©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Aug 15, 2016; 7(3): 242-255
Published online Aug 15, 2016. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v7.i3.242
Published online Aug 15, 2016. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v7.i3.242
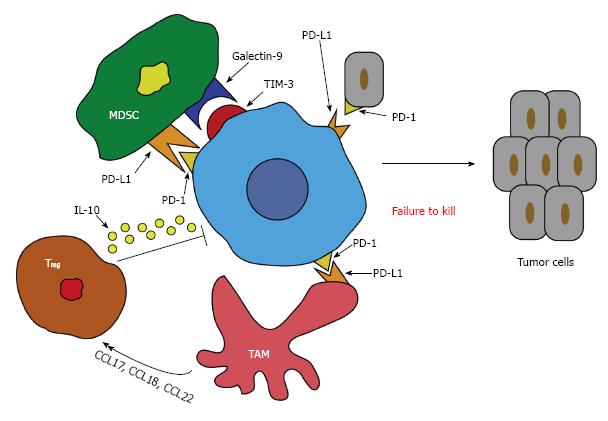
Figure 1 Mechanisms leading to CD8+ T cell suppression.
Failure of CD8+ T cells to kill tumor cells involves signals from multiple cells including MDSC, Treg, and TAMs. The interaction of PD-L1 with PD-1 on the CD8+ T cell causes suppression and decrease in its effector function leading to decreased tumor cell death. Furthermore, the Galectin-9 and TIM-3 interaction on MDSC’s and IL-10 secretion by Treg cause a similar effect. PD-1: Programmed death 1; IL: Interleukine; TAM: Tumor associated macrophages; MDSC: Myeloid derived suppressor cells; TIM-3: T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin-domain containing-3; Treg: Regulatory T cells.
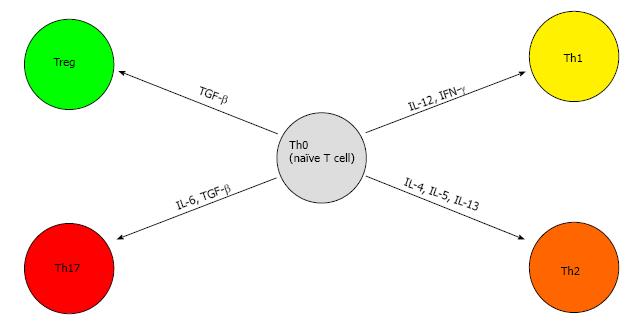
Figure 2 Differentiation of naïve T cells.
The Th0 T cell can differentiate into a variety of CD4+ cells based on stimulatory signals as seen above. TGF-β: Transforming growth factor beta; IFN-γ: Interferon gamma; IL: Interleukine; Treg: Regulatory T cells.
- Citation: Patel P, Schutzer SE, Pyrsopoulos N. Immunobiology of hepatocarcinogenesis: Ways to go or almost there? World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2016; 7(3): 242-255
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v7/i3/242.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v7.i3.242