©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. Dec 5, 2025; 16(4): 111889
Published online Dec 5, 2025. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v16.i4.111889
Published online Dec 5, 2025. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v16.i4.111889
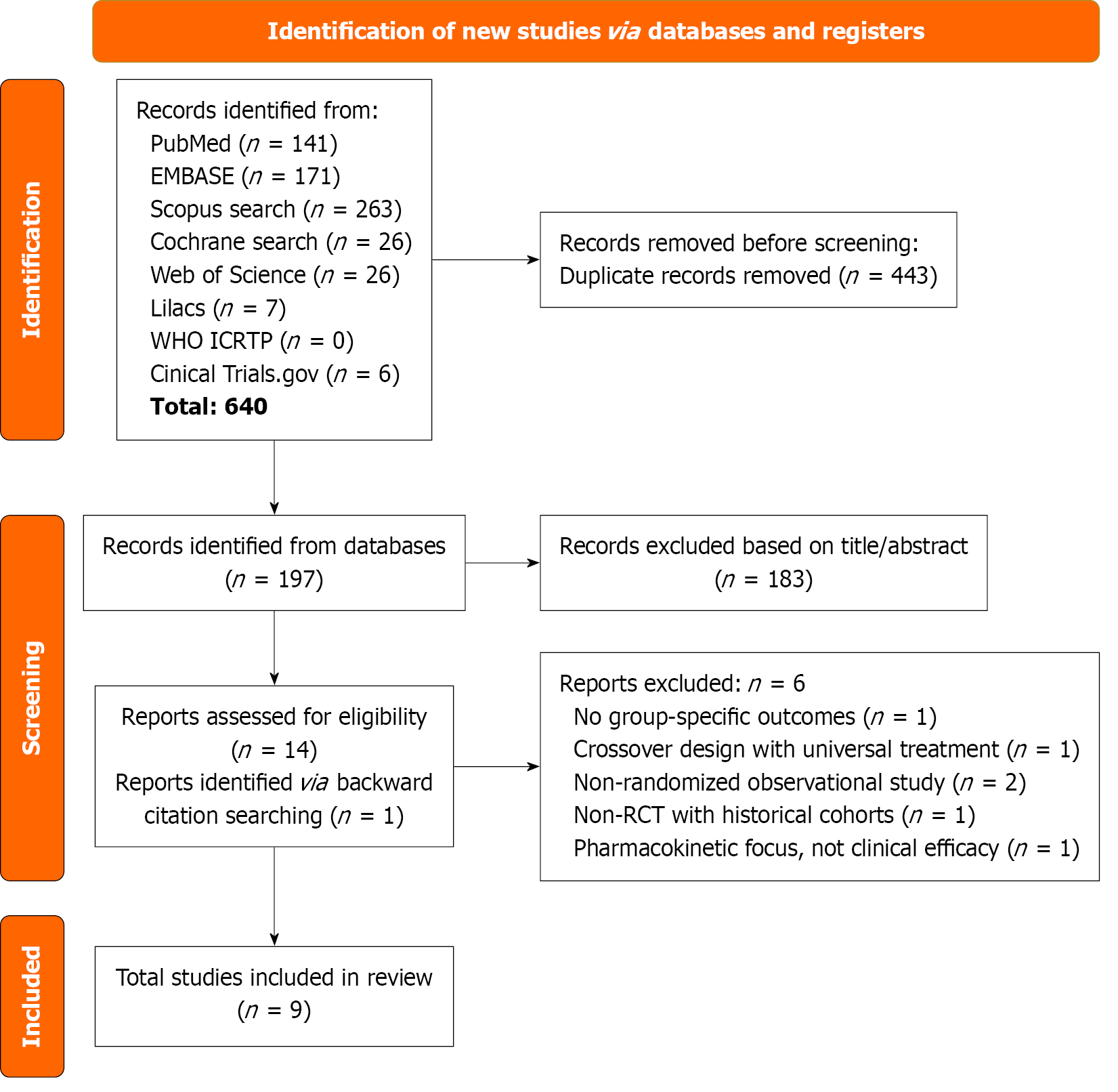
Figure 1 Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses flow diagram of study screening and selection.
The search strategy in PubMed, EMBASE, Scopus, Cochrane, Web of Science, Lilacs, World Health Organization ICRTP, and Clinical Trials.gov yielded 640 studies, of which 15 were fully reviewed for inclusion and exclusion criteria. Nine studies were included in the meta-analysis.
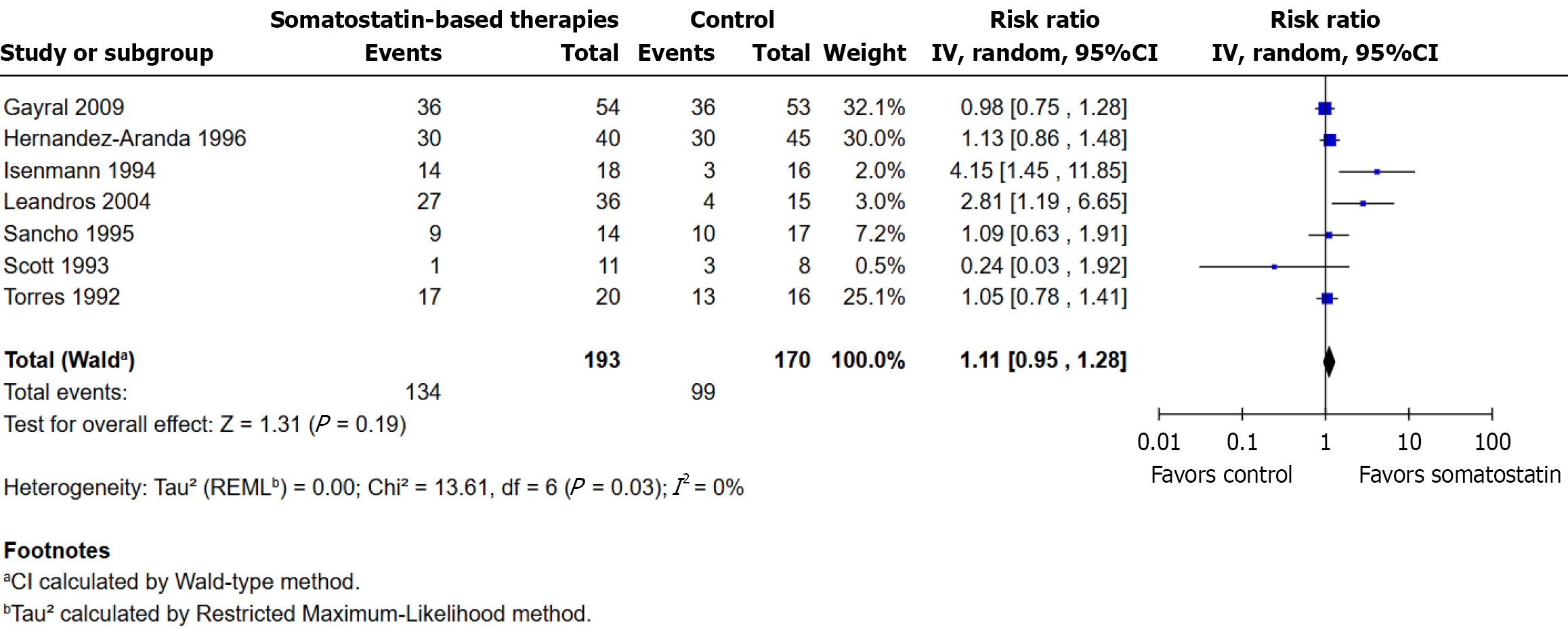
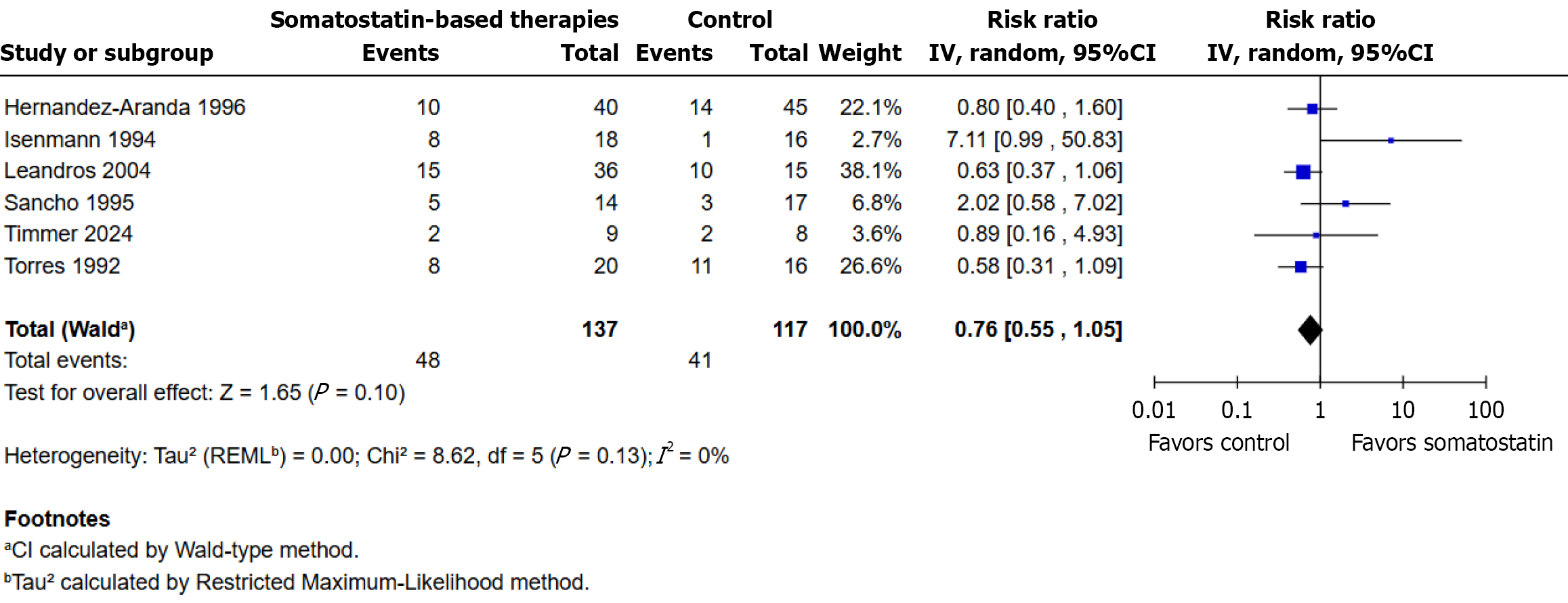
Figure 2 Fistula closure rates with somatostatin-based therapies vs control.
RR: Risk ratio.
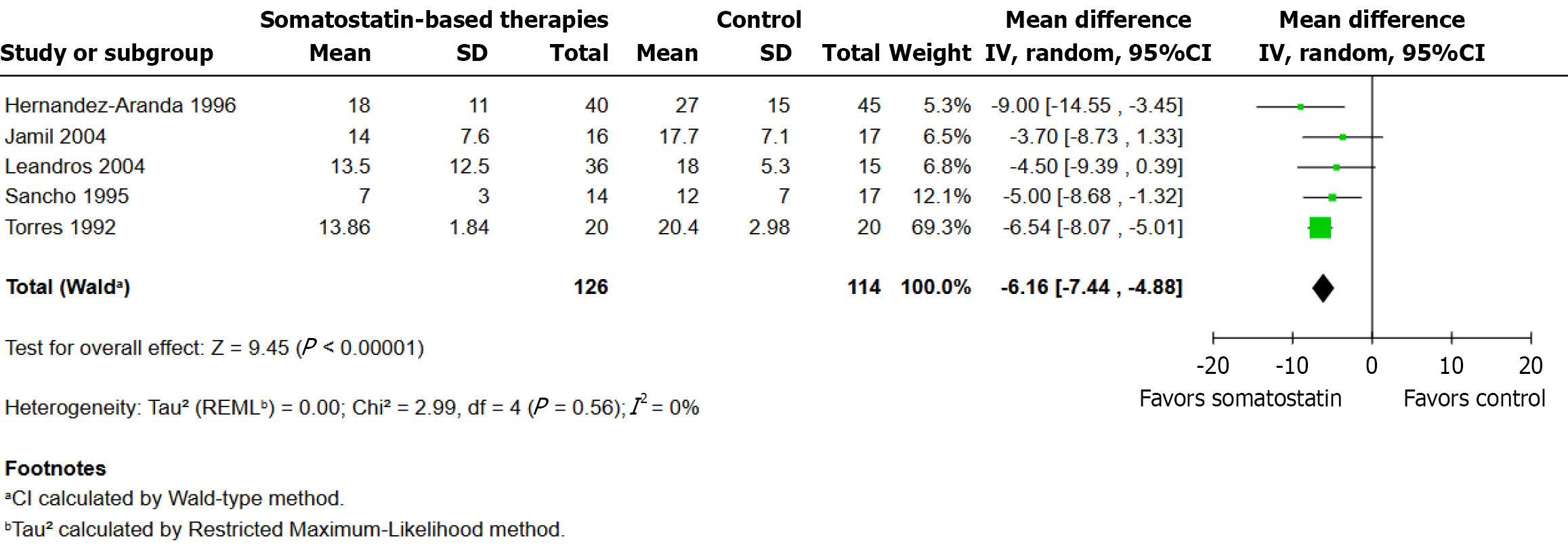
Figure 3
Effect of somatostatin-based therapies on time to fistula closure.
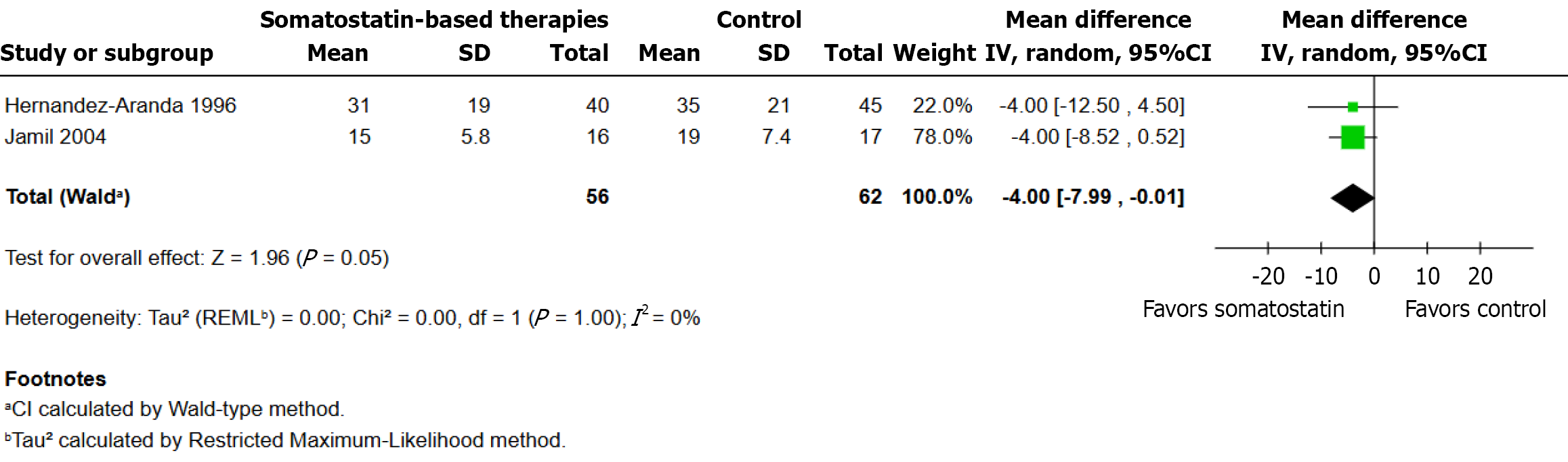
Figure 4
Effect of somatostatin on Hospital Stay Length.
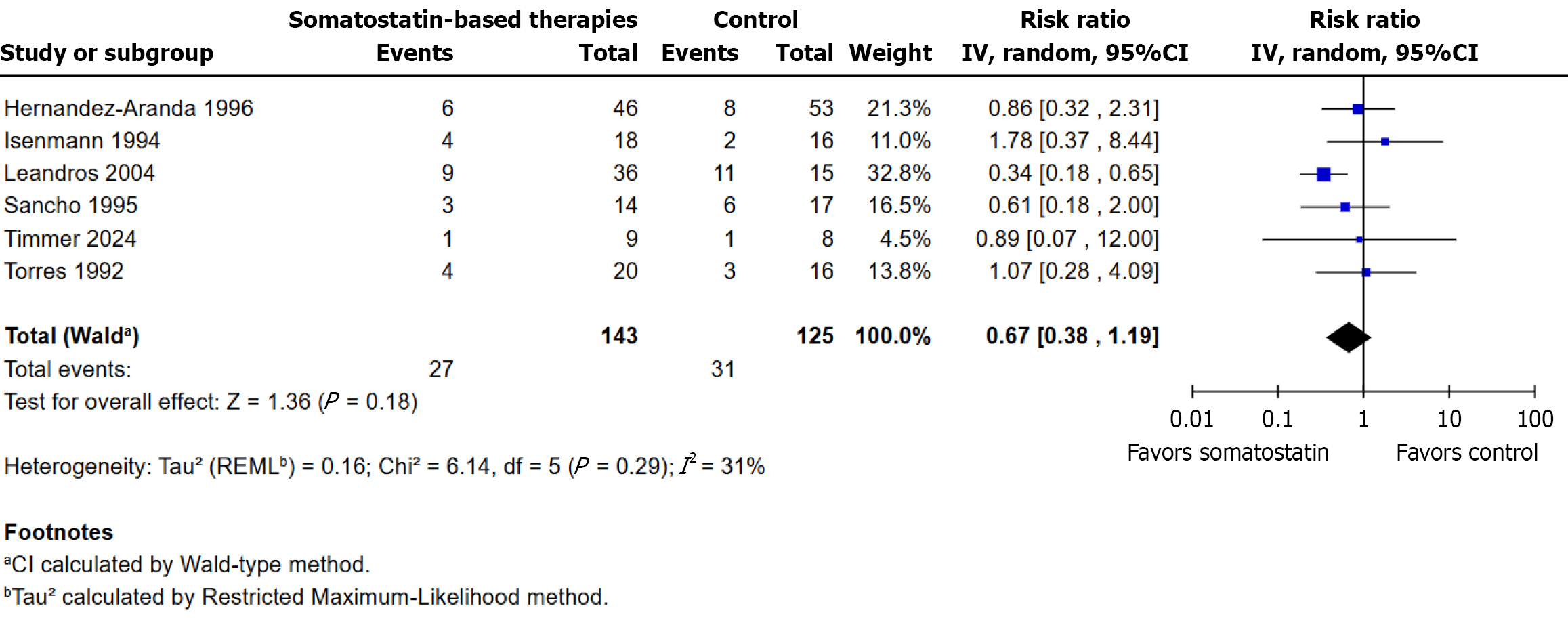
Figure 5 Adverse events with somatostatin-based therapies vs control.
RR: Risk ratio.
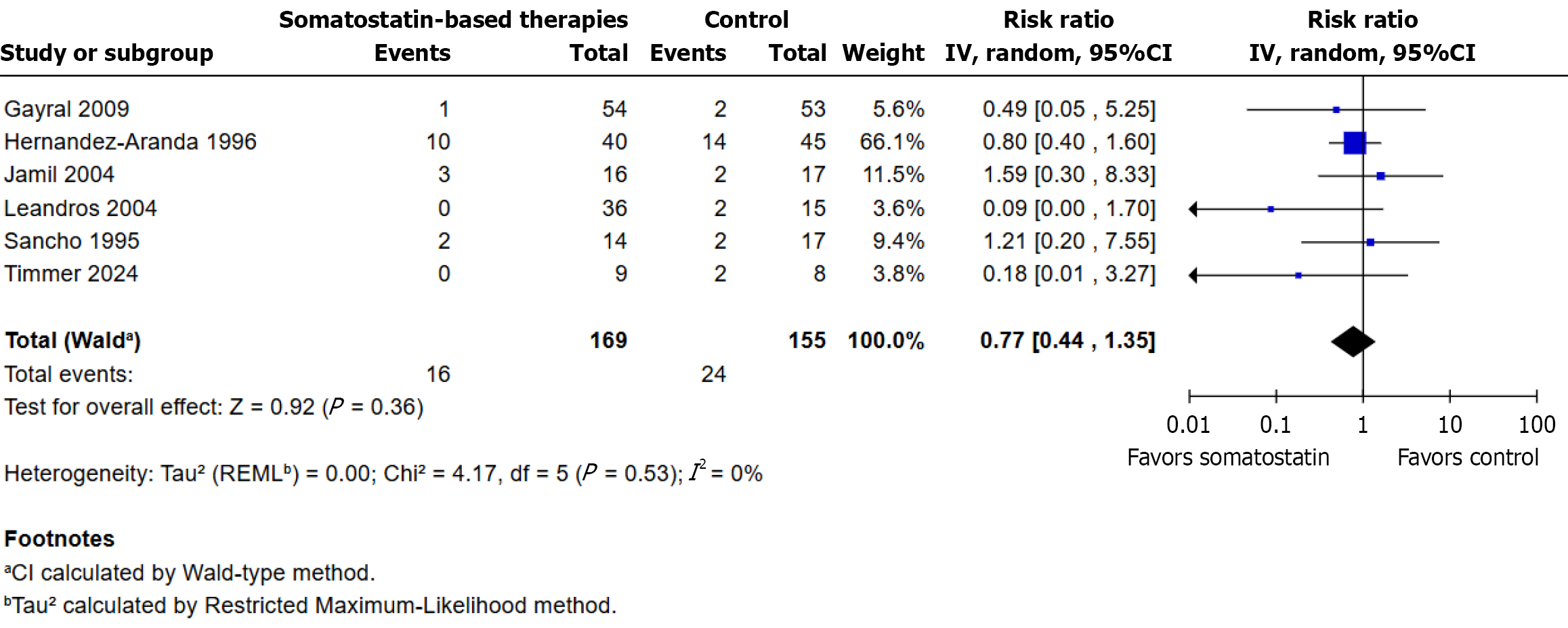
Figure 6 Surgical intervention for fistula or complications: Somatostatin vs control.
RR: Risk ratio.
Figure 7 Effect of somatostatin-based therapies on all-cause mortality.
RR: Risk ratio.
- Citation: Ribeiro Junior MAF, Fontenelle Vieira L, Thalib HI, Fouzaan Albeez S, Heba Fakruddin F, Mirza Zafar Baig A, Mohammed H, Nafeesa Hashim S, Rauf Khan AA, Dib Possiedi R. Somatostatin-based therapies for external gastrointestinal fistulas: Updated meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther 2025; 16(4): 111889
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5349/full/v16/i4/111889.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4292/wjgpt.v16.i4.111889