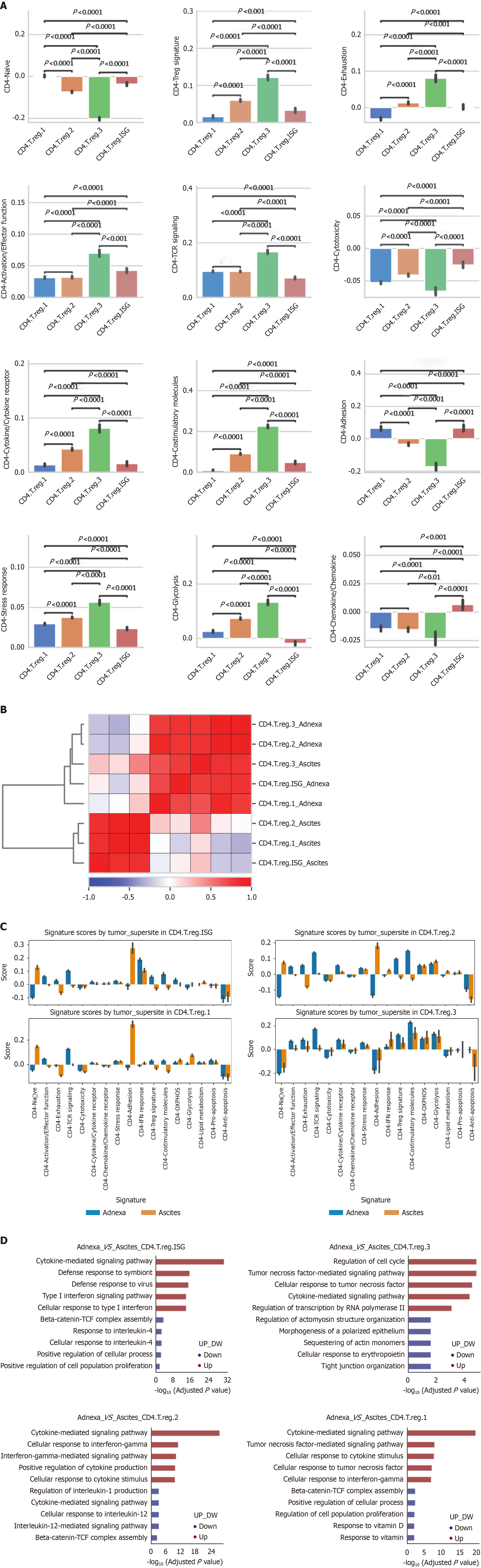
Figure 4 Tissue-specific adaptations and functional heterogeneity of CD4+ Treg subtypes in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma.
A: Functional Diversity of CD4+ Treg subtypes in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma (HGSOC); B: Hierarchical clustering of CD4+ Treg subtypes across adnexal and ascitic microenvironments in HGSOC; C: Comparative functional profiling of CD4+ Treg subtypes between adnexa and ascites in HGSOC; D: Differential pathway enrichment of CD4+ Treg subtypes between adnexa and ascites in HGSOC.
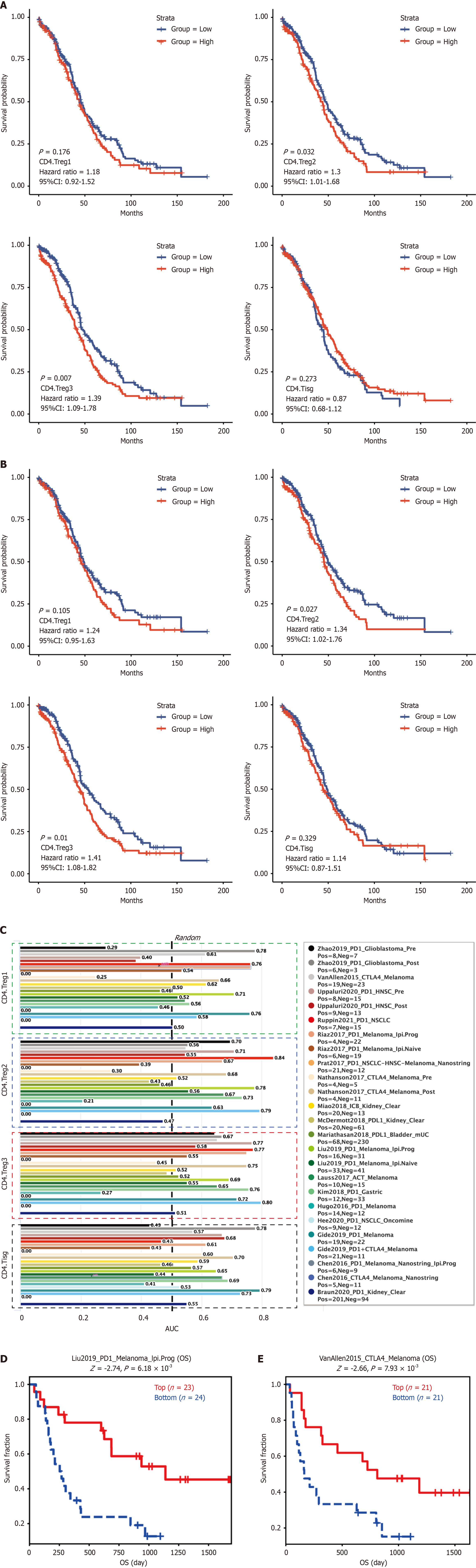
Figure 5 Prognostic significance of CD4+ T cell subtypes in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma.
A: Overall survival analysis of CD4+ Treg subtypes in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma; B: Disease-specific survival analysis of CD4+ Treg subtypes in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma; C: Predictive performance of CD4+ Treg subtypes for immunotherapy response across multiple datasets; D: Association of CD4.Treg3 expression with overall survival in melanoma patients treated with PD-1 inhibitors; E: Impact of CD4.Treg3 expression on overall survival in melanoma patients treated with CTLA-4 inhibitors.
- Citation: Zhang BL, Gao W, He L, Liu XT, Wang ZM, Tan L. Functional heterogeneity and clinical implications of CD4+ T cell subtypes in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma. World J Clin Oncol 2025; 16(5): 104138
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v16/i5/104138.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v16.i5.104138