©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Cardiol. Feb 26, 2026; 18(2): 114960
Published online Feb 26, 2026. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v18.i2.114960
Published online Feb 26, 2026. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v18.i2.114960
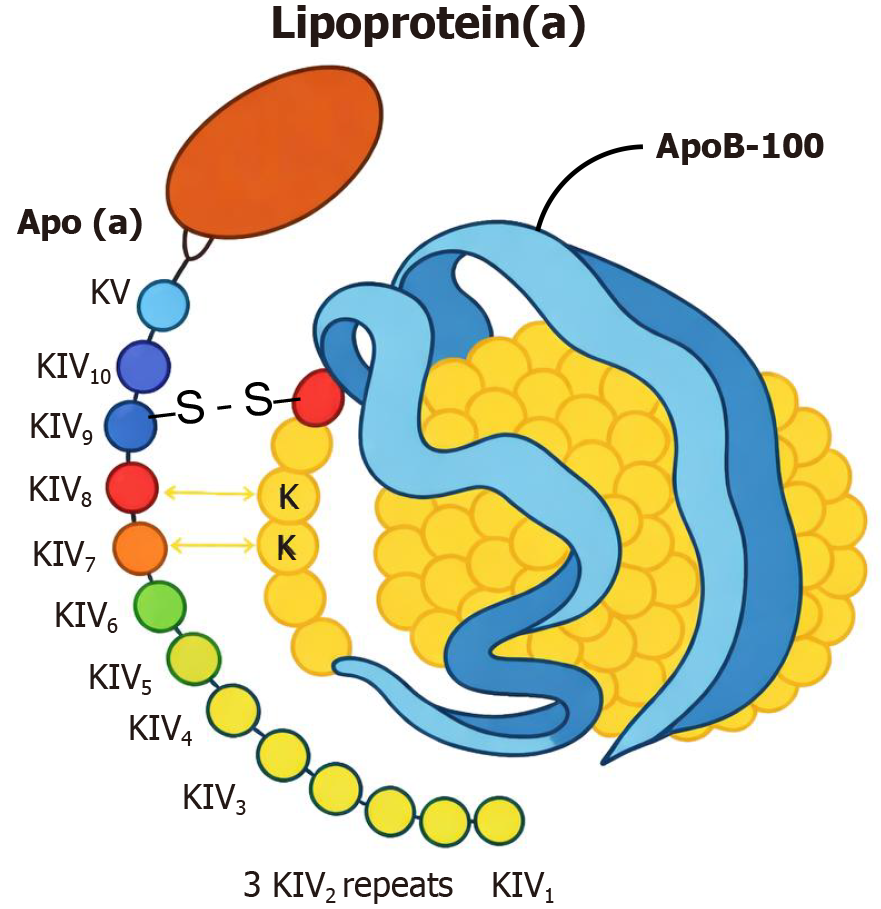
Figure 1 Structural features of lipoprotein(a).
Apo(a): Apolipoprotein(a); KIV: Kringles type IV; ApoB-100: Apolipoprotein B-100.
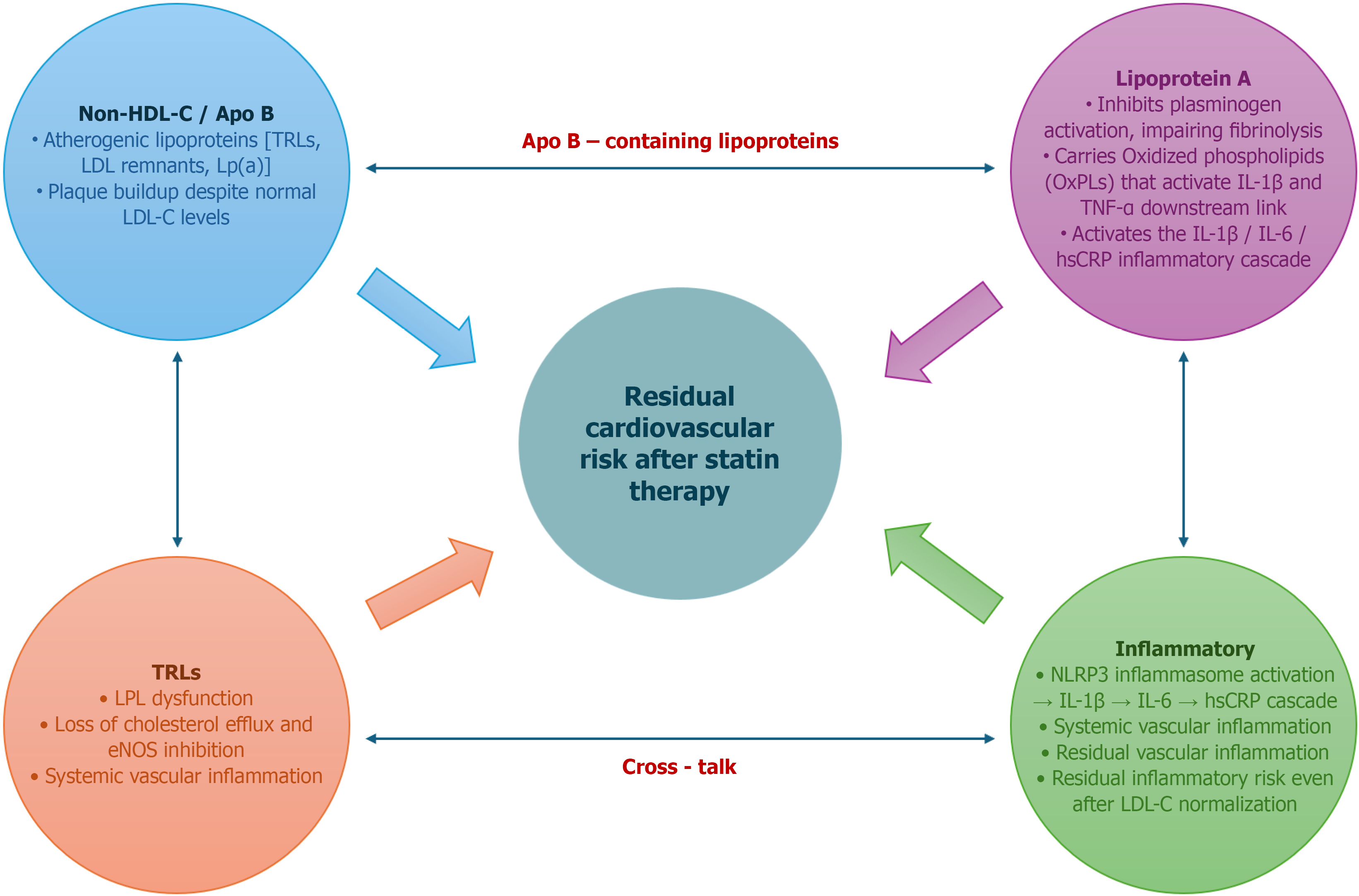
Figure 2 Mechanistic overview of residual cardiovascular risk (low-density lipoprotein-independent lipid and inflammatory pathways).
TRLs: Triglyceride-rich lipoproteins; LPL: Lipoprotein lipase; eNOS: Endothelial nitric oxide synthase; LDL: Low-density lipoprotein; Lp(a): Lipoprotein(a); HDLC: High-density lipoprotein cholesterol; Apo B: Apolipoprotein B; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; hsCRP: High-sensitivity C-reactive protein; LDL-C: Low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol.
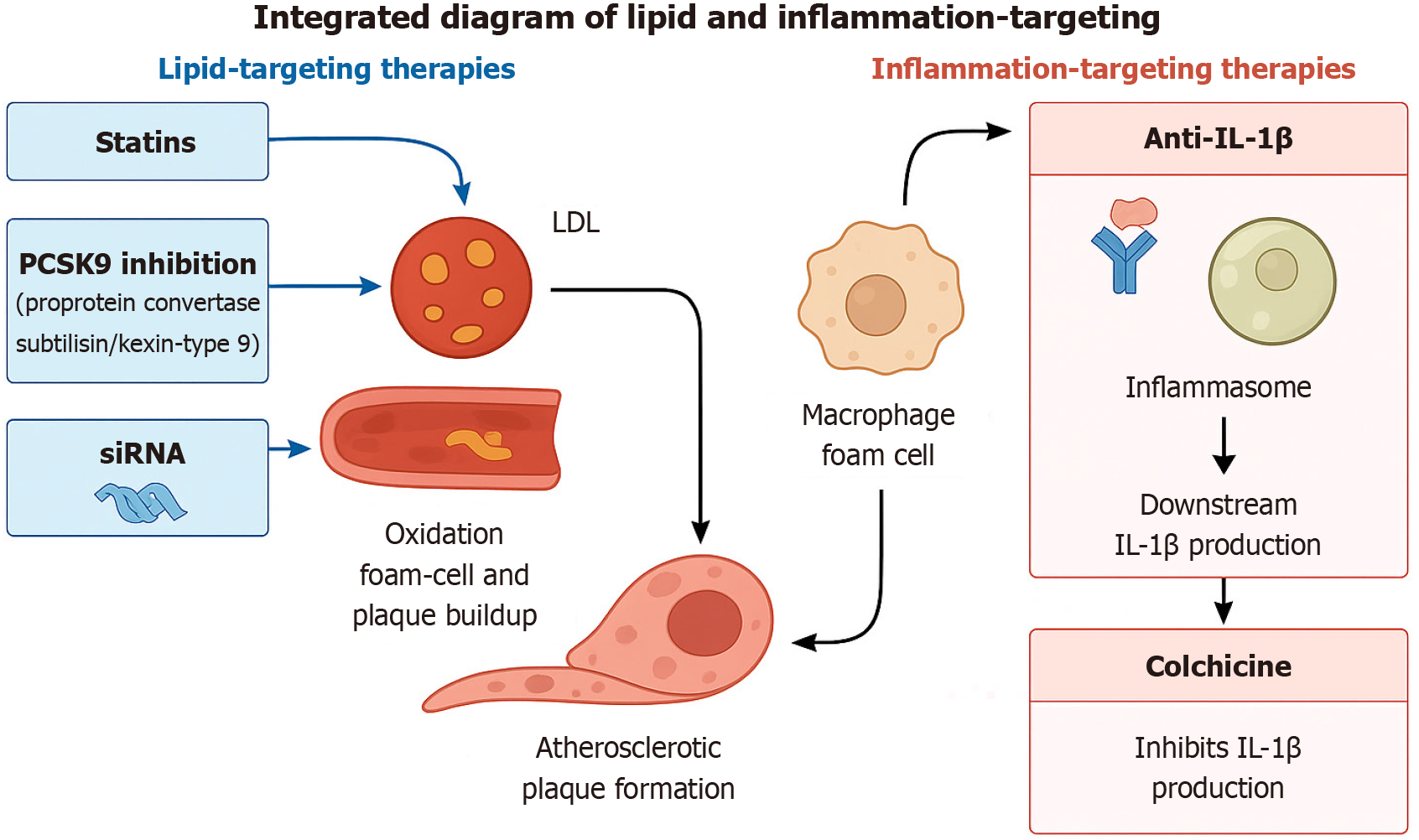
Figure 3 Integrated diagram of lipid and inflammation - targeting therapies.
LDL: Low-density lipoprotein; PCSK9: Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9; siRNA: Small interfering RNA; IL: Interleukin.
- Citation: Tan SH, Wu JL, Zhuo SX, Zhang Y, Wang M. Residual risk in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease after statin therapy: Clinical mechanisms and management strategies. World J Cardiol 2026; 18(2): 114960
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v18/i2/114960.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v18.i2.114960