©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Aug 15, 2016; 7(3): 288-295
Published online Aug 15, 2016. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v7.i3.288
Published online Aug 15, 2016. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v7.i3.288
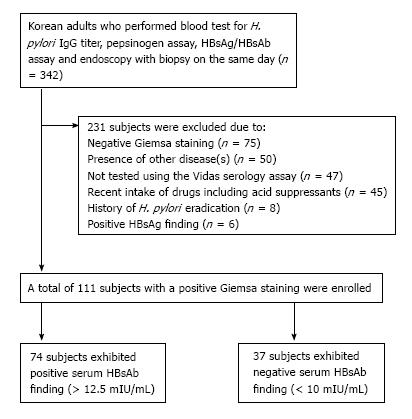
Figure 1 Flow of this study.
Of the 342 Korean adults, only the subjects with a positive Giemsa staining were included in the study. H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori; HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen; HBsAb: Hepatitis B surface antibody.
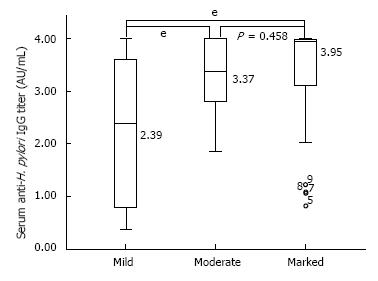
Figure 2 The serum anti-H.
pylori IgG titer according to the degree of H. pylori infiltration on gastric biopsy. Subjects with marked H. pylori infiltration showed the highest serology titer followed by those with moderate and mild infiltrations.
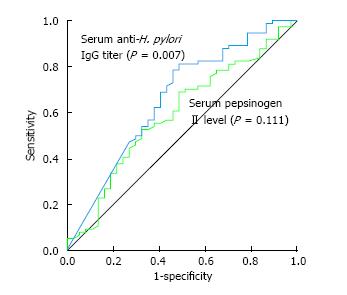
Figure 3 Receiver operating characteristic curves for correlating with the density of H.
pylori infiltration. The cut-off value of the serum anti-H. pylori IgG titer for correlating with severe density of H. pylori infiltration was 2.9 AU/ml (AUC = 0.659, 95%CI: 0.548-0.770, SE = 0.057, P = 0.007). There was no significant finding with regard to the serum PG II concentration (AUC = 0.593, 95%CI: 0.481-0.705, SE = 0.057, P = 0.111).
- Citation: Chung HA, Lee SY, Moon HW, Kim JH, Sung IK, Park HS, Shim CS, Han HS. Does the antibody production ability affect the serum anti-Helicobacter pylori IgG titer? World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2016; 7(3): 288-295
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v7/i3/288.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v7.i3.288