©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. May 6, 2016; 7(2): 179-189
Published online May 6, 2016. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v7.i2.179
Published online May 6, 2016. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v7.i2.179
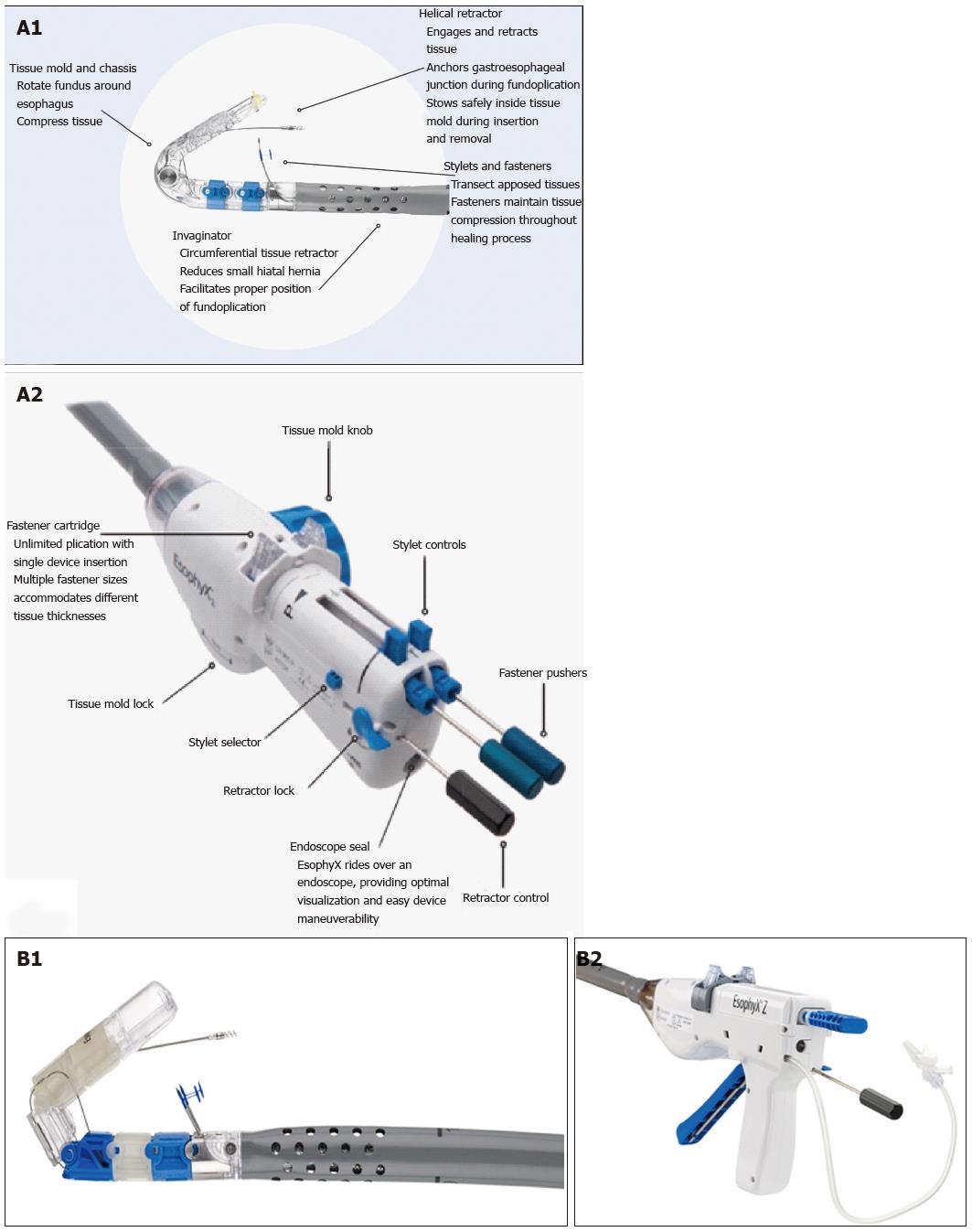
Figure 1 EsophyX® device: First and second generation devices (courtesy of EndoGastric Solutions, Inc.
Redmond, WA, United States). A1-A2: The device currently used (©2014 EndoGastric Solutions, Inc); B1-B2: The new generation device (©2014 EndoGastric Solutions, Inc).
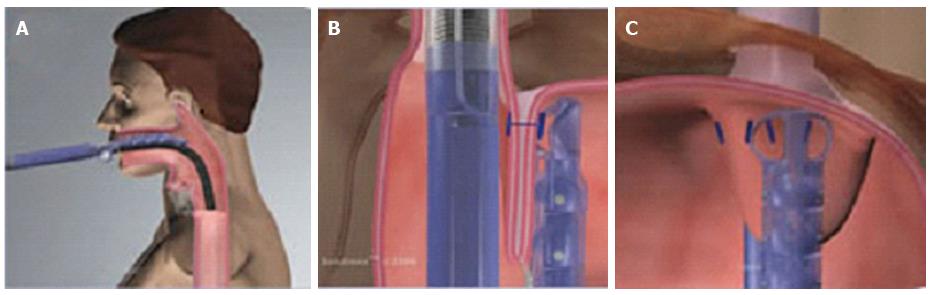
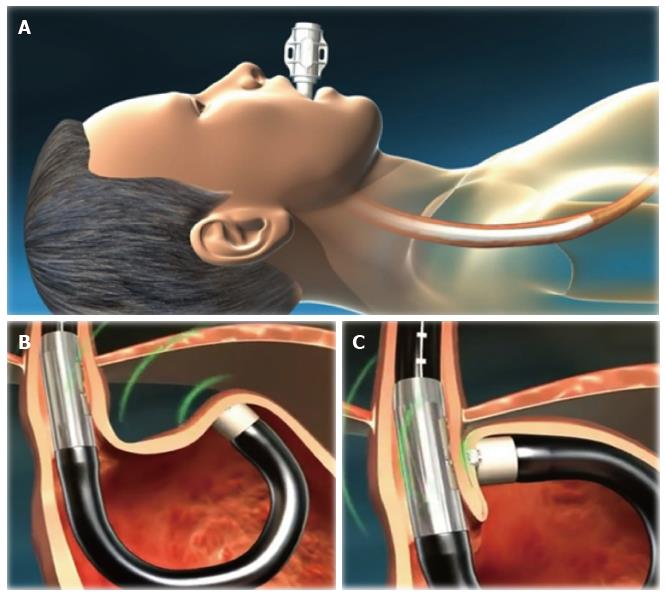
Figure 2 Schematic representation of the procedure with EsophyX® device (Courtesy of EndoGastric Solutions Inc.
Redmond, WA, United States). A: The EsophyX® device enters the esophagus through the mouth and is positioned at the gastro-esophageal junction; B: The device wraps the fundus around the distal esophagus and fastens a tissue fold; C: This step is then repeated multiple times to reconstruct a robust, tight valve (©2014 EndoGastric Solutions, Inc).
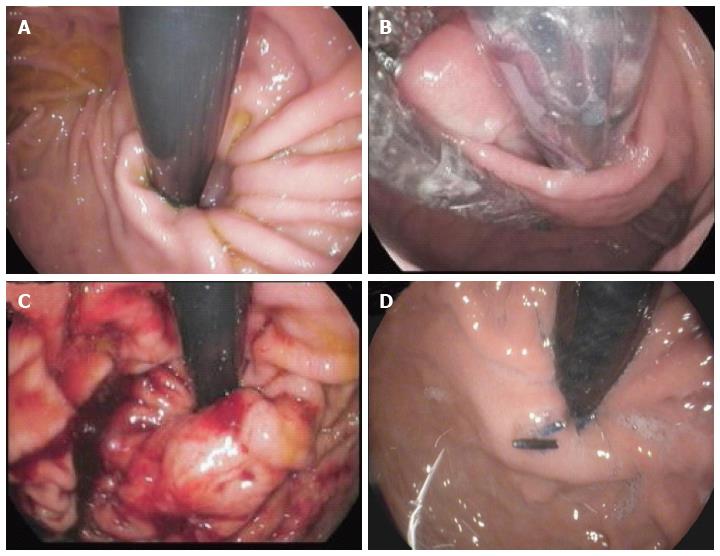
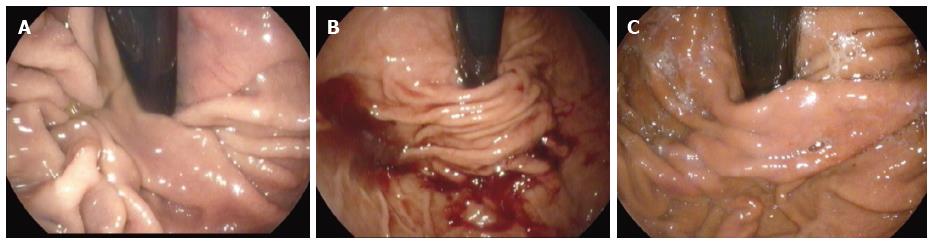
Figure 3 Endoscopic views of the gastro-esophageal valve before and immediately after the transoral incisionless fundoplication procedure by EsophyX® device (Authors’ case).
A: The gastro-esophageal valve: Before the procedure with the EsophyX® device; B: The “Bell Roll” maneuver to create the new gastro-esophageal valve; C: The gastro-esophageal valve: Immediately after the procedure with the EsophyX® device; D: The gastro-esophageal valve: Six months after the procedure.
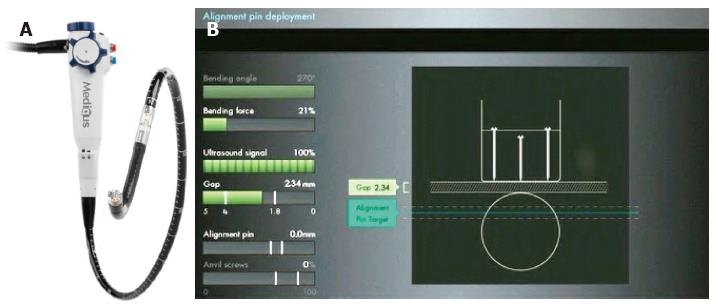
Figure 4 Medigus Surgical Ultrasonic Endostapler system, MUSE™ (Courtesy of Medigus Ltd.
, Omer, Israel). A: The MUSE™ system (© All rights reserved to Medigus Ltd 2008-2015); B: The console connected with the endostapler, containing a controller for the camera, ultrasonic range finder and various sensors (bending angle, bending force, alignment pin, anvil screws, gap) (© All rights reserved to Medigus Ltd 2008-2015).
Figure 5 Schematic representation of the Medigus Ultrasonic Surgical Endostapler (MUSE™) procedure (Courtesy of Medigus Ltd.
, Omer, Israel). A: The endostapler is inserted transorally through the overtube and gently advanced into the stomach under direct vision; B: Once in the stomach, distended by insufflation of air or CO2, the stapler is advanced until the tip is approximately 5 cm past the EGJ and then retroflexed 180° to give adequate vision of the gastric fundus and EGJ to select the stapling location. Tissue is clamped and stapled under ultrasonic guidance; C: This step is then repeated at least twice to reconstruct a robust, tight valve. Additional stapling locations should be within 60°-180° of the valve circumference (© All rights reserved to Medigus Ltd 2008-2015). EGJ: Esophago-gastric junction.
Figure 6 Endoscopic views of the gastro-esophageal valve before and after the transoral incisionless fundoplication procedure with the Medigus Ultrasonic Surgical Endostapler (MUSE™) (authors’ case).
A: The gastro-esophageal valve: before the transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF) procedure with the MUSE™ system; B: The gastro-esophageal valve: Immediately after the TIF procedure by MUSE™ system; C: The gastro-esophageal valve: Six months after the TIF procedure by MUSE™ system.
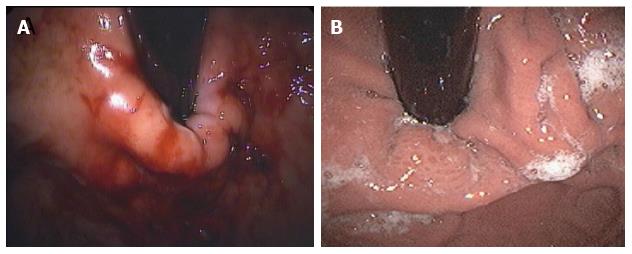
Figure 7 Endoscopic views of the gastro-esophageal valve immediately after and 24 mo after the transoral incisionless fundoplication procedure with EsophyX® device (authors’ case).
A: The gastro-esophageal valve: Immediately after the transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF) procedure with EsophyX® device; B: The gastro-esophageal valve: 24 mo after the TIF procedure with EsophyX® device.
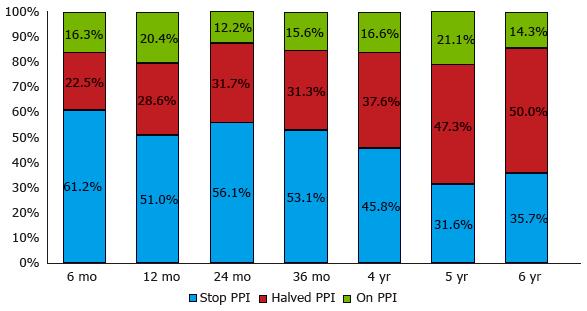
Figure 8 Symptomatic responses six months and 1-6 years after transoral incisionless fundoplication with Esophyx® device, classified according to proton pump inhibitor use.
Patients were grouped as complete responders [who completely stopped using proton pump inhibitor (PPI)] or partial responders (who halved the previous PPI dose) and non-responders (who still used the pre-TIF PPI dose): 12 mo vs 6 mo after TIF P = 0.8; 24 mo vs 12 mo, P = 0.4; 36 mo vs 24 mo, P = 0.7; 4 years vs 36 mo, P = 1.0; 5 years vs 4 years, P = 1.0; 6 years vs 5 years, P = 1.0.
- Citation: Testoni PA, Mazzoleni G, Testoni SGG. Transoral incisionless fundoplication for gastro-esophageal reflux disease: Techniques and outcomes. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther 2016; 7(2): 179-189
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5349/full/v7/i2/179.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4292/wjgpt.v7.i2.179