©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Radiol. Jun 28, 2014; 6(6): 252-260
Published online Jun 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i6.252
Published online Jun 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i6.252
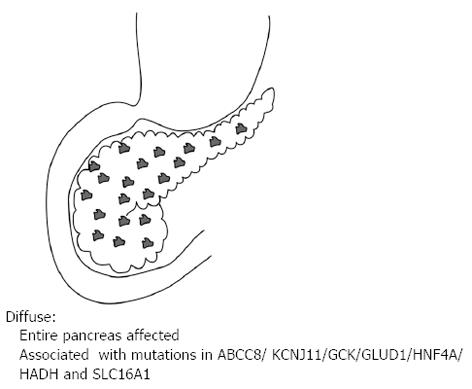
Figure 1 Diffuse lesion where the entire pancreas is affected.
It is associated with recessive and dominant mutations in the ABCC8/KCNJ11/GCK/GLUD1/HNF4A/HADH and SLC16A1.
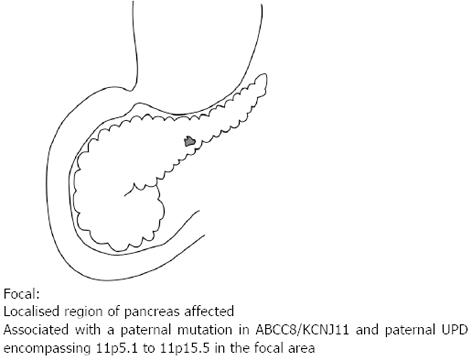
Figure 2 Focal lesion affecting only a single region of the pancreas.
It is associated with a paternal mutation in the ABCC8 or KCNJ11 and paternal uniparental disomy encompassing 11p5.1 to 11p5.5 in the focal area.
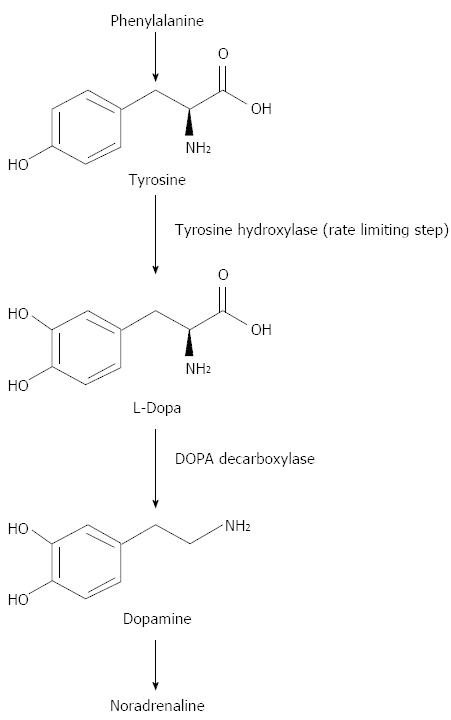
Figure 3 Dopamine biochemistry.
Phenylalanine is converted into L-Tyrosine. L-Tyrosine is then converted into L-Dopa by Tyrosine Hydroxylase. L-Dopa is then converted into Dopamine by DOPA decarboxylase.
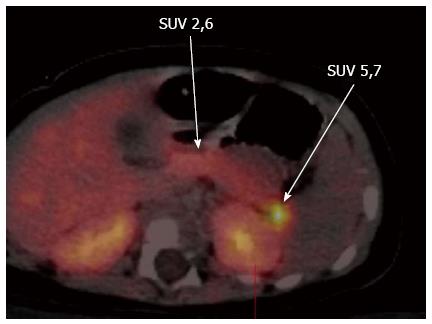
Figure 4 Fluorine-18L-3, 4-hydroxyphenylalanine positron emission tomography scan showing the focal lesion in the tail of the pancreas.
- Citation: Gopal-Kothandapani JS, Hussain K. Congenital hyperinsulinism: Role of fluorine-18L-3, 4 hydroxyphenylalanine positron emission tomography scanning. World J Radiol 2014; 6(6): 252-260
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v6/i6/252.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v6.i6.252