©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Nov 27, 2025; 17(11): 111148
Published online Nov 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i11.111148
Published online Nov 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i11.111148
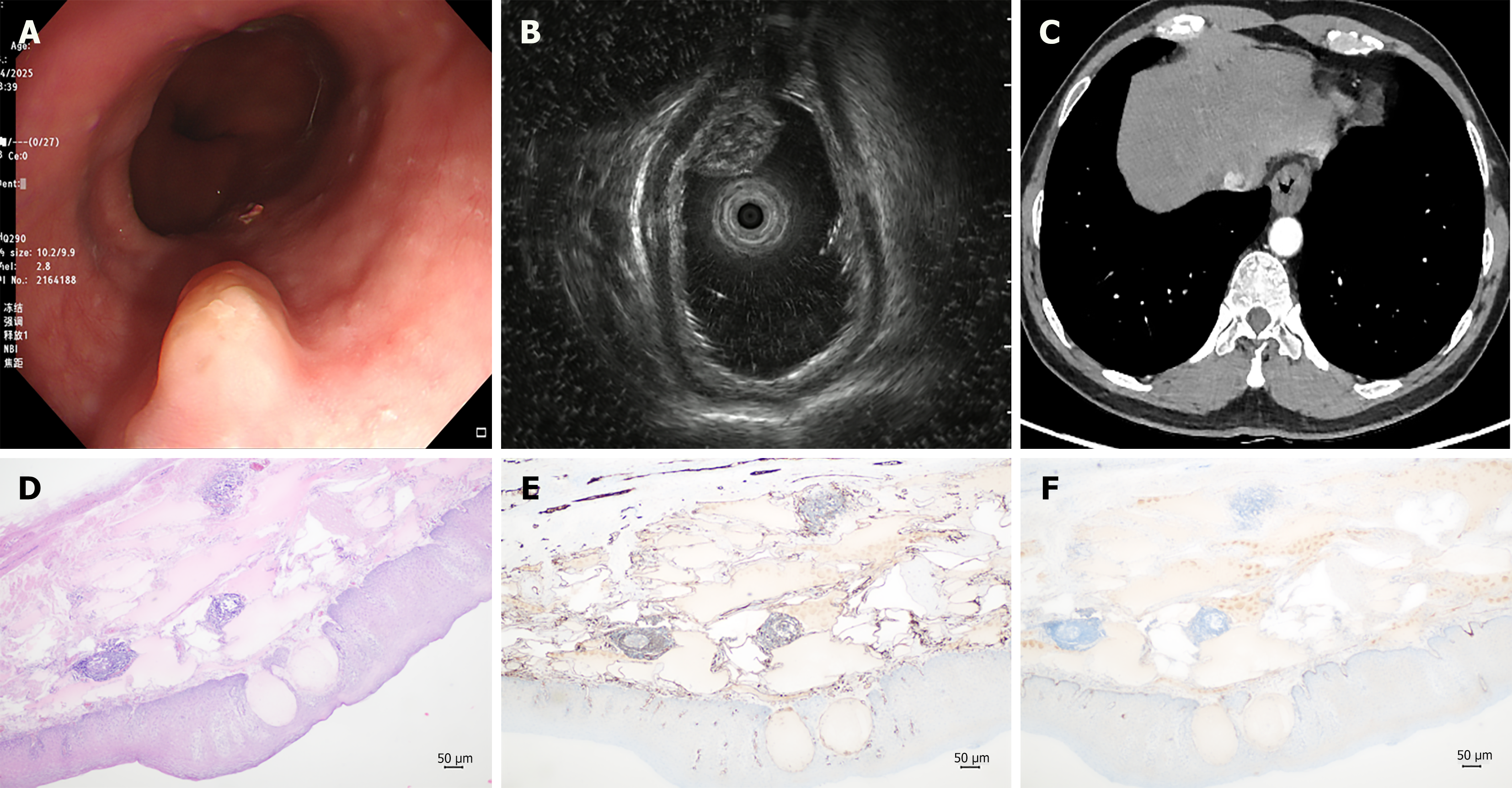
Figure 1 Diagnostic features of esophageal lymphangioma.
A: Endoscopic examination reveals a hemispherical mucosal elevation measuring approximately 1.5 cm × 0.8 cm in the lower segment of the esophagus, with a smooth surface and color consistent with the surrounding mucosa; B: Endoscopic ultrasound indicates that the lesion is located in the submucosal layer, presenting as a mixed hypoechoic mass with heterogeneous internal structure, exhibiting small septal changes and no significant blood flow signal; C: Chest computed tomography suggests localized wall thickening in the lower segment of the esophagus; D: Histological examination reveals numerous dilated tubular structures within the lamina propria; E and F: Immunohistochemical analysis indicated cluster of differentiation 31 positivity and partial positivity for D2-40, confirming the diagnosis of esophageal lymphangioma.
- Citation: Zheng XL, Yu XX. Esophageal lymphangioma: A case report and review of literature. World J Gastrointest Surg 2025; 17(11): 111148
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v17/i11/111148.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v17.i11.111148