©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Nov 27, 2025; 17(11): 112058
Published online Nov 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i11.112058
Published online Nov 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i11.112058
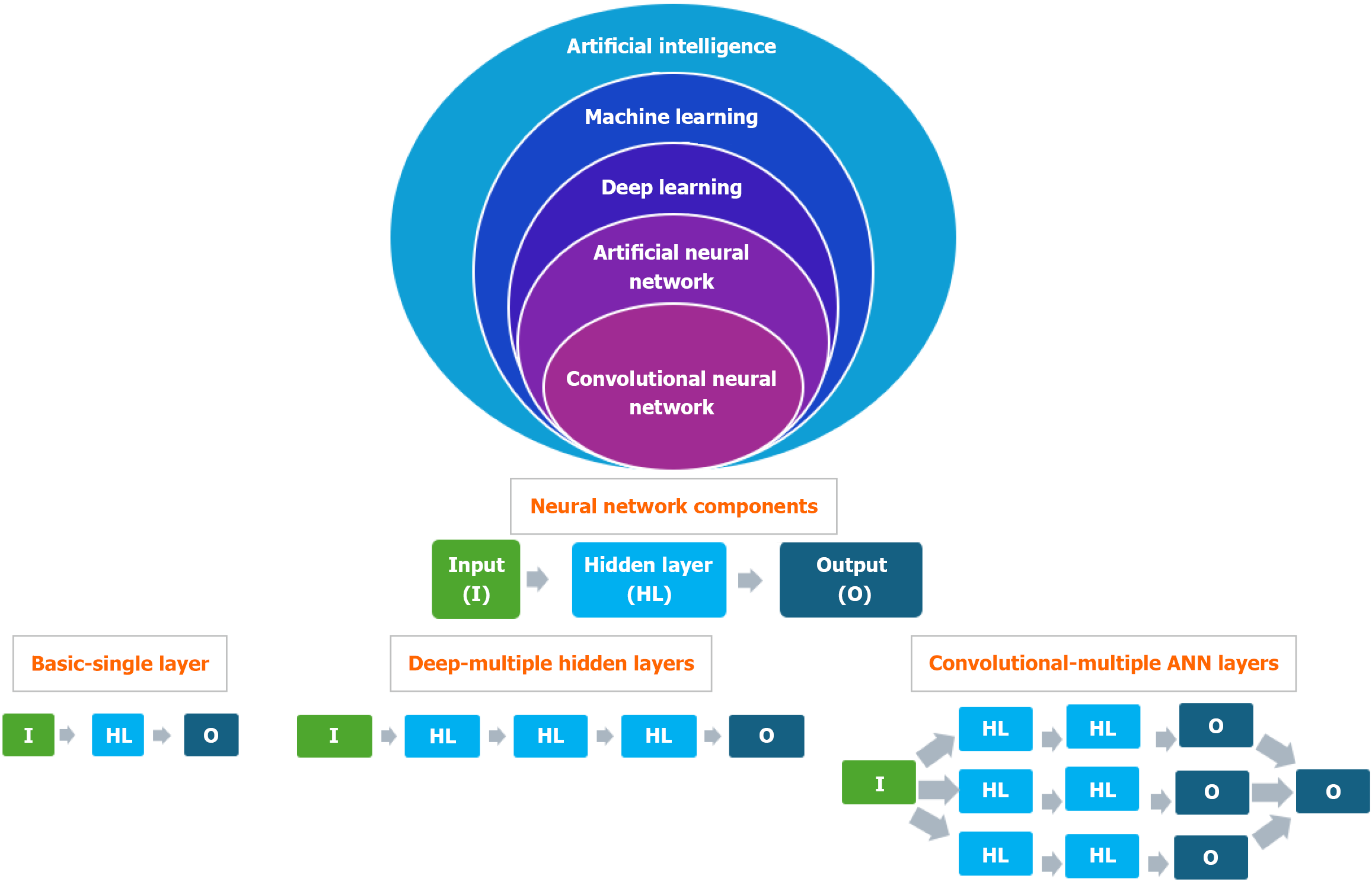
Figure 1 Artificial intelligence nomenclature.
ANN: Artificial neural network.
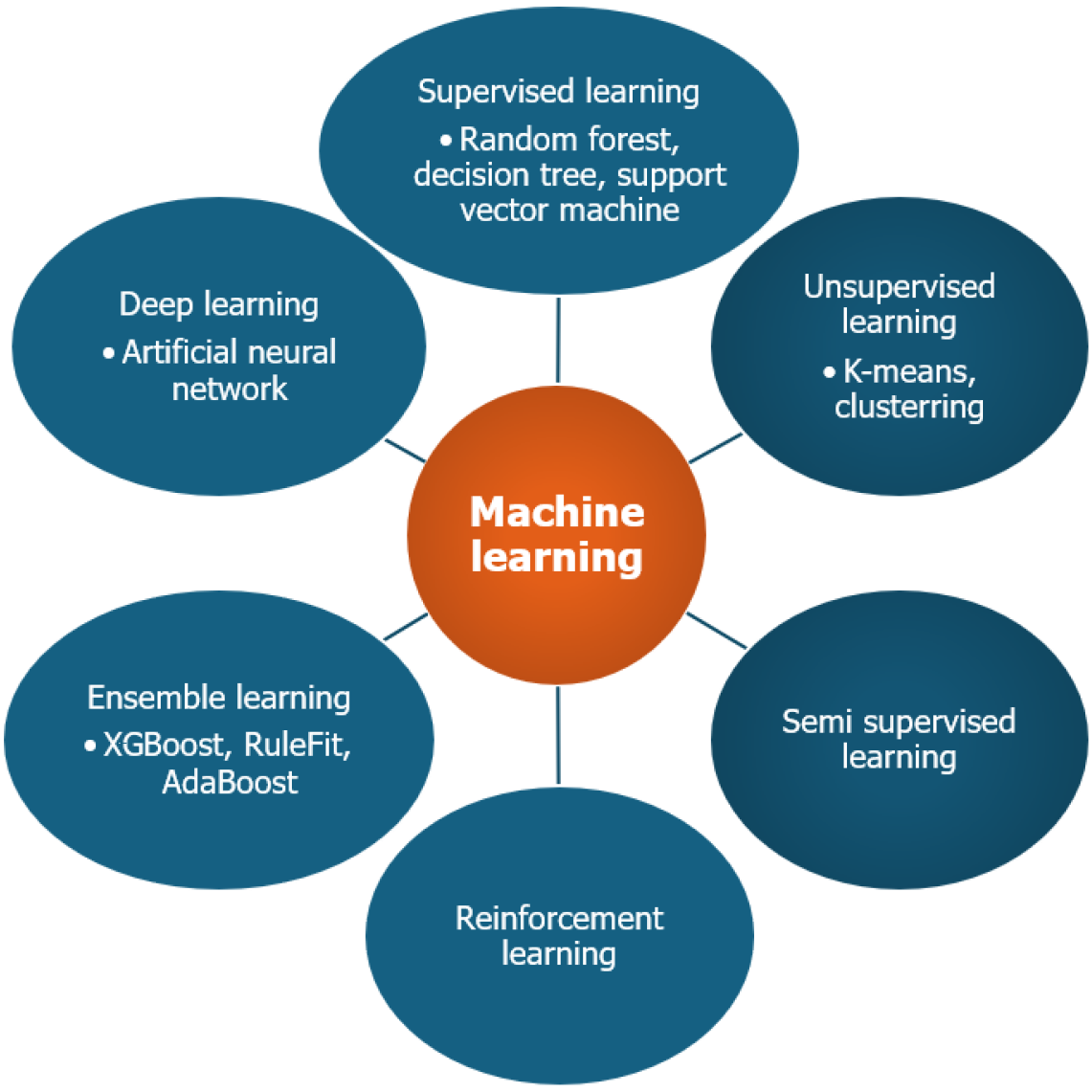
Figure 2 Types of machine learning model.
XGBoost: eXtreme Gradient Boosting.
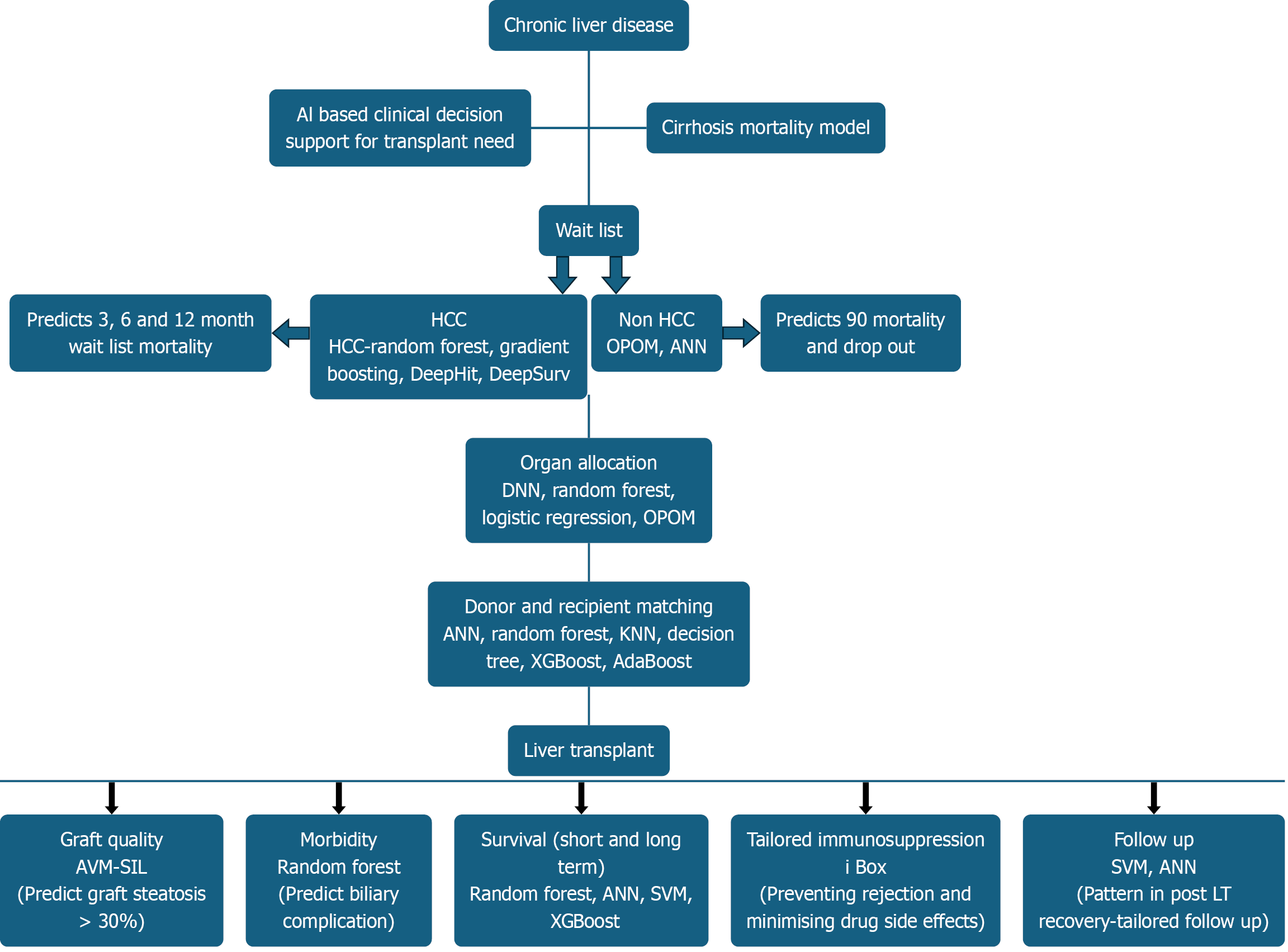
Figure 3 Application of artificial intelligence in deceased donor liver transplantation.
HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; ANN: Artificial neural network; OPOM: Optimised prediction of mortality; SVM: Support vector machines; AVM-SIL: Support vector machine-single instance learning; XGBoost: eXtreme Gradient Boosting; LT: Liver transplantation.
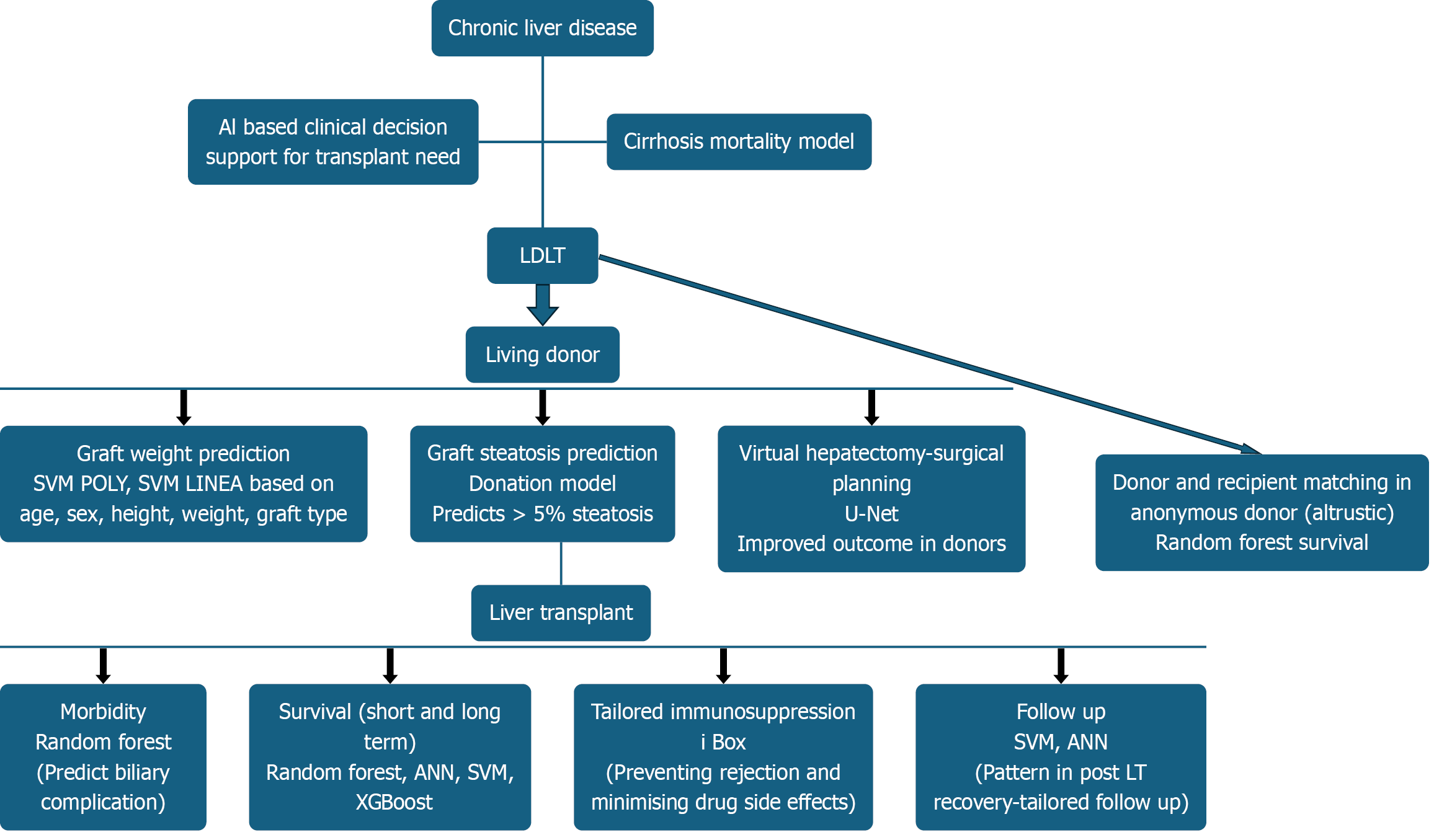
Figure 4 Application of artificial intelligence in living donor liver transplantation.
SVM-POLY: Support Vector Machine-Polynomial kernel; SVM-LINEA: Support Vector Machine Linear; U-Net: Convolutional neural network architecture, named after distinctive U shape; ANN: Artificial neural network; SVM: Support vector machine; XGBoost: eXtreme Gradient Boosting; LDLT: Living donor liver transplantation.
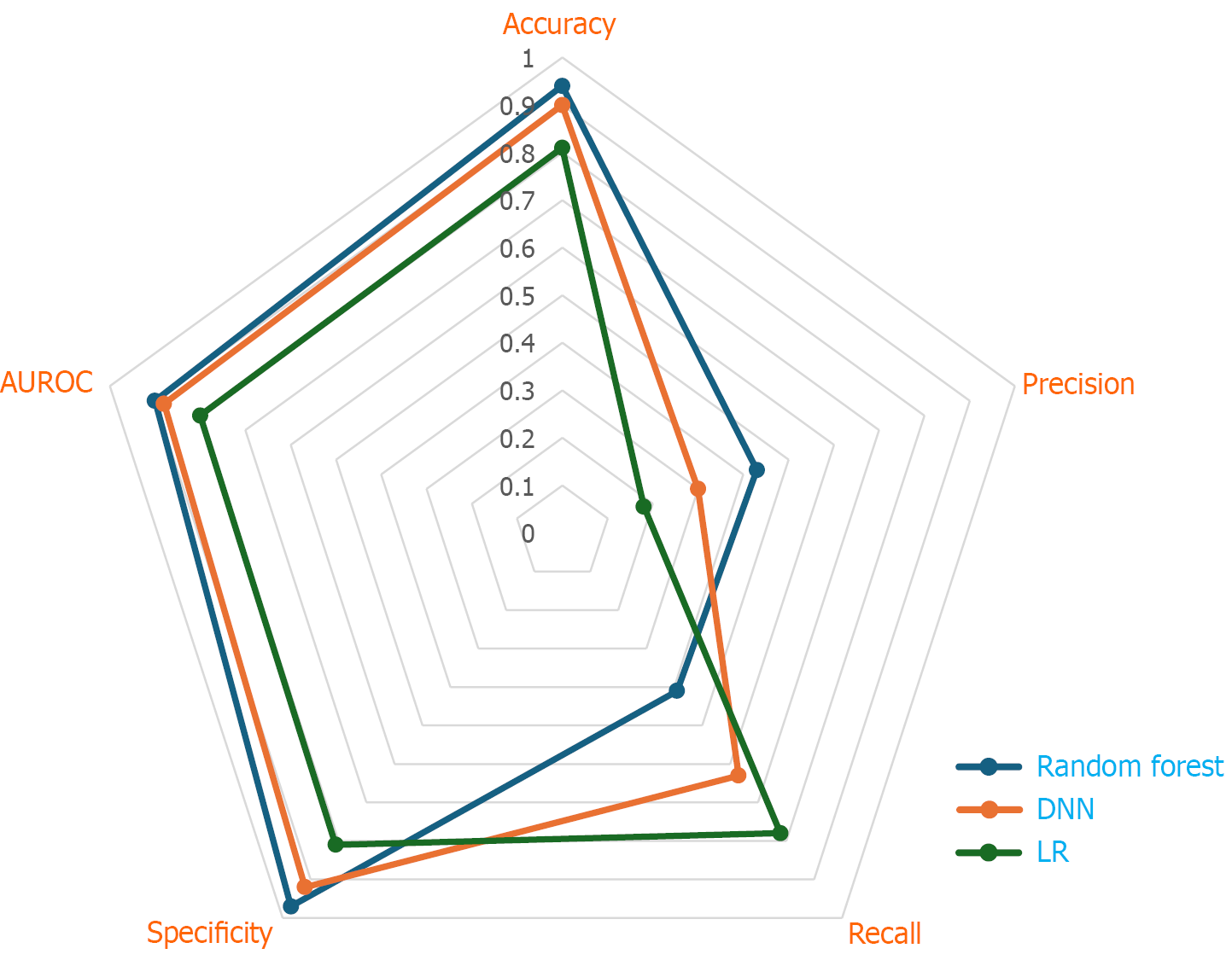
Figure 5 Radar plot for prediction of 90 days mortality in cirrhosis.
AUROC: Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; DNN: Deep neural networks; LR: Logistic regression.
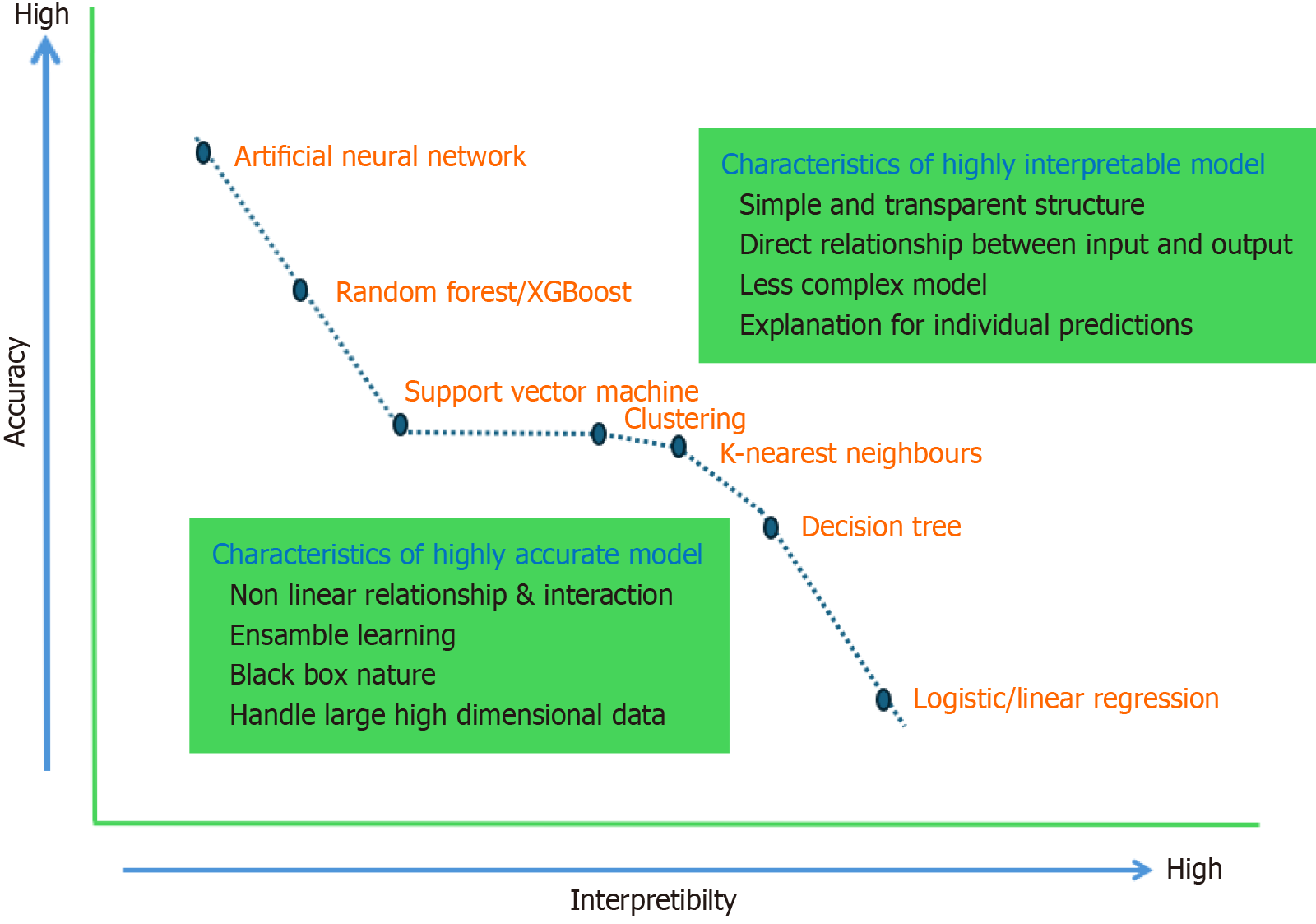
Figure 6 Accuracy and interpretability of various machine learning models.
XGBoost: eXtreme Gradient Boosting.
- Citation: Goja S, Yadav SK. Artificial intelligence in liver transplantation: Opportunities and challenges. World J Gastrointest Surg 2025; 17(11): 112058
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v17/i11/112058.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v17.i11.112058