©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Oncol. Dec 24, 2020; 11(12): 1076-1083
Published online Dec 24, 2020. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v11.i12.1076
Published online Dec 24, 2020. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v11.i12.1076
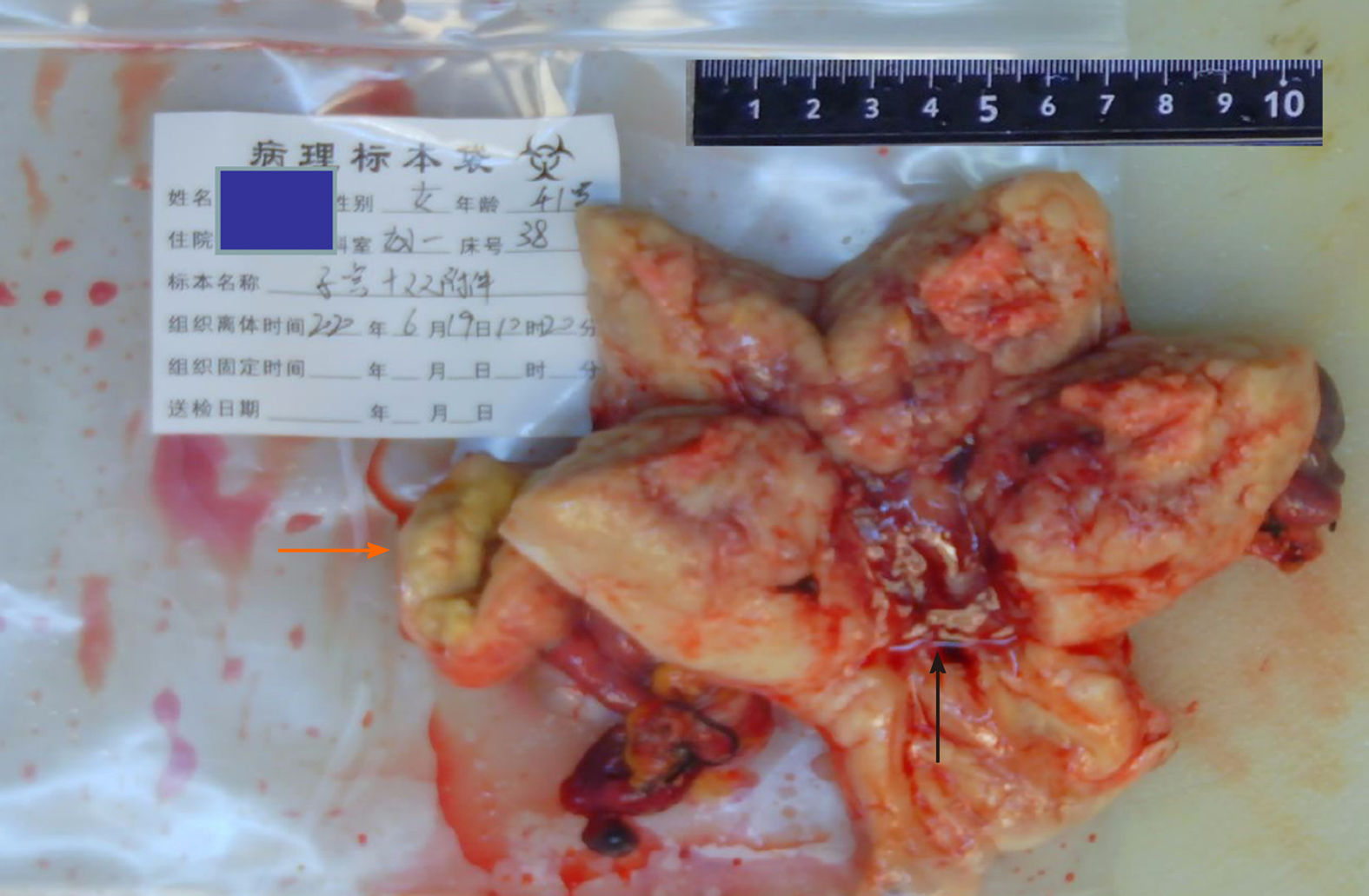
Figure 1 Cauliflower mass in the uterine cavity (black arrow) and right oviduct mass (orange arrow).
Figure 2 Histology of the uterine tumor (hematoxylin and eosin staining).
A: The cancer tissue showed nest-like and solid infiltration into the myometrium; B: The cytoplasm of tumor cells was clear; C: Tumor cells were papillary and had a stud-like arrangement; D: Tumor cells were arranged in a glandular tube. Mucus was present in the gland cavity.
Figure 3 Immunohistochemical staining of the intrauterine tumor.
A: Positivity for CK7; B: Positivity for Napsin-A; C: Positivity for P16; D: High Ki-67 index; E: Negativity for vimentin; F: Negativity for ER; G: Wild type p53; H: Negativity for Wilms’ tumor 1.
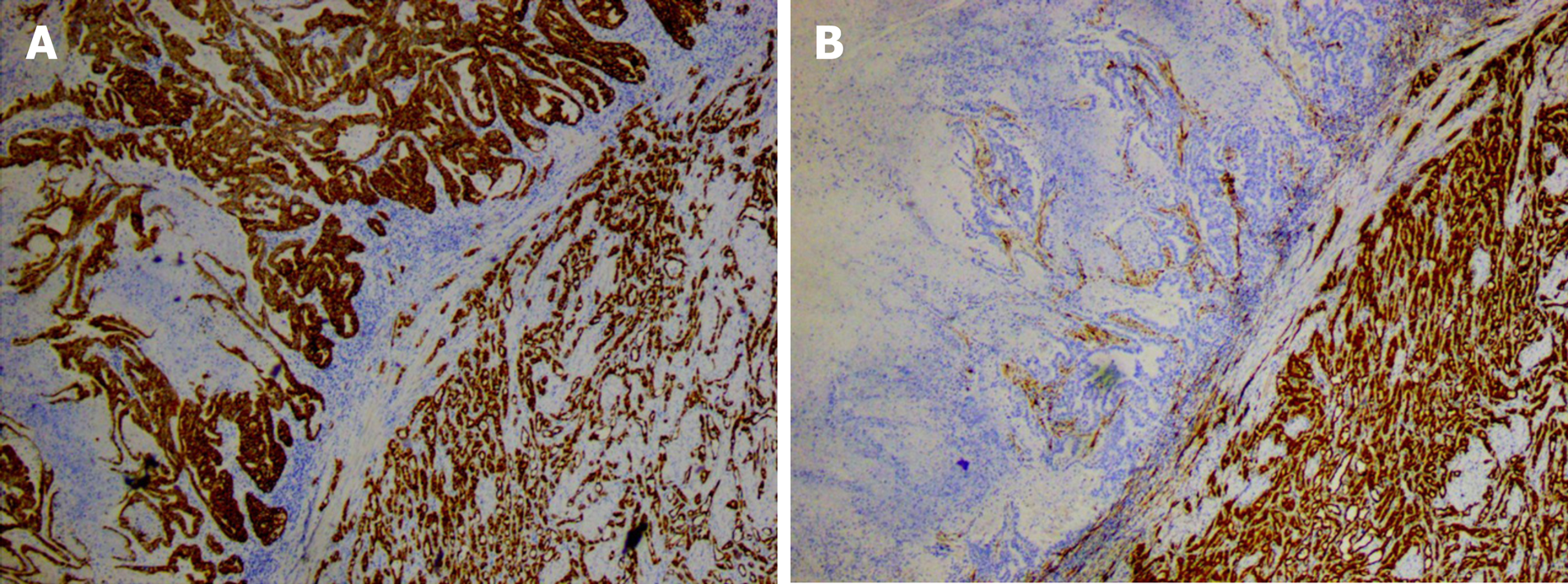
Figure 4 Immunohistochemical staining of the oviduct tumor.
A: The tumor tissue and adenomatoid tumor were CK positive; B: The tumor tissue was calretinin negative and adenomatoid tumor was calretinin positive.
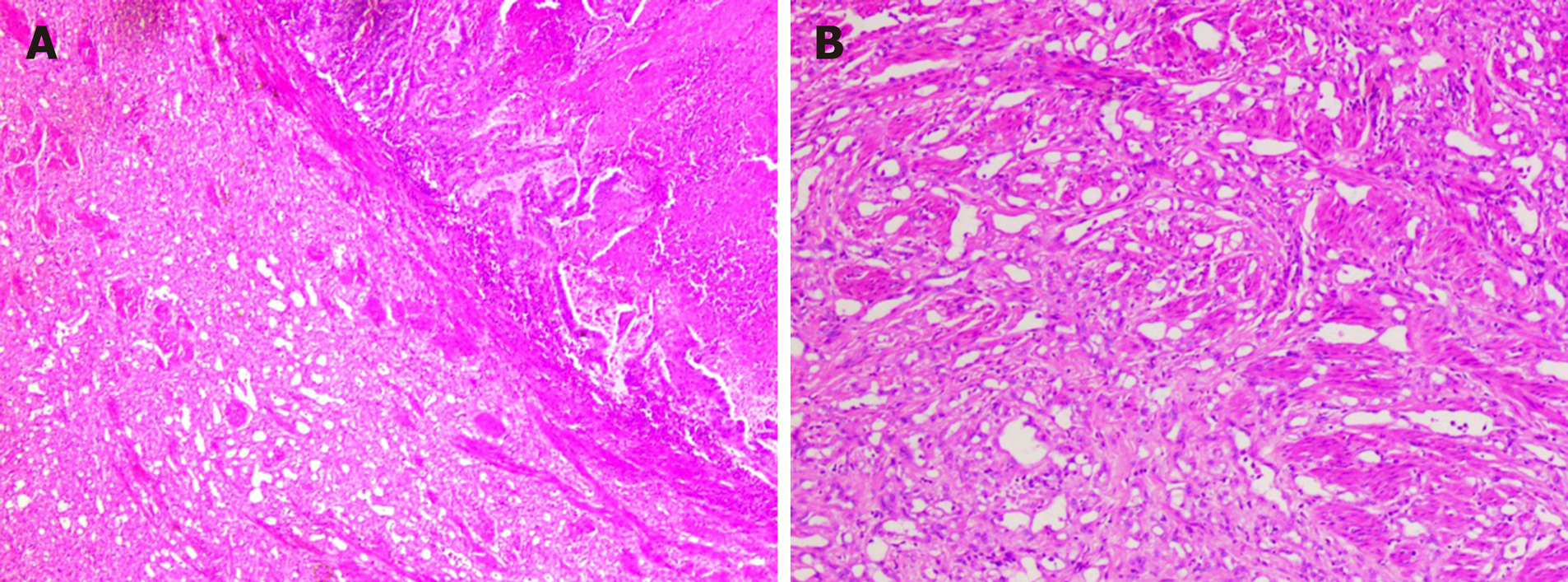
Figure 5 Histology of the oviduct mass (hematoxylin and eosin staining).
A: Cancer tissue coexisted with adenomatoid tumor area; B: Microcapsule-like structure of adenomatoid tumor area.
- Citation: Hu ZX, Tan MH, Li QZ, Xu JL, Chen W, Xie ZH, Zhou YJ, Liang Q, An JH, Shen H. Endometrial clear cell carcinoma invading the right oviduct with a cooccurring ipsilateral oviduct adenomatoid tumor: A case report. World J Clin Oncol 2020; 11(12): 1076-1083
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v11/i12/1076.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v11.i12.1076