©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Cardiol. Dec 26, 2025; 17(12): 112978
Published online Dec 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i12.112978
Published online Dec 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i12.112978
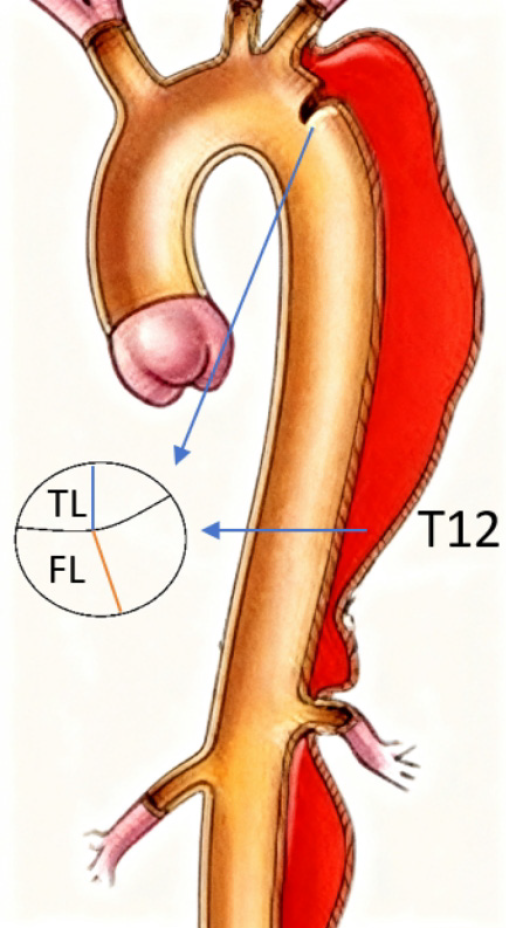
Figure 1 Schematic illustration showing the standardized measurement of true and false lumen diameters at the primary entry tear levels and the T12 level.
TL: Ture lumen; FL: False lumen; T12: The twelfth thoracic vertebra.
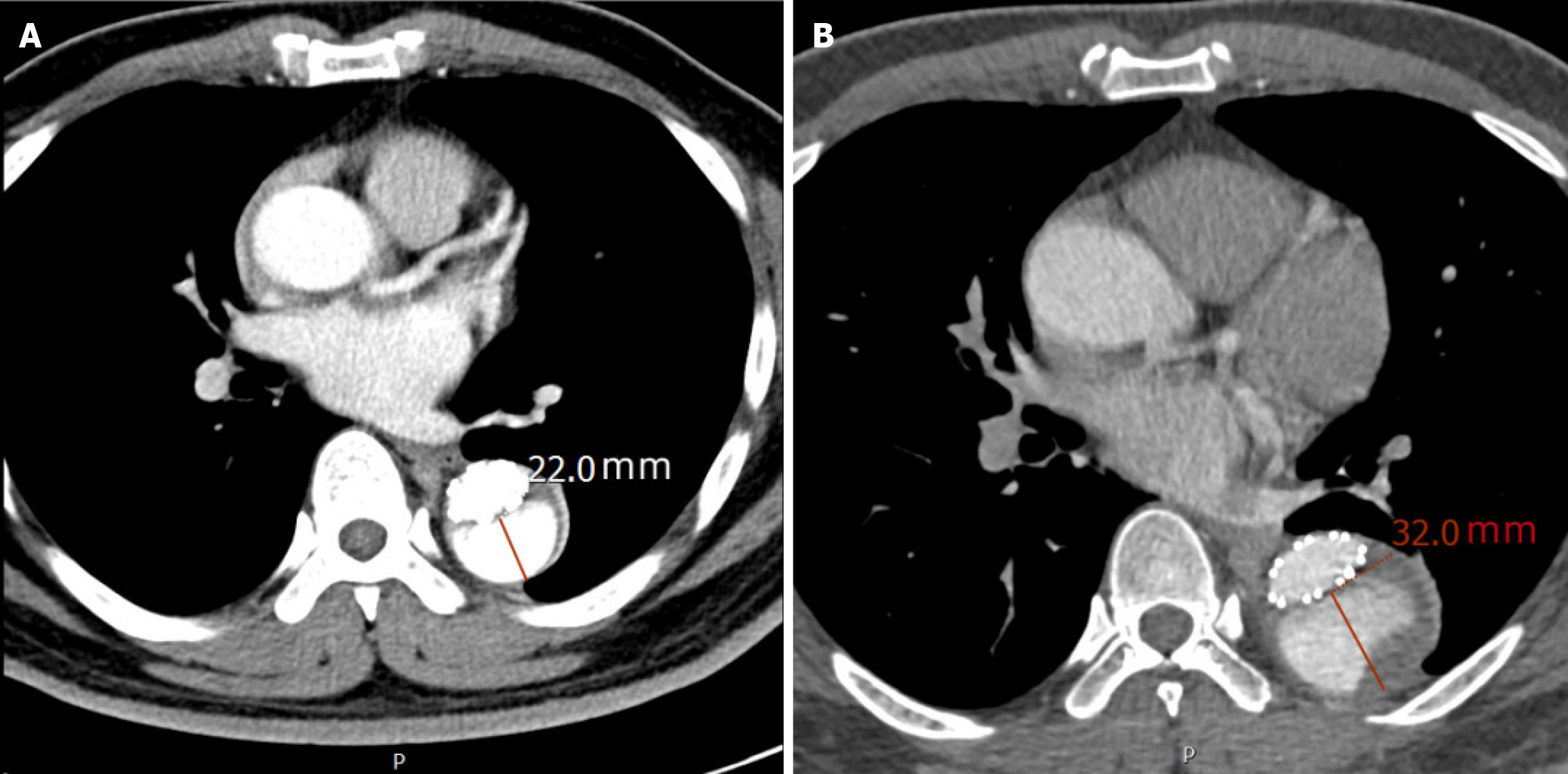
Figure 2 Representative computed tomography angiography images demonstrating aortic adverse remodeling in the same patient.
A: Post-operative computed tomography angiography (CTA) at 1 month after thoracic endovascular aortic repair (TEVAR), showing persistent perfusion within the false lumen of the aorta, with a short-axis diameter of the false lumen measuring 22 mm; B: Post-operative CTA at 6 months after TEVAR demonstrates ongoing perfusion and progressive expansion of the false lumen in the descending aorta, with the short-axis diameter increasing to 32 mm, indicative of adverse aortic remodeling.
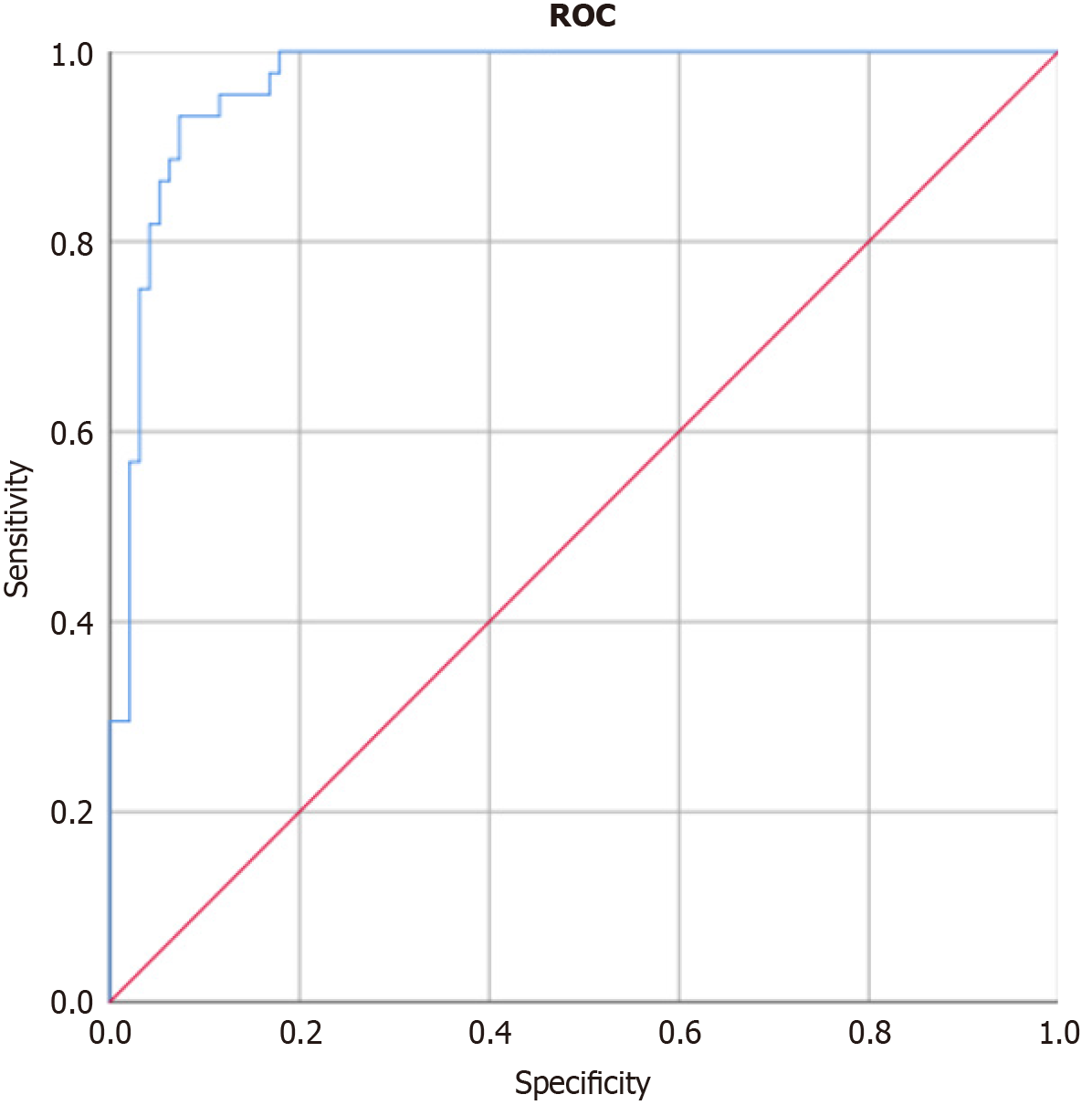
Figure 3 Receiver operating characteristic curve for predicting adverse aortic remodeling post-thoracic endovascular aortic repair in type B aortic dissection patients.
ROC: Receiver operating characteristic.
- Citation: Wang LF, Zhu HJ, Wang C, Yan F, Qu CZ. Logistic regression-based risk prediction of aortic adverse remodeling following thoracic endovascular aortic repair in patients with aortic dissection. World J Cardiol 2025; 17(12): 112978
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v17/i12/112978.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v17.i12.112978