©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. Nov 6, 2015; 6(4): 199-206
Published online Nov 6, 2015. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v6.i4.199
Published online Nov 6, 2015. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v6.i4.199
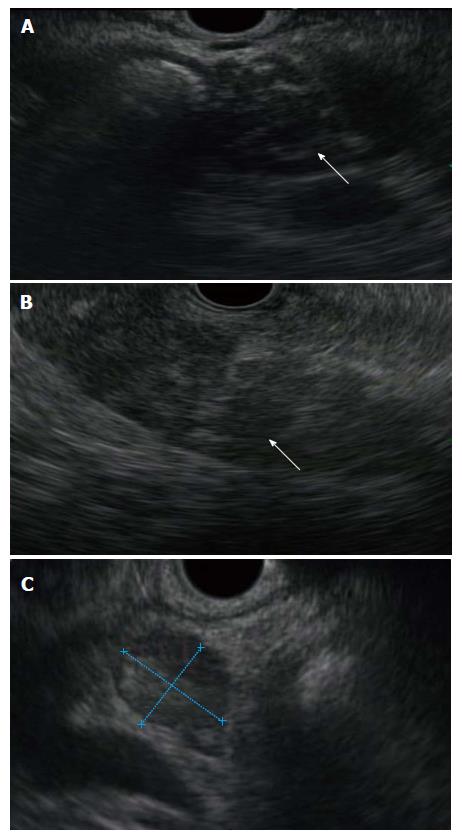
Figure 1 Endoscopic ultrasound features of autoimmune pancreatitis include diffuse hypoechoic changes in the head (A) and body (B) of the pancreas (note the metallic stent placed when the mass was assumed to represent carcinoma), and hypoechoic peripancreatic lymph nodes (C) of a similar echogenicity are frequently seen.
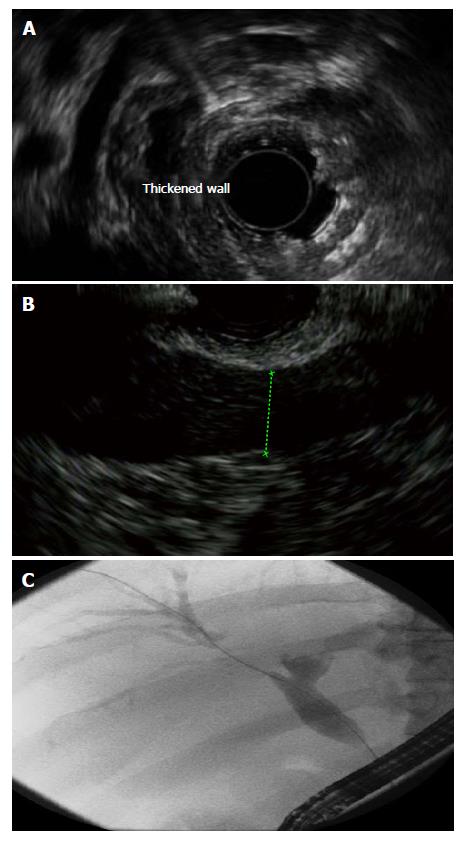
Figure 2 Endoscopic ultrasound reveals marked bile duct thickening (A) in a patient with longstanding autoimmune pancreatitis as evidenced by diffuse hypoechoic changes in the pancreas (B), and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography demonstrated segmental narrowing with prestenotic dilation (C).
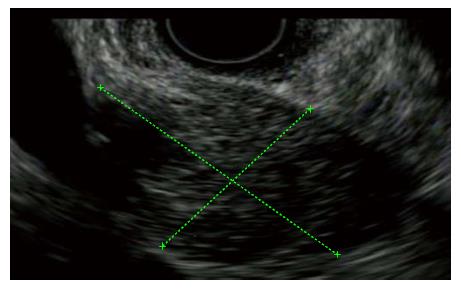
Figure 3 Endoscopic ultrasound reveals a hypoechoic pancreas mass in a jaundiced sixteen-year-old patient with crohn’s disease confirmed by histologic sampling to have type II autoimmune pancreatitis.
- Citation: Jani N, Buxbaum J. Autoimmune pancreatitis and cholangitis. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther 2015; 6(4): 199-206
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5349/full/v6/i4/199.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4292/wjgpt.v6.i4.199