©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Dec 27, 2025; 17(12): 112256
Published online Dec 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i12.112256
Published online Dec 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i12.112256
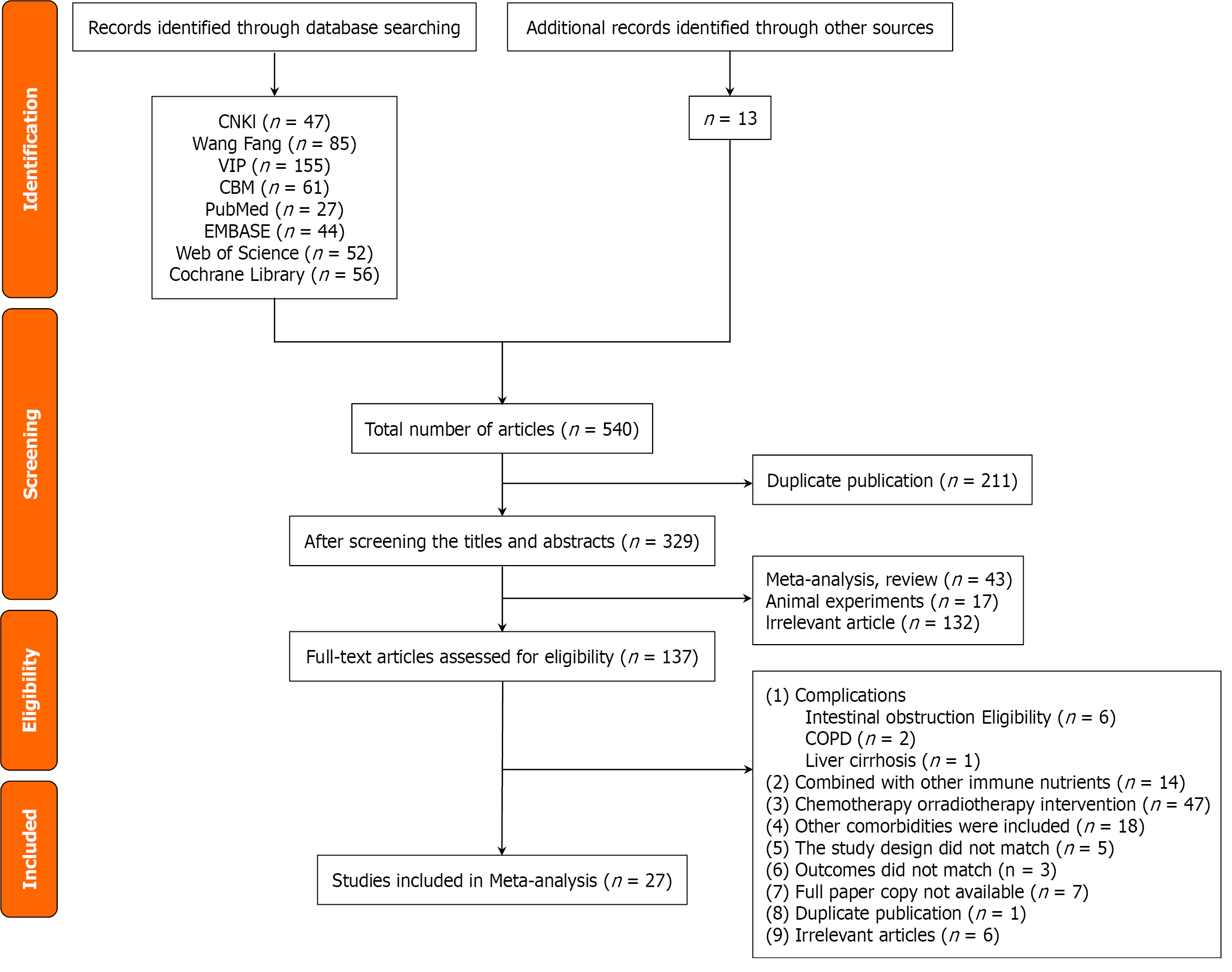
Figure 1 Flow chart for literature screening.
COPD: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
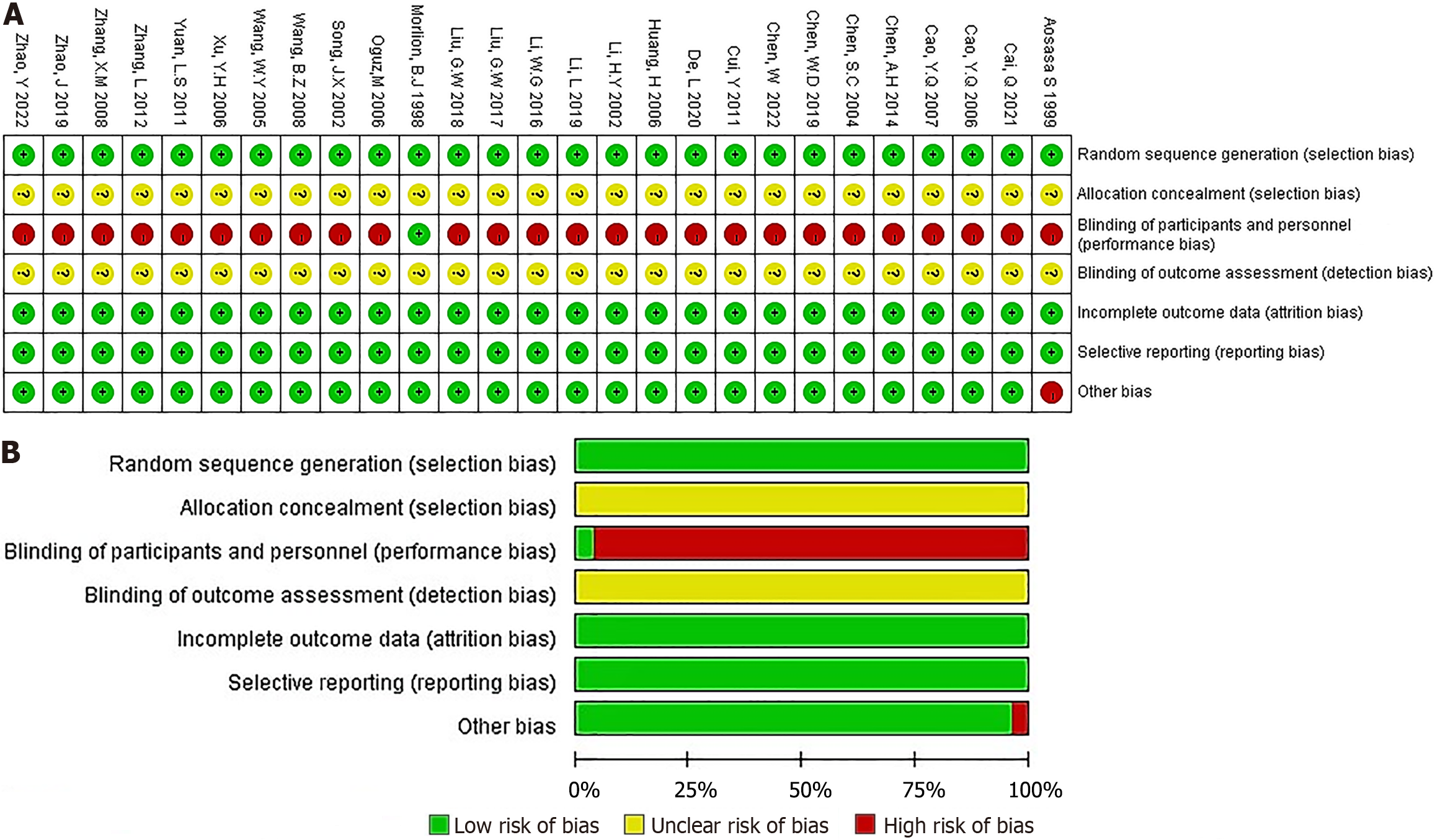
Figure 2 Methodological quality graph and summary of the included studies.
A: Risk of bias summary; B: Risk of bias graph.
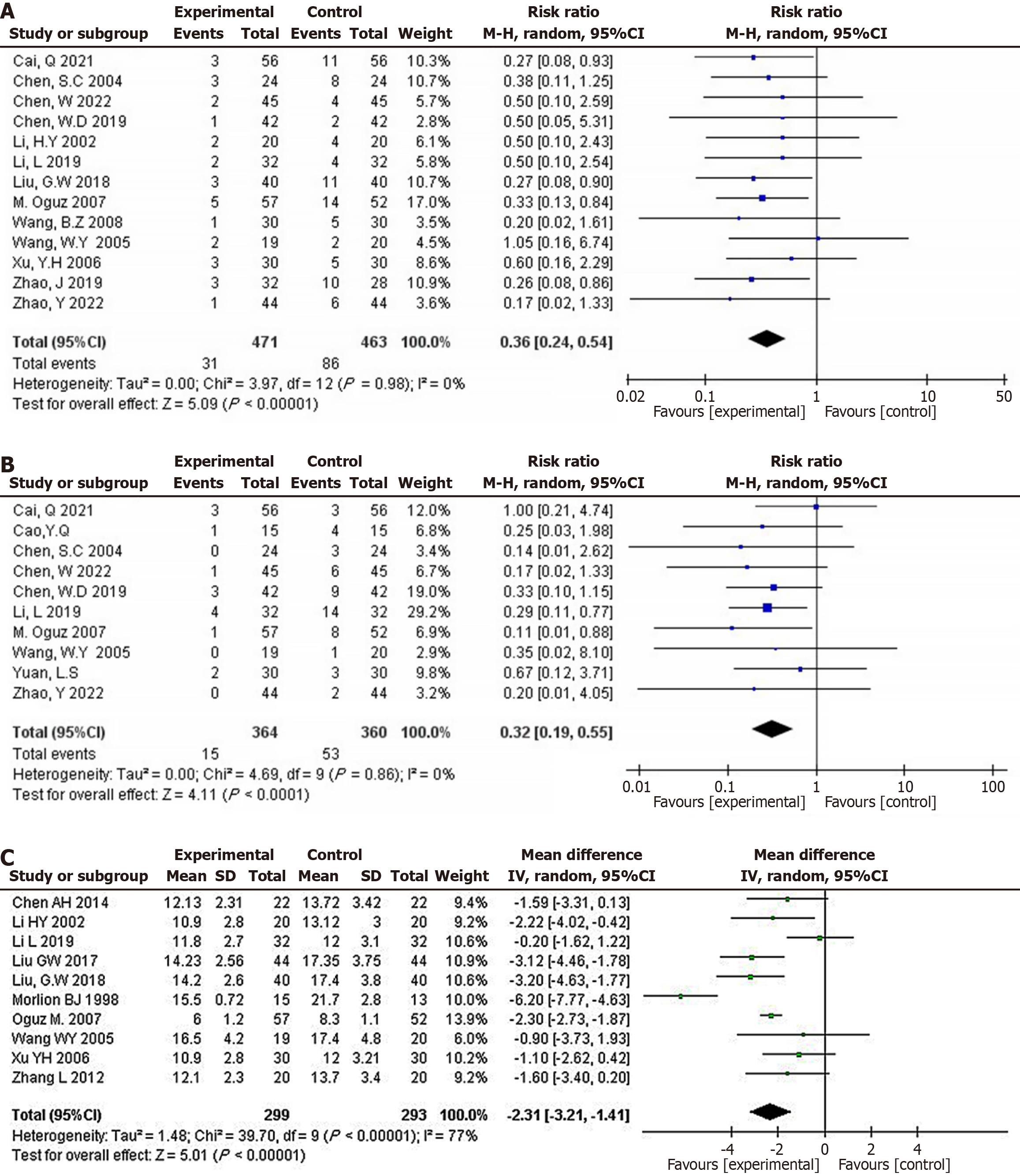
Figure 3 Pooled effect estimates for randomized controlled trials assessing the effect of glutamine supplementation on changes in primary outcomes between the intervention and control groups.
A: Morbidity of infectious complications; B: Morbidity of non-infectious complications; C: The length of stay (day).
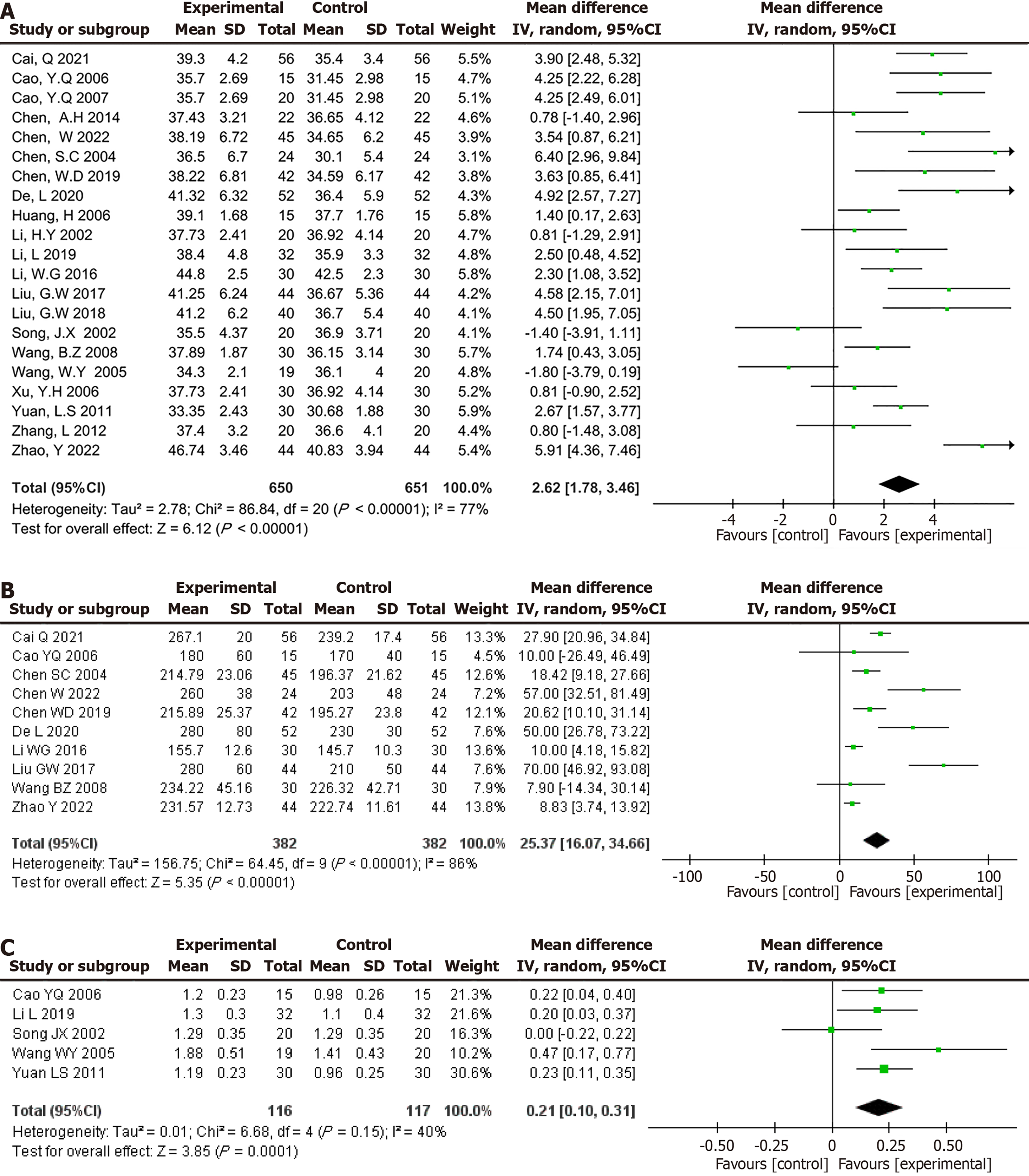
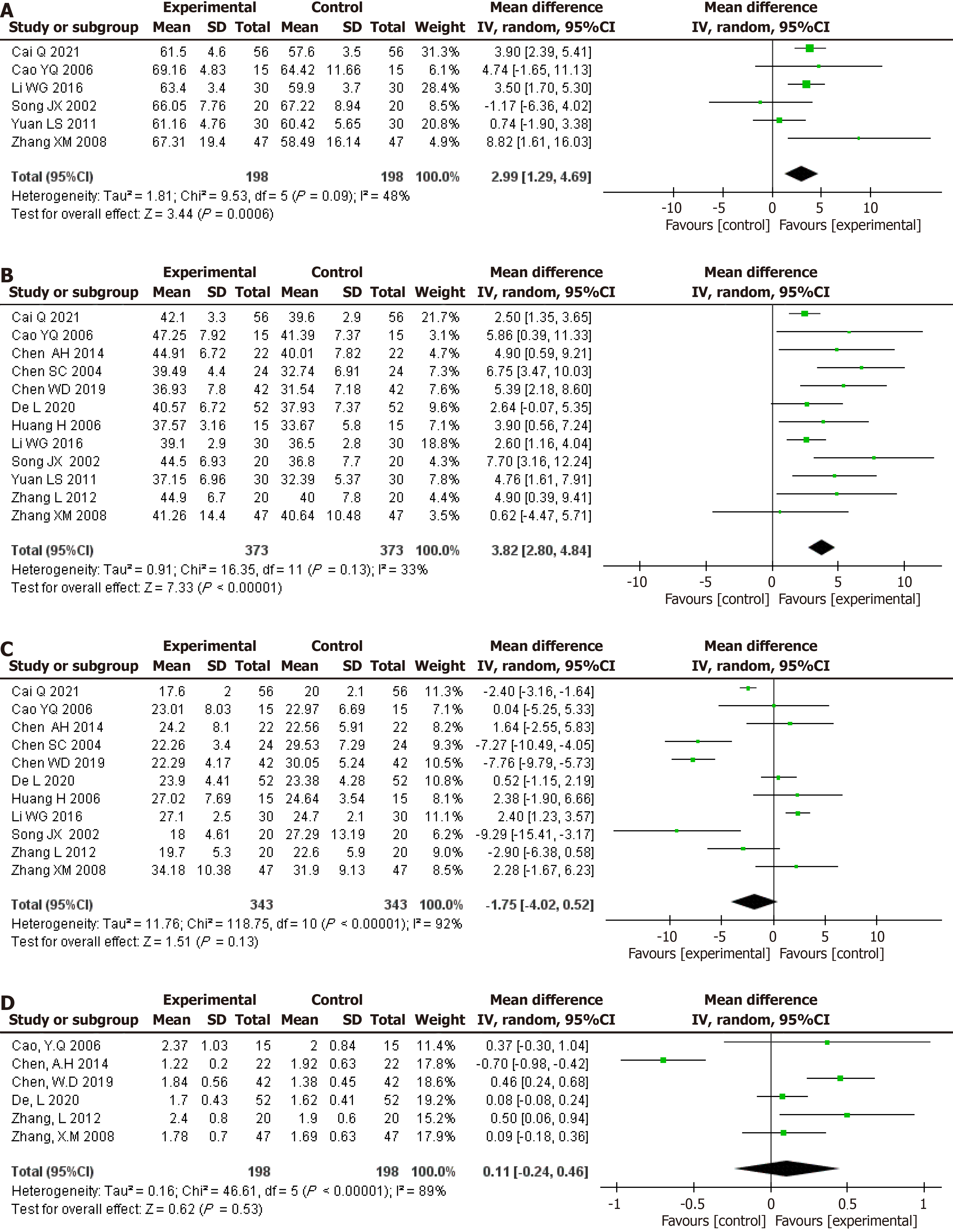
Figure 4 Pooled effect estimates for randomized controlled trials assessing the effect of glutamine supplementation on changes in nutritional status between the intervention and control groups.
A: Albumin level (g/L); B: Prealbumin level (mg/L); C: Peripheral blood lymphocyte counts (× 109/L) levels.
Figure 5
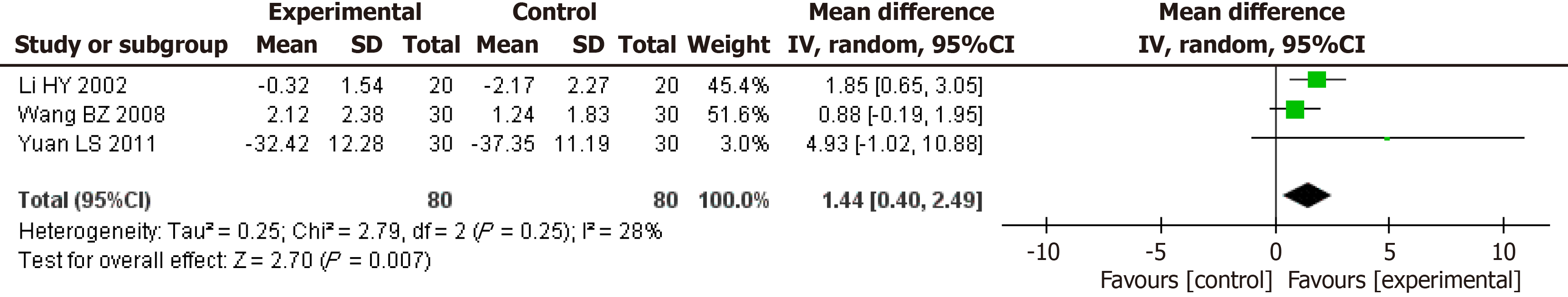
Pooled effect estimates for randomized controlled trials assessing the effect of glutamine supplementation on changes in nitrogen balance levels (g/d) between the intervention and control groups.
Figure 6 Pooled effect estimates for randomized controlled trials assessing the effect of glutamine supplementation on changes in cellular immune function between the intervention and control groups.
A: CD3+ levels (%); B: CD4+ levels (%); C: CD8+ levels (%); D: CD4+/CD8+ levels.
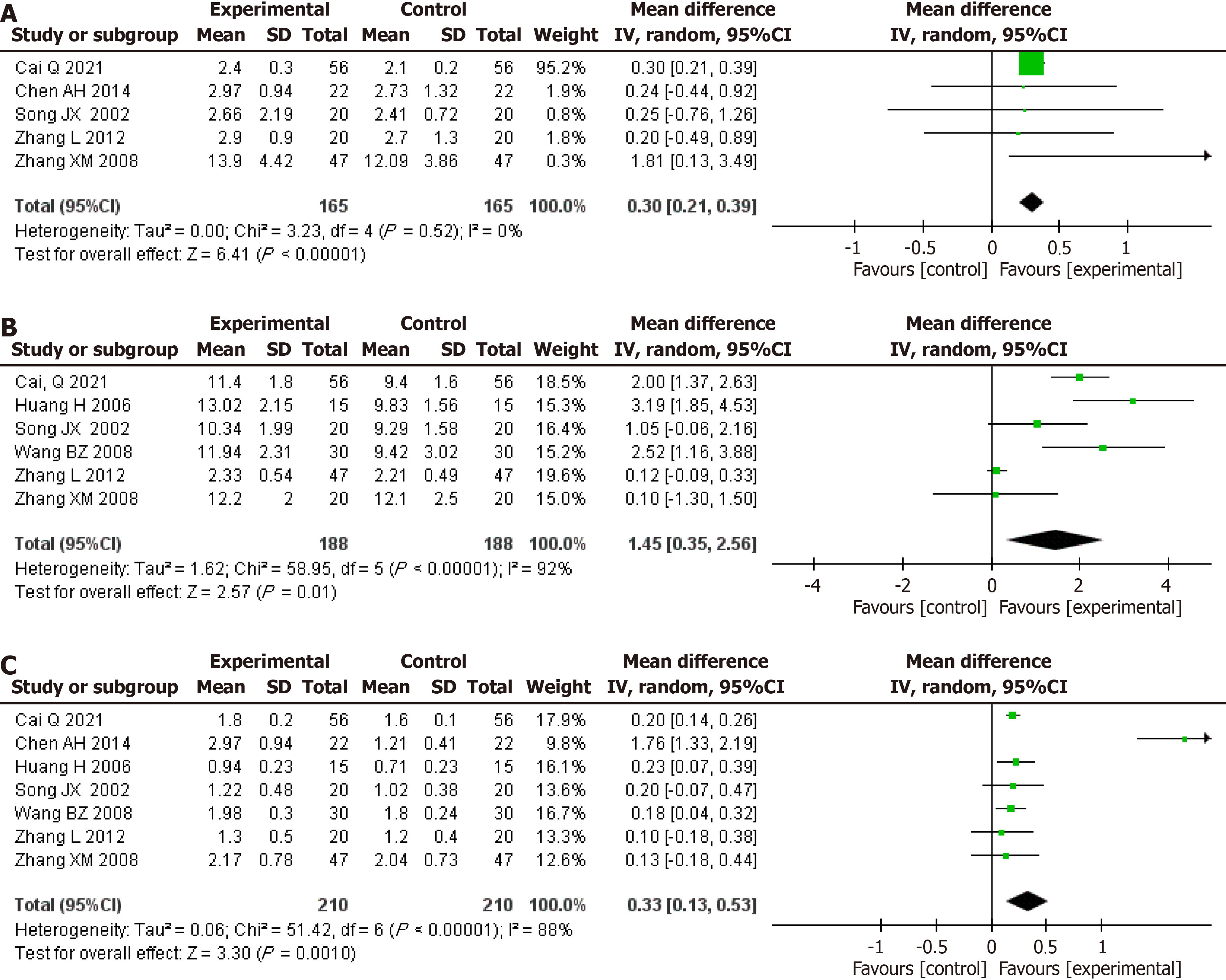
Figure 7 Pooled effect estimates for randomized controlled trials assessing the effect of glutamine supplementation on changes in humoral immune function between the intervention and control groups.
A: IgA levels (g/L); B: IgG levels (g/L); C: IgM levels (g/L).
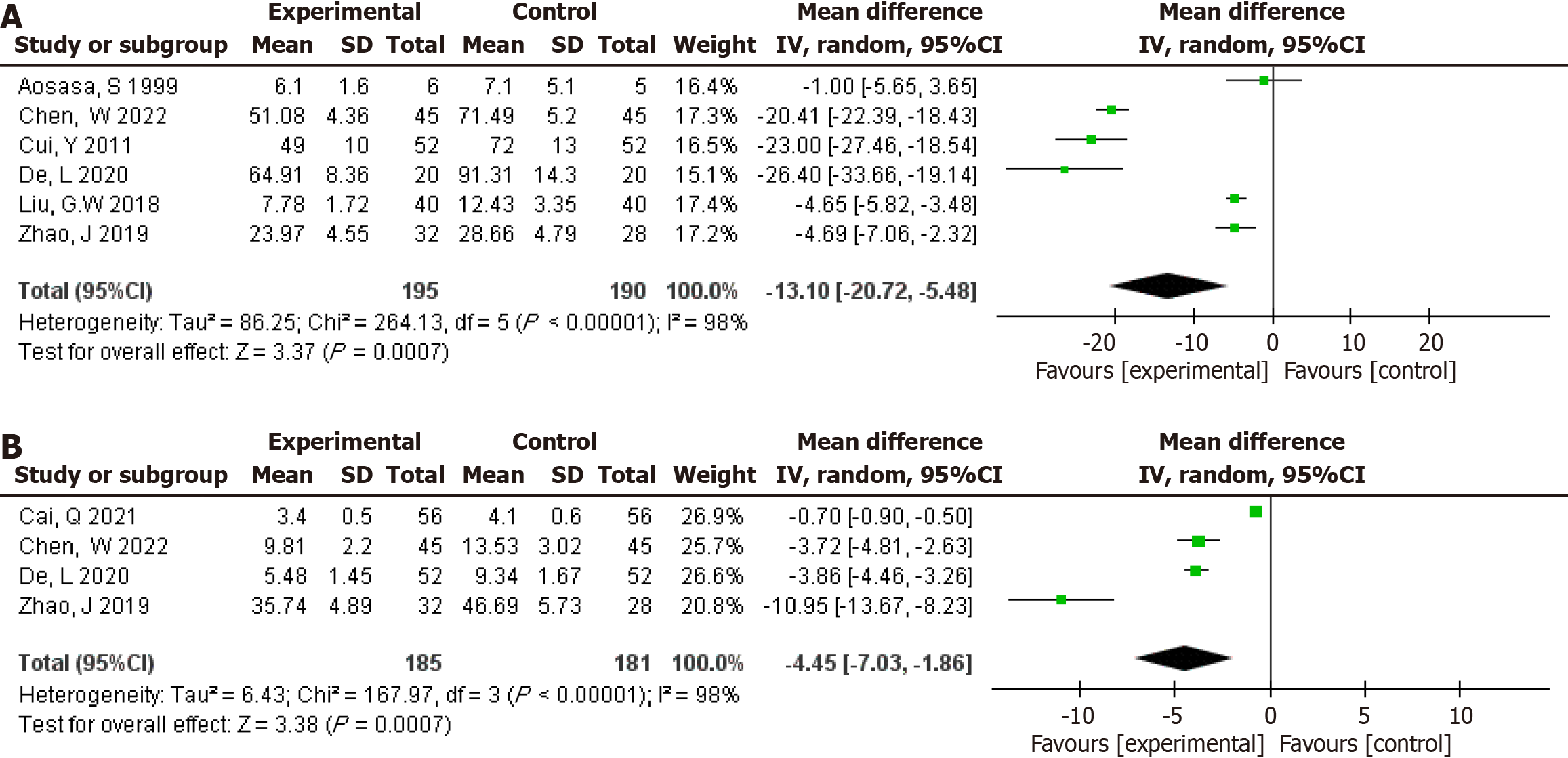
Figure 8 Pooled effect estimates for randomized controlled trials assessing the effect of glutamine supplementation on changes in inflammation level between the intervention and control groups.
A: Tumor necrosis factor-α levels (pg/mL); B: C-reactive protein levels (mg/L).
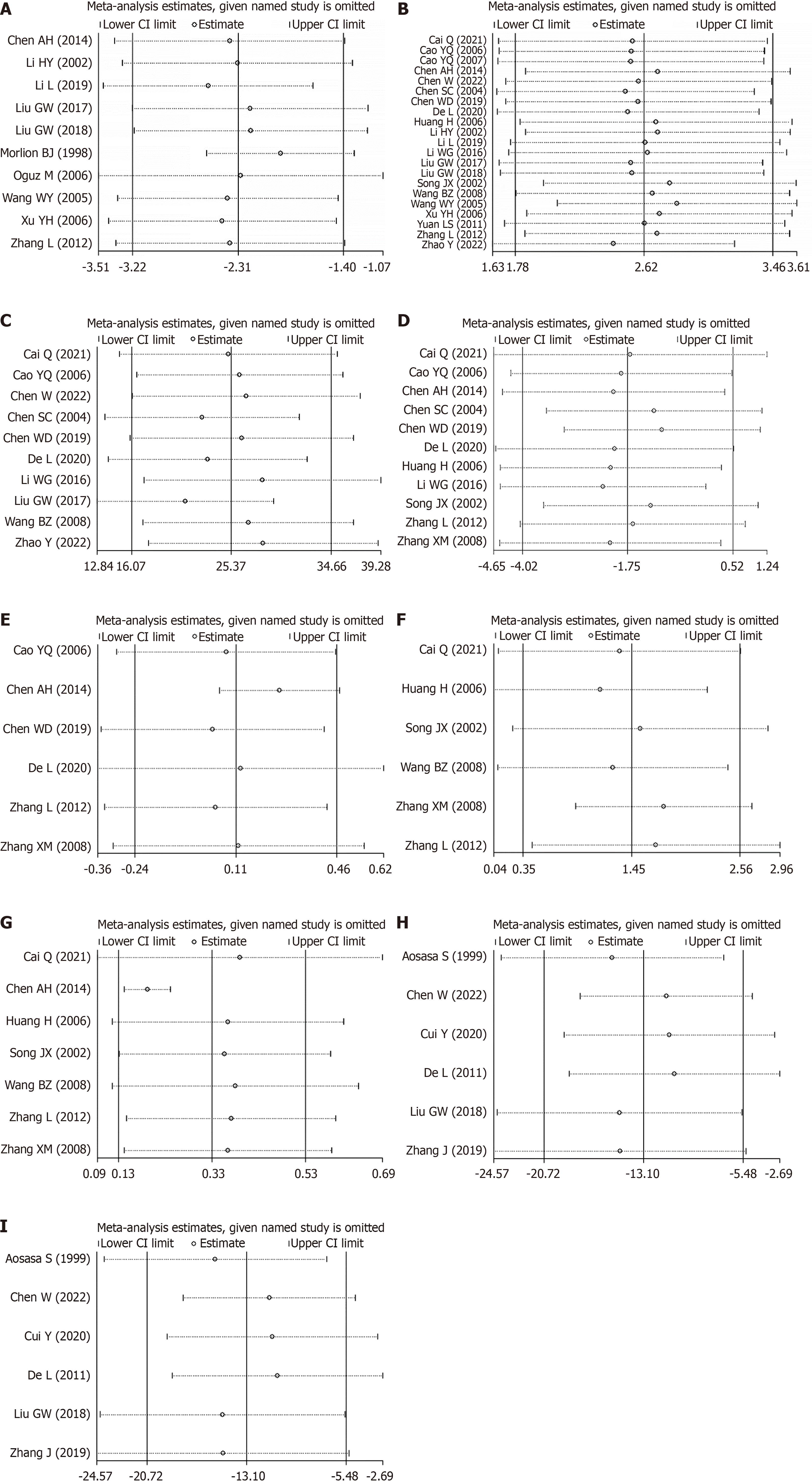
Figure 9 Sensitivity analyses (removing one by one) was performed on the pooled analysis results with high heterogeneity (I2 > 75%) to verify the robustness of the pooled analysis.
A: Length of hospital stay; B: Albumin levels; C: Prealbumin levels; D: CD8+ levels; E: CD4+/CD8+ levels; F: IgG levels; G: IgM levels; H: Tumor necrosis factor-α levels; I: C-reactive protein levels.
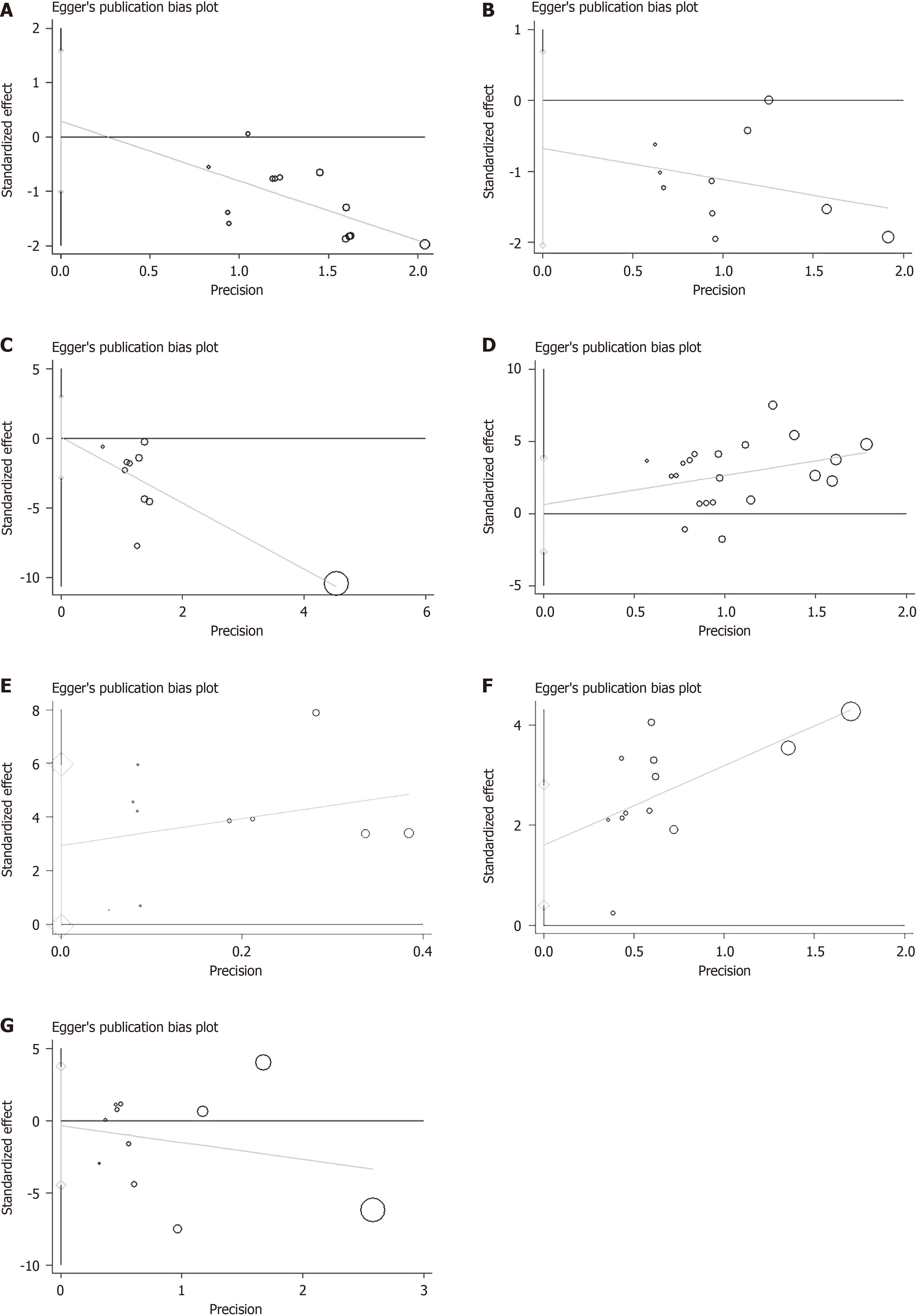
Figure 10 Egger's test.
A: Morbidity of infectious complications; B: The morbidity of non-infectious complications; C: Length of hospital stay; D: Albumin levels; E: Prealbumin levels; F: CD4+ levels; G: CD8+ levels.
- Citation: Huang Y, Yang XZ, Qin SH, Zhang T, Xie M, Wang JW. Effect of perioperative glutamine-enriched nutritional support on patients with colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Gastrointest Surg 2025; 17(12): 112256
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v17/i12/112256.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v17.i12.112256