©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Oncol. Apr 24, 2024; 15(4): 531-539
Published online Apr 24, 2024. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i4.531
Published online Apr 24, 2024. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i4.531
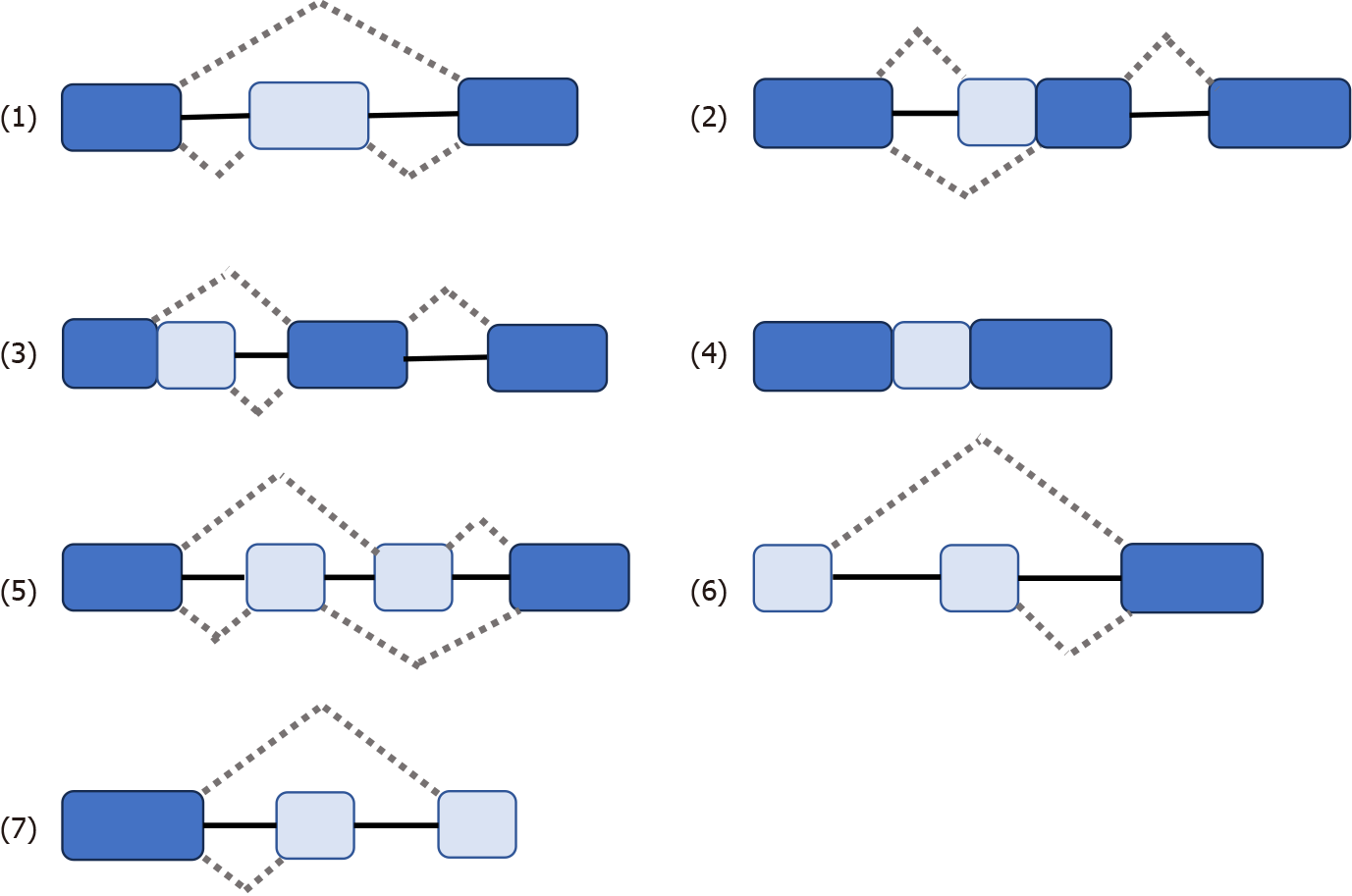
Figure 1 Seven types of variable splicing in vivo.
(1) ES: Exon skip; (2) RI: Retained intron; (3) AD: Alternate Donor site; (4) AA: Alternate acceptor site; (5) AP: Alternate promoter; (6) AT: Alternate terminator; (7) ME: Mutually exclusive exons.
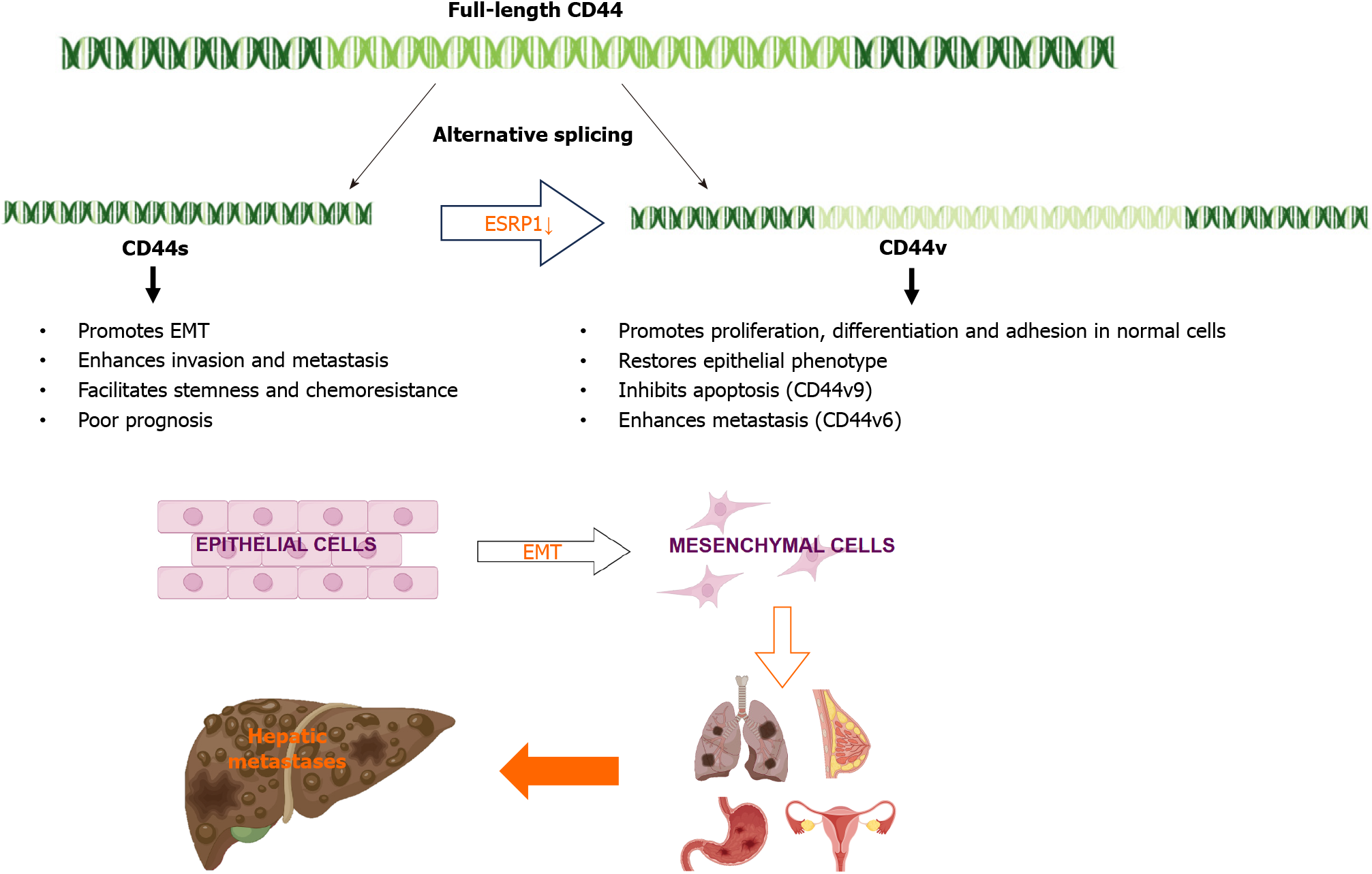
Figure 2 During Epithelial-mesenchymal transition, epithelial splicing regulatory protein 1 expression is reduced, promoting the transition from variant CD44 to standard CD44, and can promote liver metastasis of lung, breast, stomach, and ovarian cancers.
CD44s: Standard CD44; CD44v: Variant CD44; ESRP1: Epithelial splicing regulatory protein 1; EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
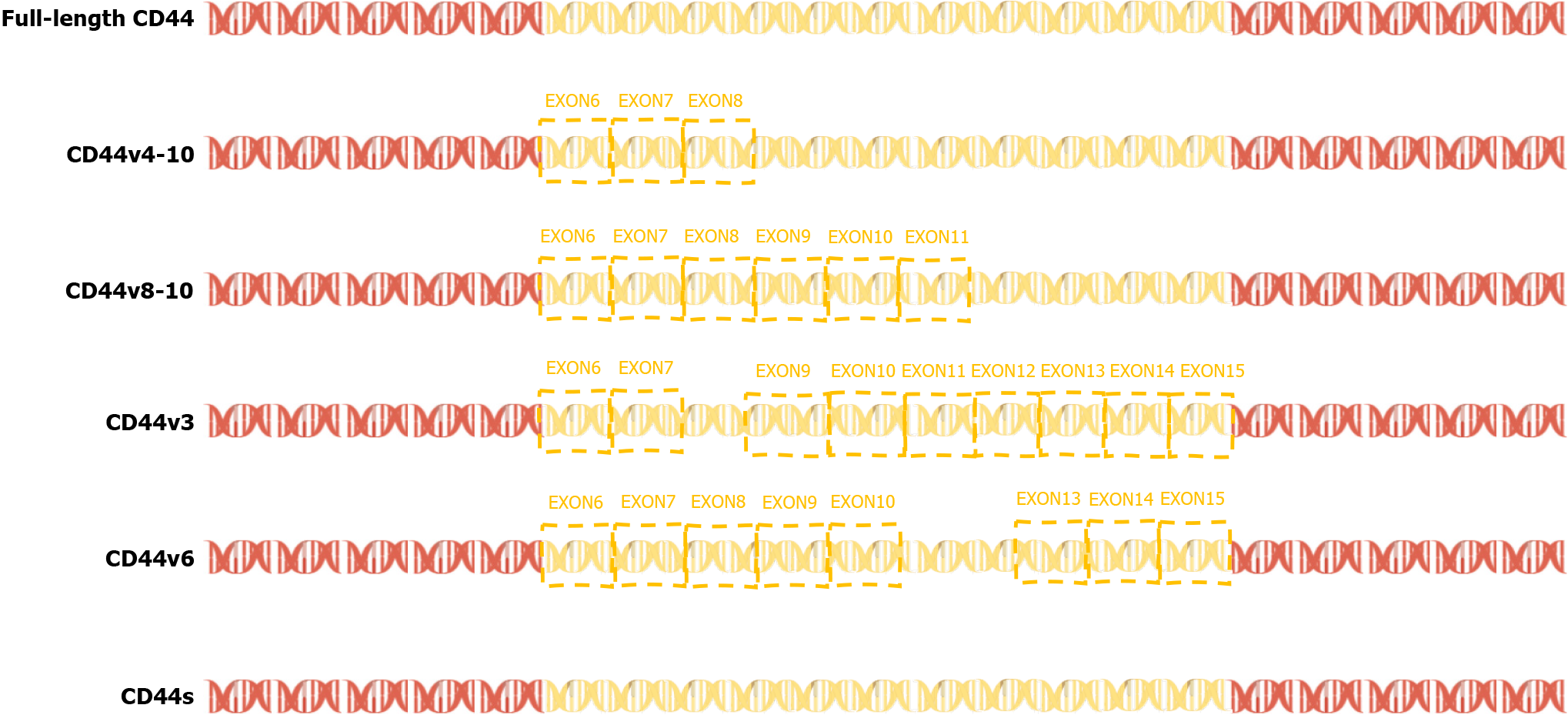
Figure 3 Exons 6-14 of CD44 gene undergo alternative splicing in the membrane-proximal stem region, resulting in a variety of variable splicing variants (CD44 variant isoform, variant CD44; Including CD44v2-v10).
CD44s: Standard CD44; CD44v: Variant CD44.
- Citation: Geng DY, Chen QS, Chen WX, Zhou LS, Han XS, Xie QH, Guo GH, Chen XF, Chen JS, Zhong XP. Molecular targets and mechanisms of different aberrant alternative splicing in metastatic liver cancer. World J Clin Oncol 2024; 15(4): 531-539
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v15/i4/531.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v15.i4.531