©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Radiol. Jan 28, 2025; 17(1): 99207
Published online Jan 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i1.99207
Published online Jan 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i1.99207
Figure 1 Patients flowchart.
DLBCL: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; PET/CT: Positron emission tomography/computed tomography; PS ECOG: Performance status according to Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; wbMRI: Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging.
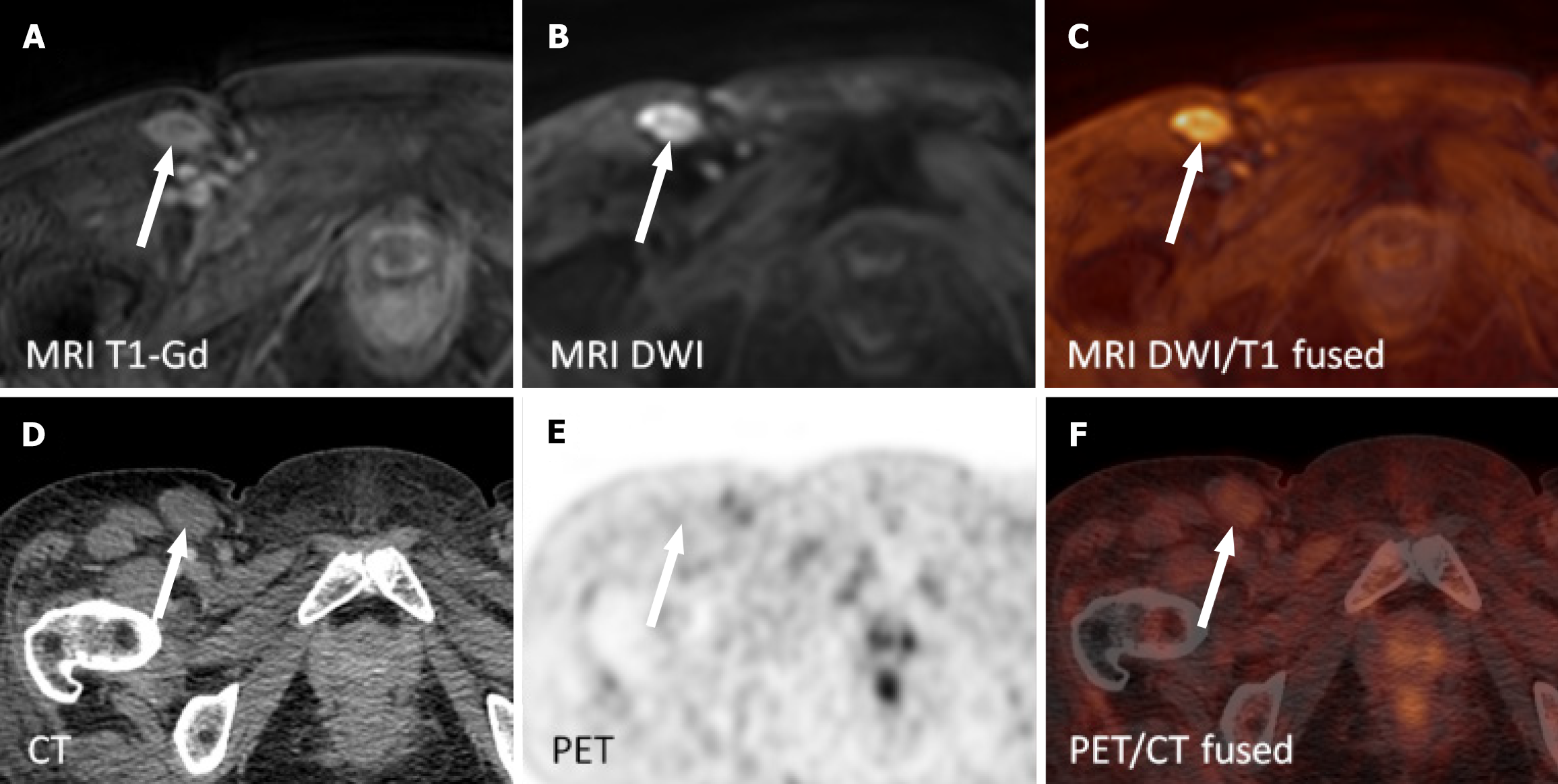
Figure 2 Left axillary lymph node with fatty hilum 23 mm × 9 mm with avid focus in the cortex on fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (SUVmax 5.
5) was reported as negative on whole-body magnetic resonance imaging two days earlier. A: Contrast-enhanced single breath-hold T1 weighted images; B: Diffusion weighted images; C: Diffusion weighted images and contrast-enhanced T1 weighted images on magnetic resonance imaging (fused); D: Computed tomography; E: Positron emission tomography; F: Positron emission tomography/computed tomography images (fused). MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; T1-Gd: Contrast-enhanced T1 weighted single breath-hold images; DWI: Diffusion weighted images; PET/CT: Positron emission tomography/computed tomography.
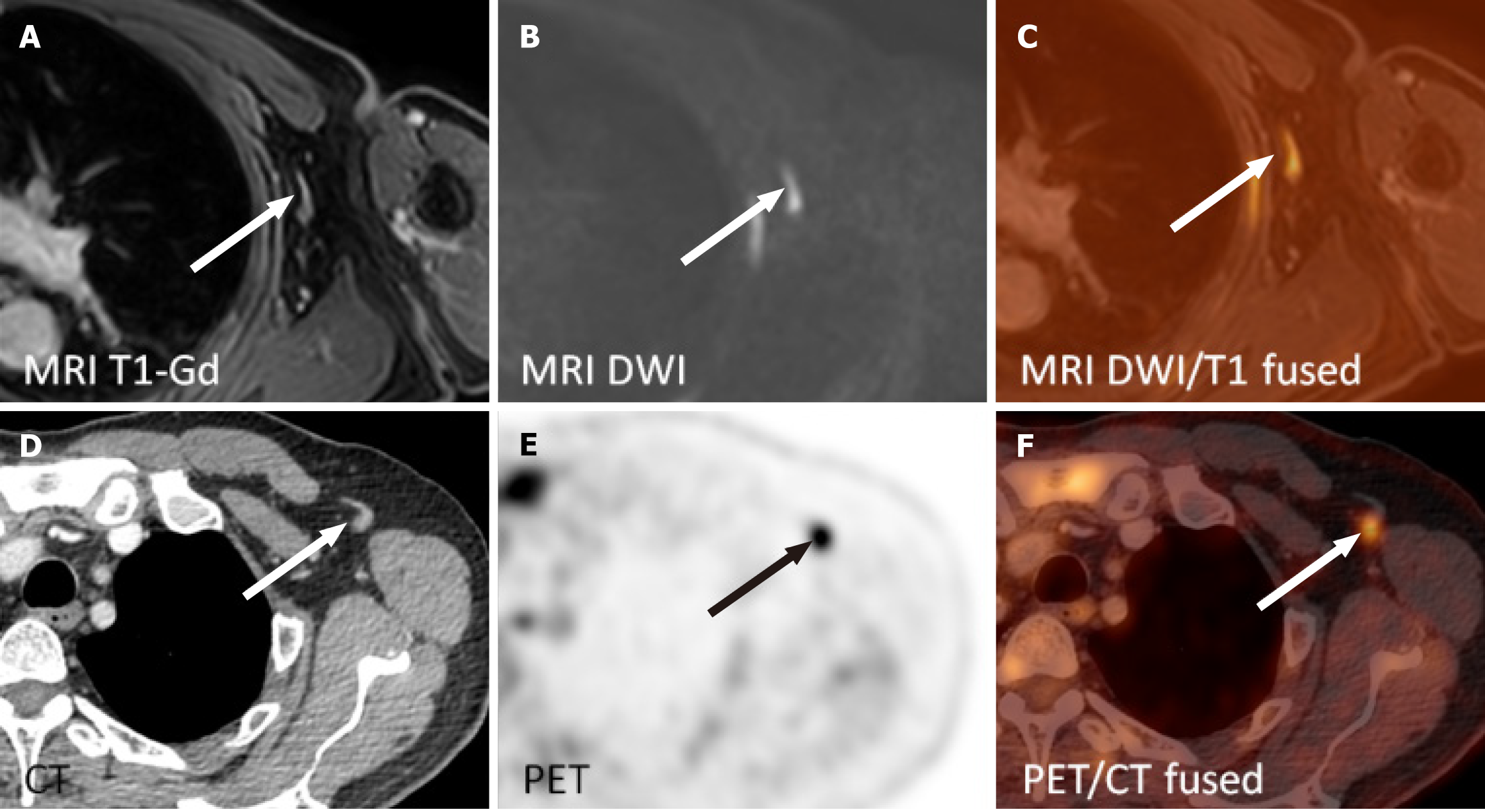
Figure 3 Non-avid right inguinal lymph node on fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography was reported positive on whole-body magnetic resonance imaging five days later.
The patient underwent extirpation of a lymph node from the right groin with persisting reactive changes and seroma. A: Contrast-enhanced T1 weighted single breath-hold images; B: Diffusion weighted images; C: Diffusion weighted images and contrast-enhanced T1 weighted images on magnetic resonance imaging (fused); D: Computed tomography; E: Positron emission tomography; F: Positron emission tomography/computed tomography images (fused). MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; T1-Gd: Contrast-enhanced T1 weighted single breath-hold images; DWI: Diffusion weighted images; PET/CT: Positron emission tomography/computed tomography.
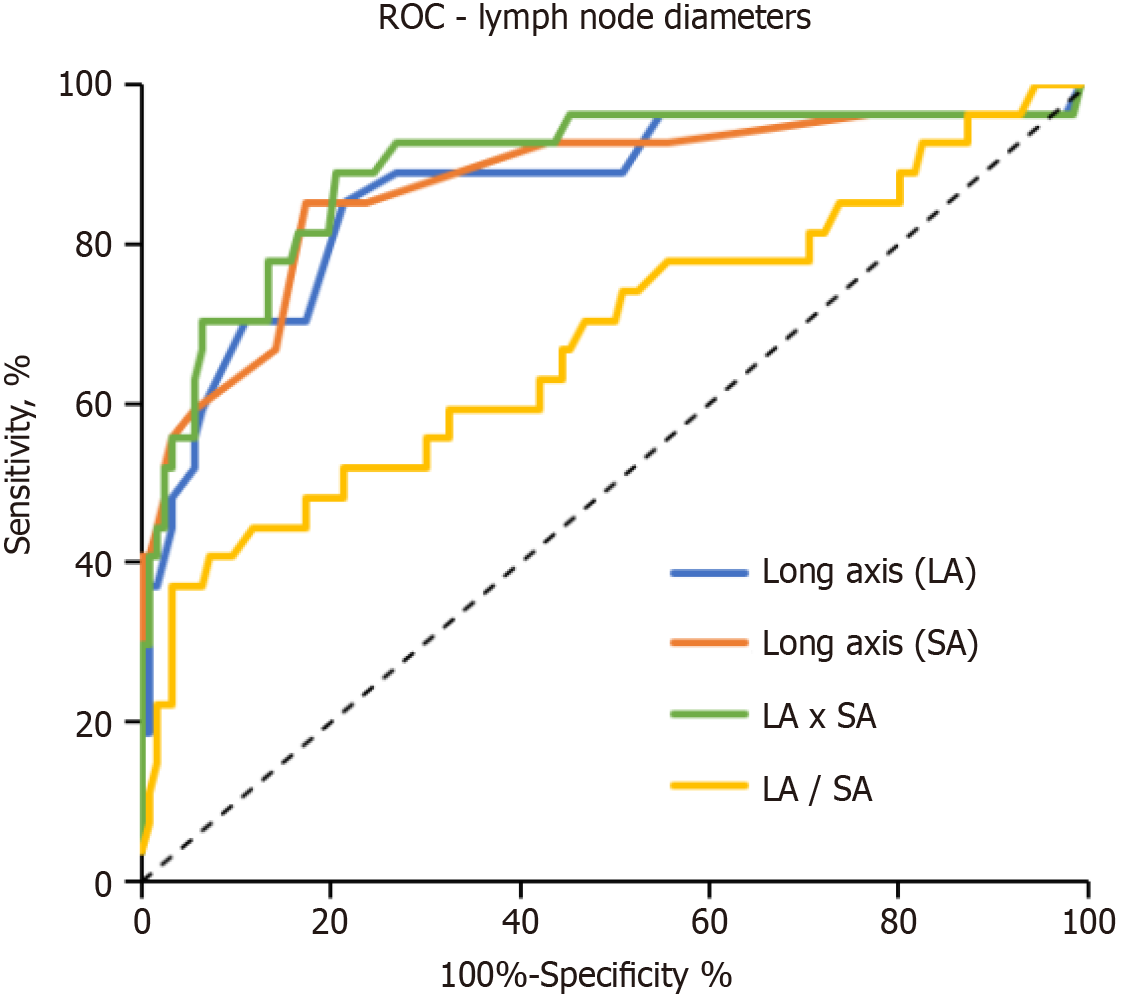
Figure 4 Receiver operator curve for lymph node long axis and short axis diameters and derived values (product and ratio of long axis and short axis) to differentiate nodal involvement by diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
ROC: Receiver operator curve; LA: Long axis; SA: Short axis.
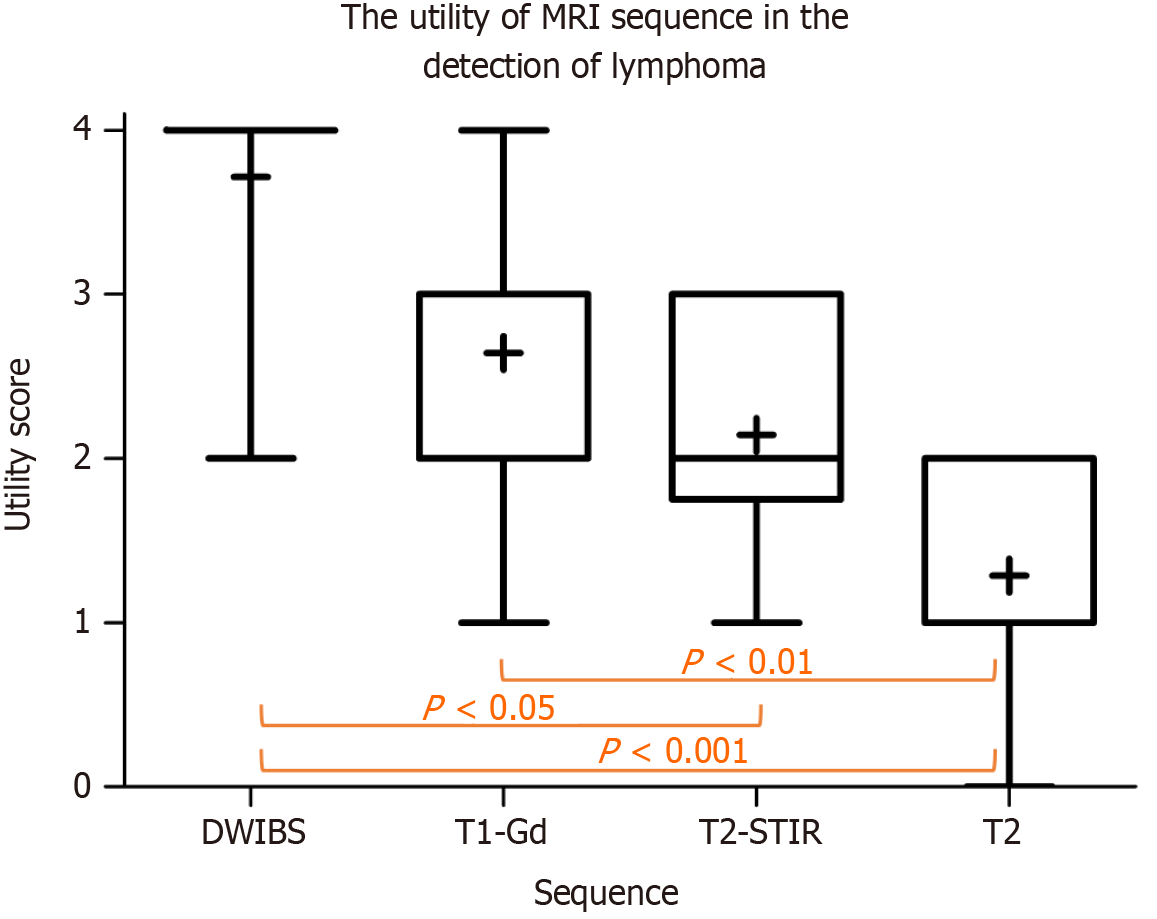
Figure 5 Mean utility scores of whole-body magnetic resonance imaging sequences in the detection of lymphoma rated on a 5-point scale: 0: Not useful to 4: Very useful (critical sequence).
P values denote statistically significant differences in post hoc tests. MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; T1-Gd: Contrast-enhanced T1 weighted single breath-hold images; DWIBS: Diffusion weighted images with background suppression; STIR: Short tau inversion recovery.
- Citation: Lambert L, Wagnerova M, Vodicka P, Benesova K, Zogala D, Trneny M, Burgetova A. Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging provides accurate staging of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, but is less preferred by patients. World J Radiol 2025; 17(1): 99207
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v17/i1/99207.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v17.i1.99207