©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Oct 27, 2025; 17(10): 111558
Published online Oct 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i10.111558
Published online Oct 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i10.111558
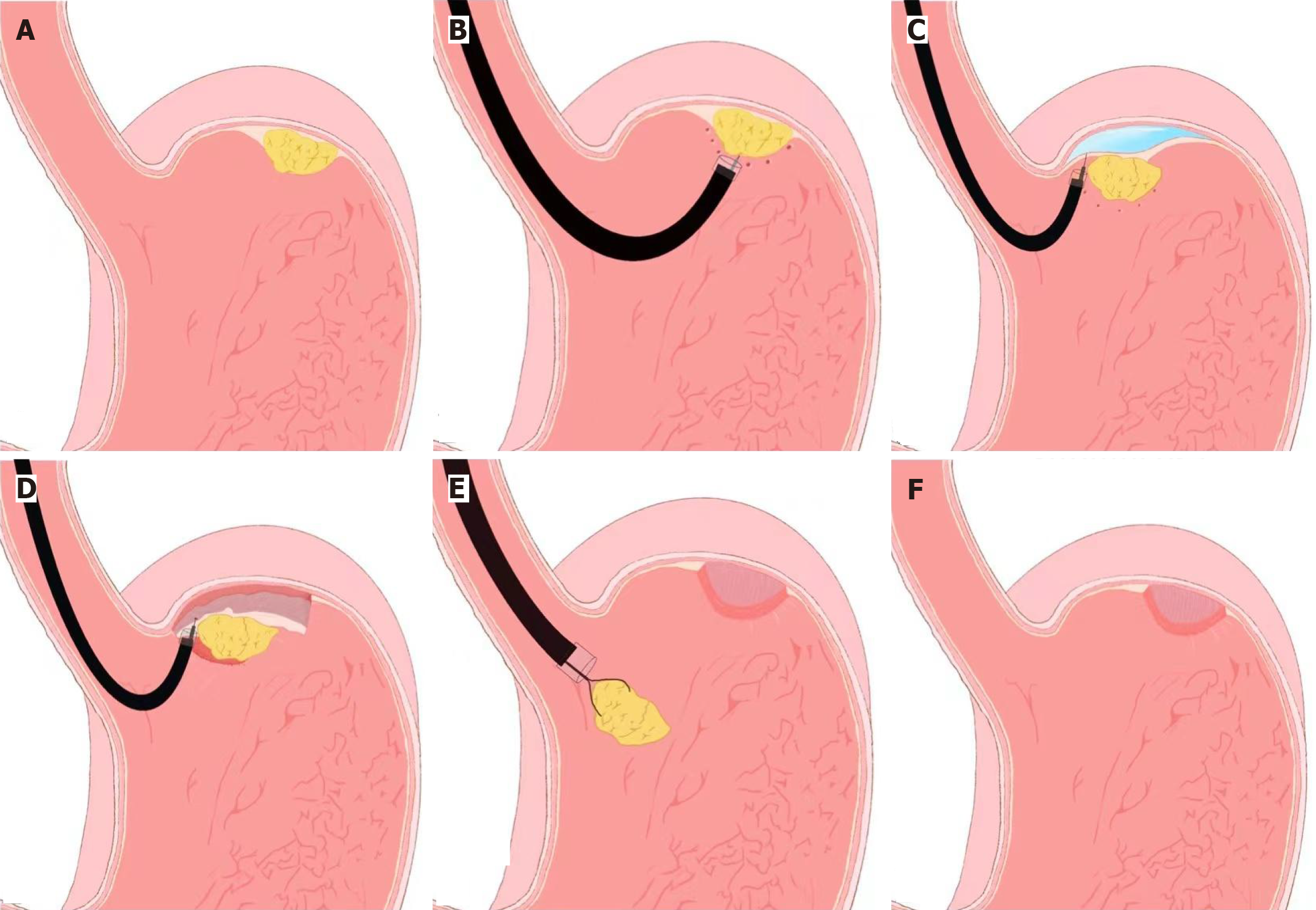
Figure 1 Schematic illustration of the endoscopic submucosal dissection technique used in the management of gastrointestinal stromal tumors.
A: Lesion (tumor); B: Marking around the lesion; C: Saline injection into the submucosa; D: Lesion resection using hook/IT knives; E: Dissection completed and lesion removal; F: Resection site after lesion removed. This procedure enables en bloc resection with negative margins by sequentially marking, lifting, dissecting, and closing the lesion.
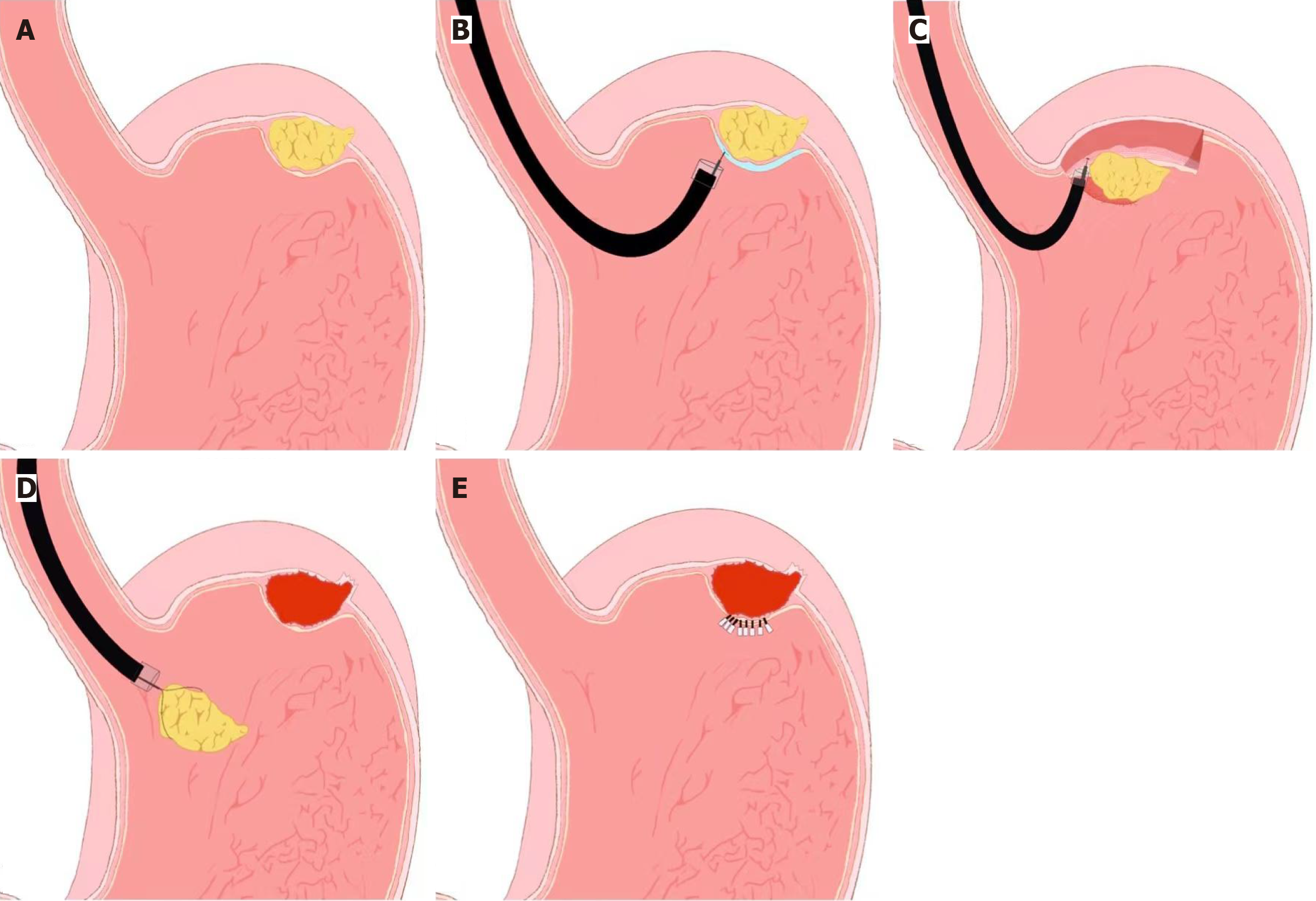
Figure 2 Schematic illustration of endoscopic full-thickness resection for gastrointestinal stromal tumors involving the muscularis propria or deeper layers.
A: Lesion (gastrointestinal stromal tumor) in the gastric fundus; B: Saline injection; C: Resection the lesion using hook/IT knives; D: Remove the resected specimen; E: Wound closure using endoclips. The procedure includes lesion marking, submucosal lifting, full-thickness resection, and defect closure using clips or sutures.
- Citation: Wu J, Jin ZD. Advancements in endoscopic resection of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: Techniques, outcomes, and perspectives. World J Gastrointest Surg 2025; 17(10): 111558
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v17/i10/111558.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v17.i10.111558