©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Cardiol. Dec 26, 2024; 16(12): 689-706
Published online Dec 26, 2024. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v16.i12.689
Published online Dec 26, 2024. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v16.i12.689
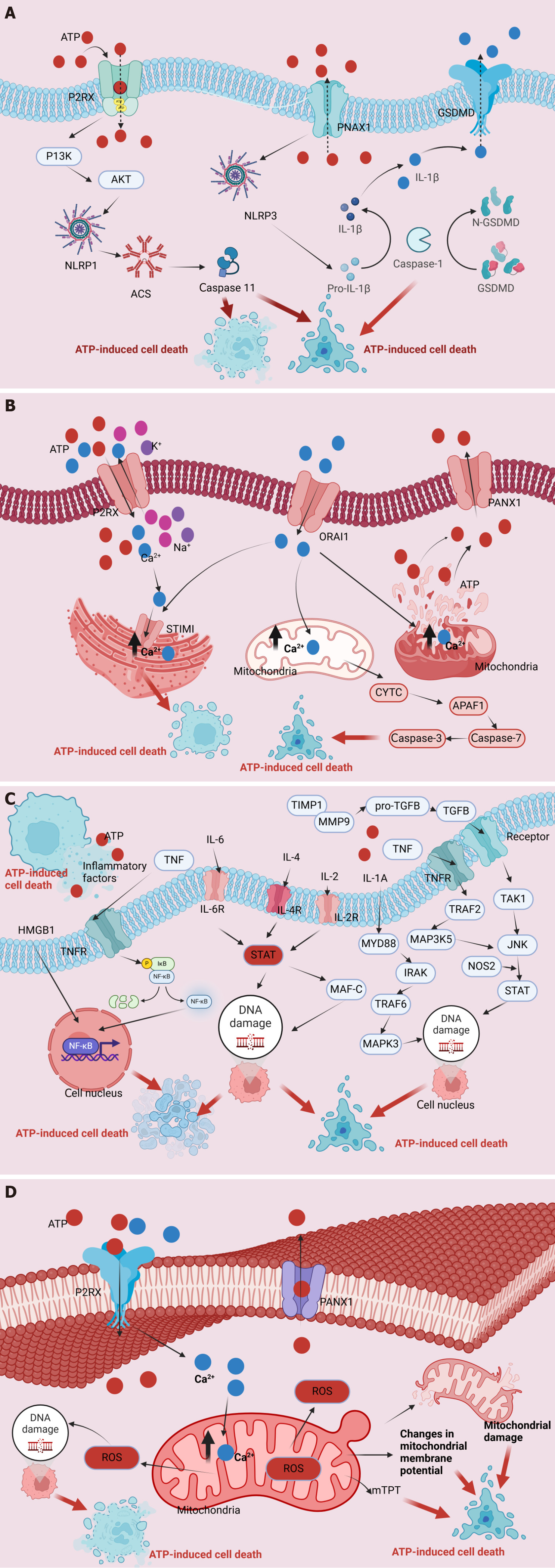
Figure 1 Regulation mechanism of adenosine triphosphate homeostasis and adenosine triphosphate-induced cell death.
A: P2 receptor activation pathway; B: Ca2+ pathway induces cell death pathways; C: The induction of cell death by adenosine triphosphate results in the release of immune inflammatory factors and activation of immune pathways that further promote cell death; D: The concurrent depletion of mitochondrial membrane potential, disruption of mitochondrial integrity, generation of reactive oxygen species, and alterations in mitochondrial membrane permeability jointly contribute to the ultimate demise of the cell. ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT: Protein kinase B; PNAX1: Pannexin-1; GSDMD: Gasdermin D; NLRP3: NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing protein 3; IL: Interleukin; ACS: Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase recruitment domain; ORAI1: Calcium release activated calcium channel protein 1; STIM1: Stromal interaction molecule 1; CYTC: Cytochrome c; APAF1: Apoptotic protease-activating factor 1; HMGB: High-mobility group box; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; TIMP1: Tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloprotease 1; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase; TGF: Transforming growth factor; NF-κB: Nuclear factor κB; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; MYD88: Myeloid differentiation factor-88; TRAF2: Tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 2; TAK1: Beta-activated kinase 1; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase; MAP3K5: Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 5; IRAK: Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase; MAF-C: MAF BZIP transcription factor C; NOS2: Nitric oxide synthase; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; mTPT: Mitochondrial permeability transition.
- Citation: Wang W, Wang XM, Zhang HL, Zhao R, Wang Y, Zhang HL, Song ZJ. Molecular and metabolic landscape of adenosine triphosphate-induced cell death in cardiovascular disease. World J Cardiol 2024; 16(12): 689-706
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v16/i12/689.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v16.i12.689