©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Radiol. Dec 28, 2025; 17(12): 116453
Published online Dec 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i12.116453
Published online Dec 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i12.116453
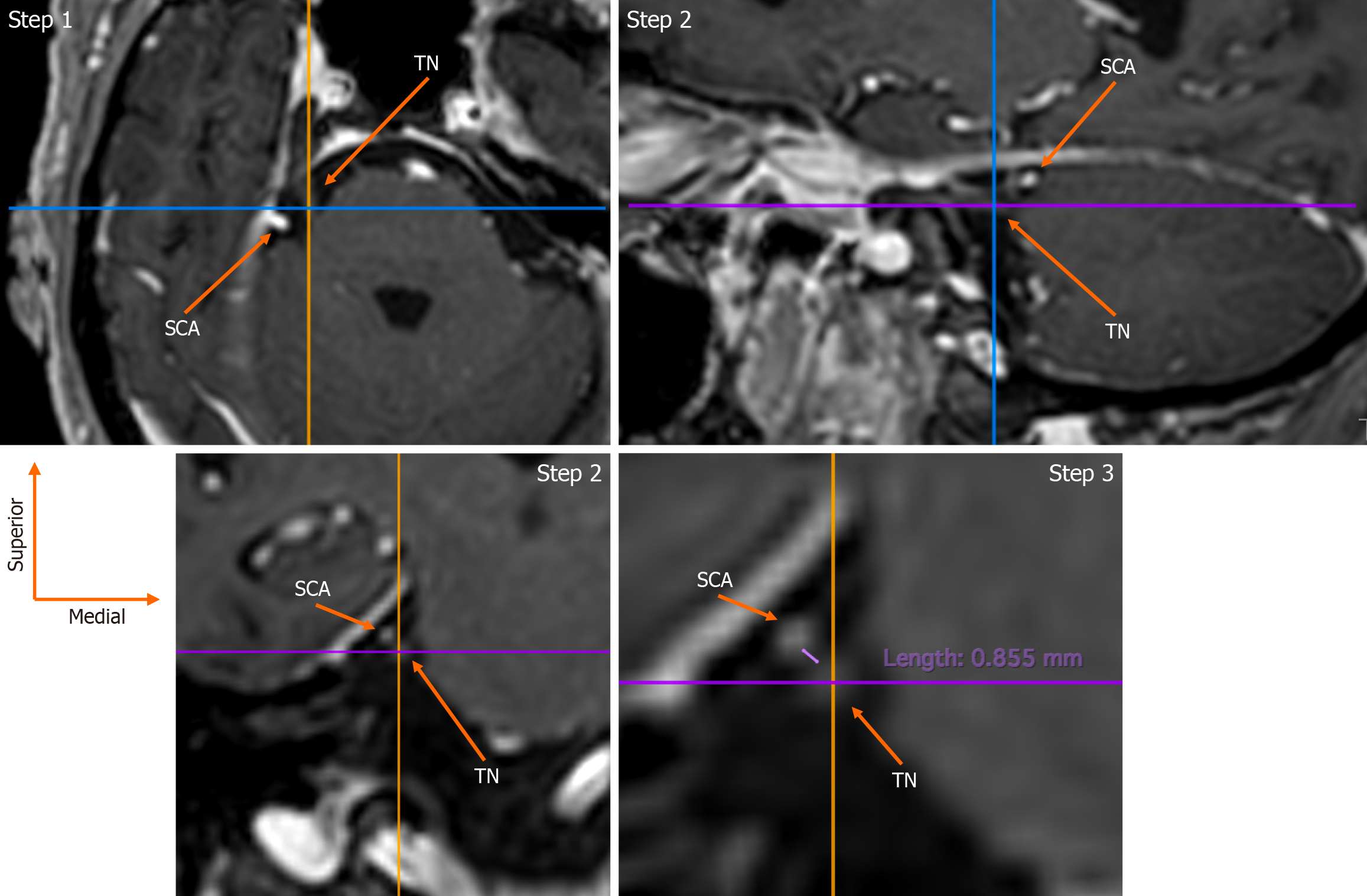
Figure 1 Workflow for identifying the trigeminal nerve and its relationship with the superior cerebellar artery.
Step 1: Identification of the trigeminal nerve root on axial slices; Step 2: Confirmation on sagittal and coronal planes; Step 3: Measurement of superior cerebellar artery-trigeminal nerve distance on coronal reconstruction. TN: Trigeminal nerve; SCA: Superior cerebellar artery.
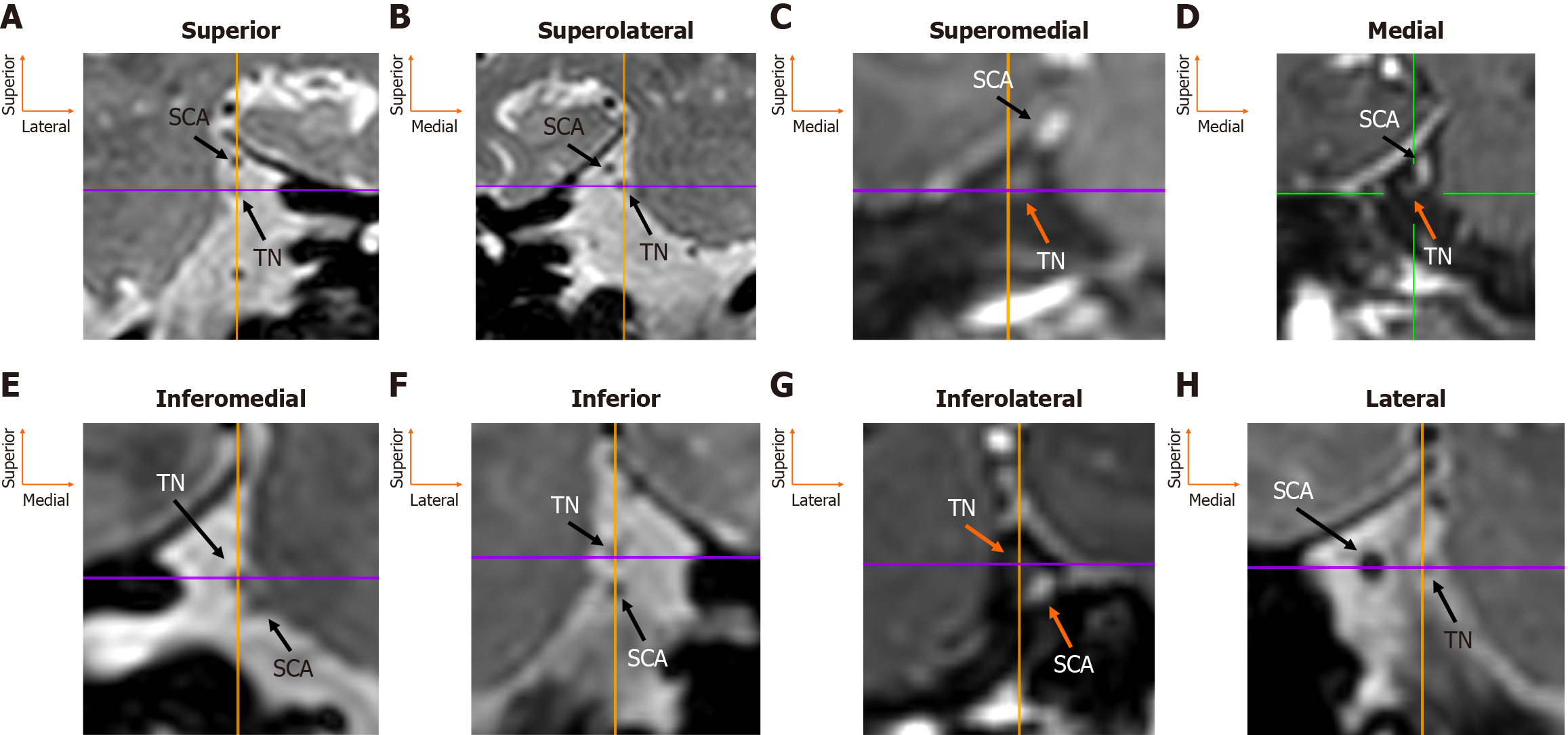
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance imaging-based classification of superior cerebellar artery-trigeminal nerve 8 anatomical types.
A-H: Magnetic resonance imaging-based classification of the eight anatomical relationship types between the superior cerebellar artery and the trigeminal nerve: Superior (A), superolateral (B), superomedial (C), medial (D), inferomedial (E), inferior (F), inferolateral (G), and lateral (H). TN: Trigeminal nerve; SCA: Superior cerebellar artery.
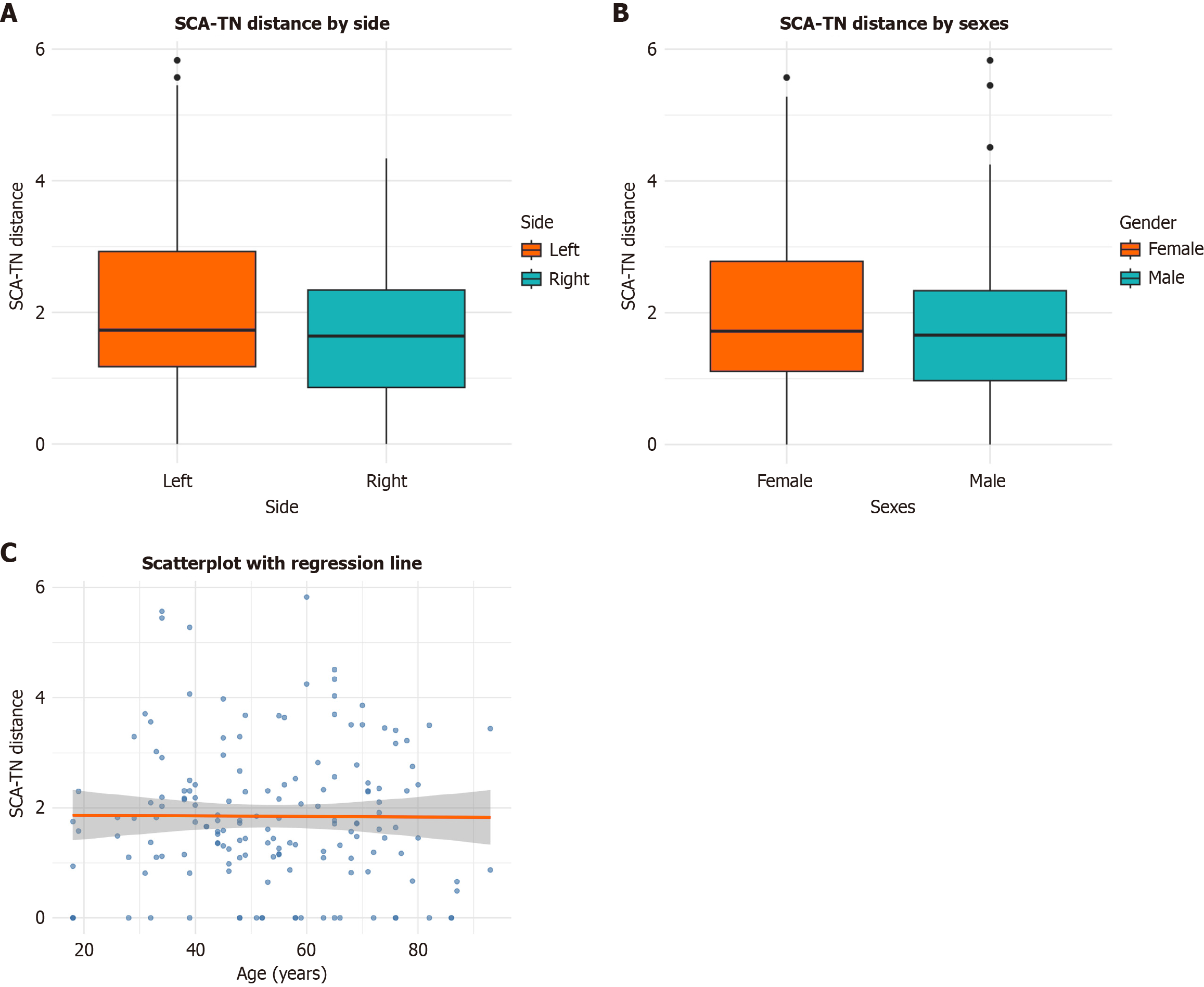
Figure 3 Distribution of the superior cerebellar artery-trigeminal nerve distance by demographic factors.
A: Boxplot comparing left vs right sides; B: Boxplot comparing female and male patients; C: Scatterplot with regression line comparing superior cerebellar artery-trigeminal nerve distance across age. SCA-TN: Superior cerebellar artery-trigeminal nerve.
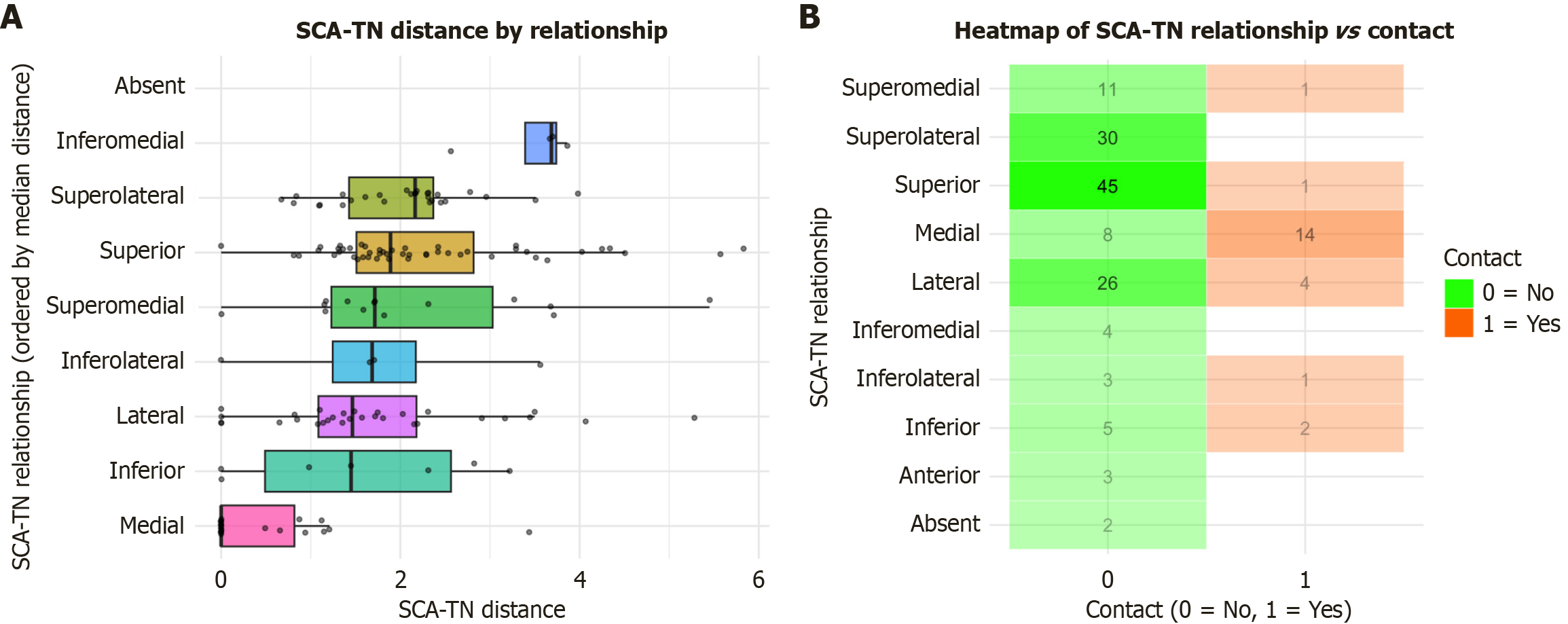
Figure 4 Distance and contact frequency according to the superior cerebellar artery-trigeminal nerve superior cerebellar artery-trigeminal nerve relationship.
A: Boxplot of superior cerebellar artery-trigeminal nerve distances for each anatomical relationship; B: Heatmap illustrating frequency of superior cerebellar artery-trigeminal nerve contact by relationship type (green = no contact, orange = contact). SCA-TN: Superior cerebellar artery-trigeminal nerve.
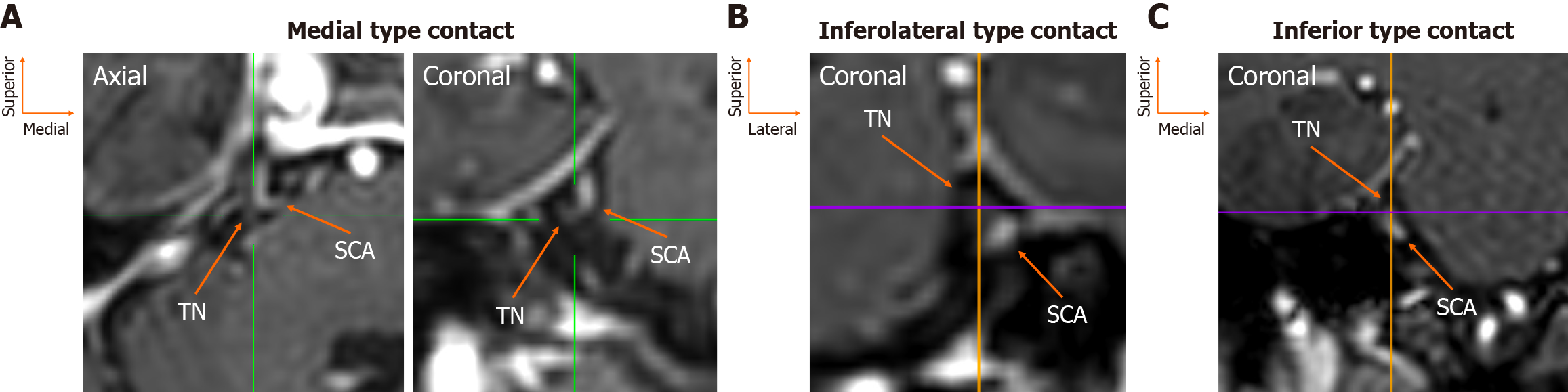
Figure 5 Examples of neurovascular contact between the superior cerebellar artery and the trigeminal nerve in different anatomical configurations.
A: Medial type; B: Inferolateral type; C: Inferior type. TN: Trigeminal nerve; SCA: Superior cerebellar artery.
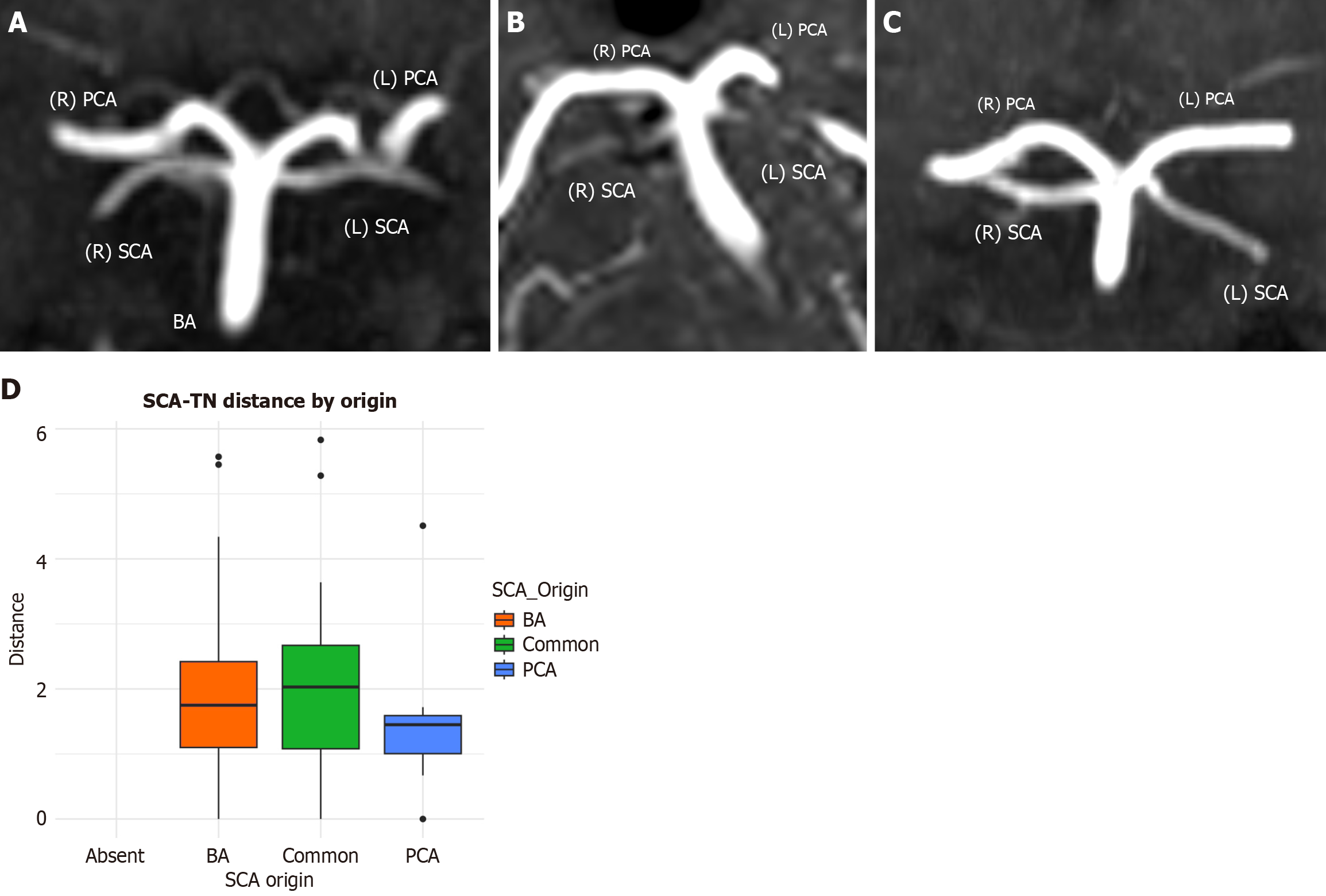
Figure 6 Variability in the origin of the superior cerebellar artery.
A: Bilateral origin from the basilar artery; B: Common origin with the posterior cerebral artery; C: Unilateral origin from the posterior cerebral artery; D: Boxplot comparing superior cerebellar artery-trigeminal nerve distance according to origin. BA: Basilar artery; PCA: Posterior cerebral artery; SCA: Superior cerebellar artery.
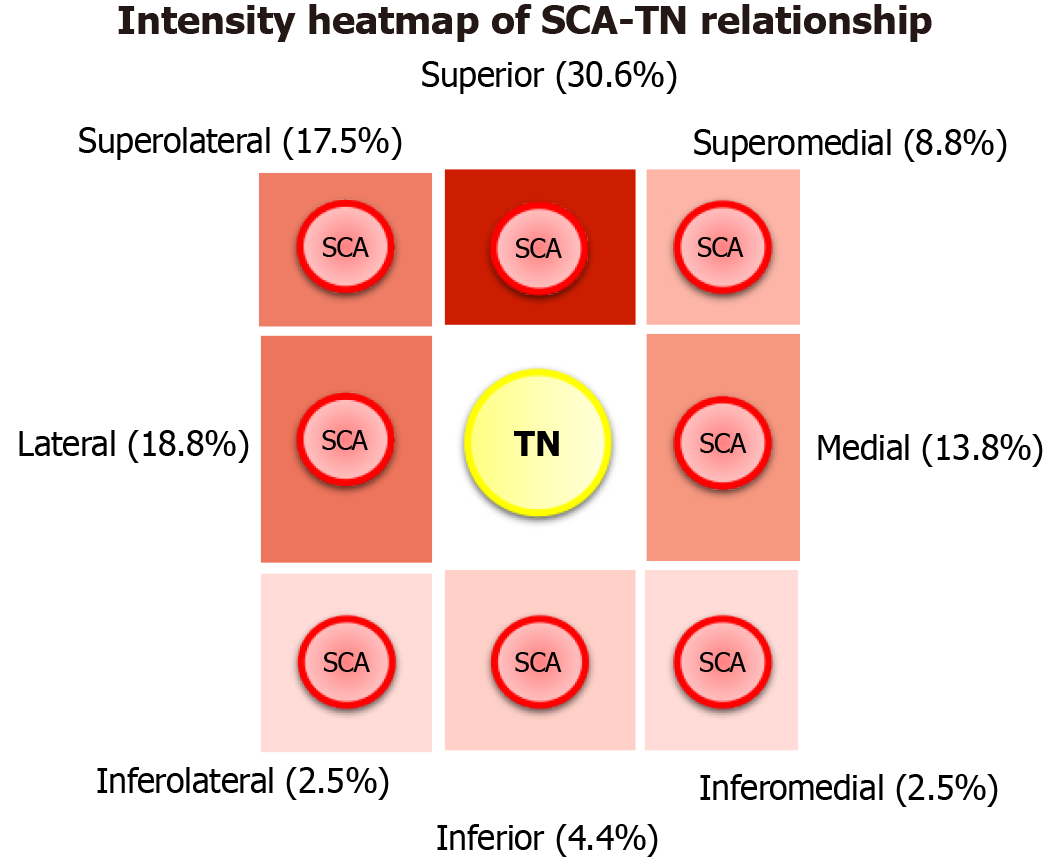
Figure 7 Proposed magnetic resonance imaging-based classification system of the superior cerebellar artery-trigeminal nerve rela
- Citation: Triantafyllou G, Papadopoulos-Manolarakis P, Arkoudis NA, Moschovaki-Zeiger O, Velonakis G, Piagkou M. Magnetic resonance imaging-based classification of trigeminal nerve-superior cerebellar artery relationships. World J Radiol 2025; 17(12): 116453
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v17/i12/116453.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v17.i12.116453