©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Diabetes. Feb 15, 2015; 6(1): 175-183
Published online Feb 15, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i1.175
Published online Feb 15, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i1.175
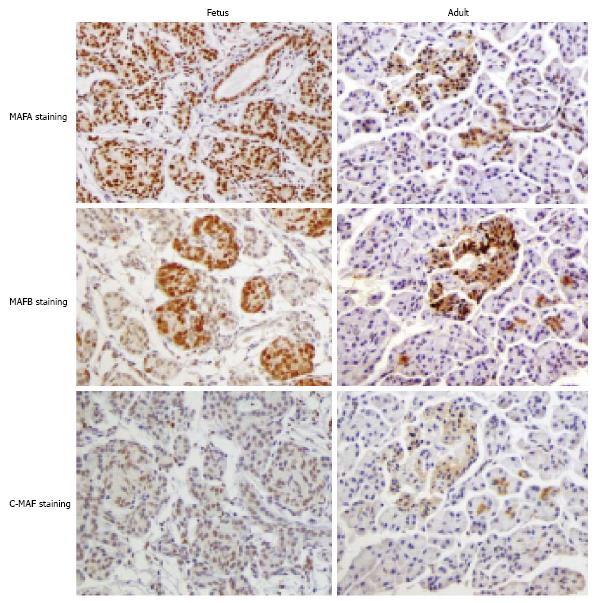
Figure 1 Immunostaining for MAFA, MAFB, and c-MAF in fetal and adult human pancreas tissues.
An immunohistochemical analysis was performed using primary antibodies against MAFA (BL1069; Bethyl Laboratories, Inc.), MAFB (P20; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.), and c-MAF (M153; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.). The details are described in reference[28]. Samples of human normal fetal tissue (female, 20 wk, catalog No. T2244188, Lot No. A607380) and adult pancreas tissue (male, 23 years, catalog No. T2234188, Lot No. A604382) were purchased from BioChain. The fetal pancreas tissues were diffusely stained for the Maf transcription factors, and characteristic histological differences were observed between the fetal and adult tissues, with a more intense staining pattern observed in the islet areas of the adult pancreas tissue.
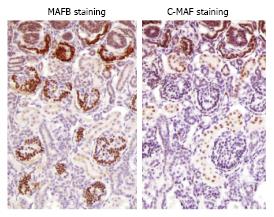
Figure 2 Immunostaining for MAFB and c-MAF in fetal human kidney tissue.
An immunohistochemical analysis was performed using primary antibodies against MAFA (BL1069; Bethyl Laboratories, Inc.), MAFB (P20; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.), and MAF c-Maf (M153; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.). The details are described in reference[40]. A sample of human normal fetal kidney tissue (male, 25 wk) was purchased from BioChain (catalog No. T8244431, Lot No. A606275). Glomerular podocyte lesions stained positive for MAFB, and while the proximal tubules stained positive for c-MAF.
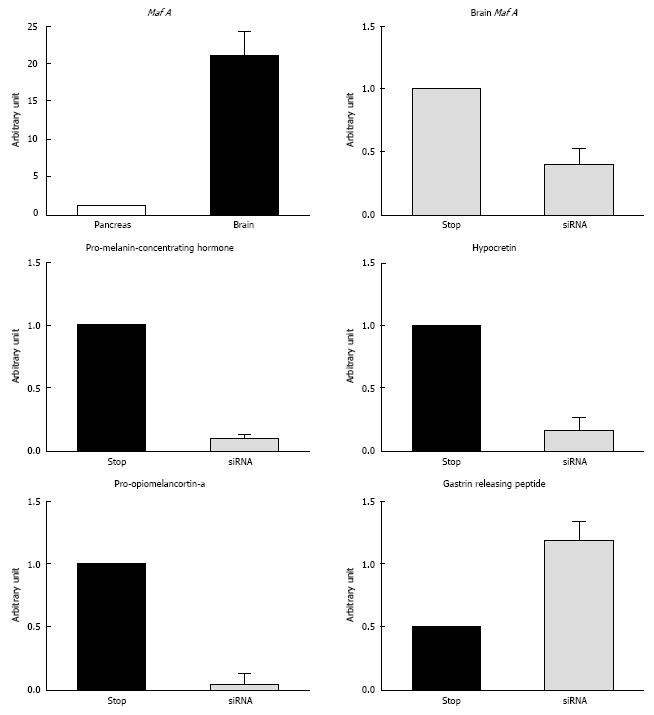
Figure 3 Suppression of MafA mRNA by siRNA in the brain and resulting alternation of related genes.
A designed small interfering RNA (siRNA) oligomer for mouse Mafa was intravenously injected using the hydrodynamic method according to a procedure described by Hamar et al[58]. A DNA microarray analysis was then performed using Affymetrix GeneChip technology. The mRNA levels were quantified using real-time PCR. The details of the experiment have been described previously. Expression level of Mafa mRNA in the brain. The expression level of Mafa mRNA in the brain was 20 times higher than that of Mafa mRNA in the pancreas, as assessed using real-time PCR. Suppression of Mafa in mice using siRNA in the brain. The mRNA expression level take out in the brain tissue are shown. The Mafa mRNA expression level was significantly downregulated by the siRNA. Pro-melanin-concentrating hormone, Hypocretin, and Pro-opiomelanocortin-a were downregulated, and Gastrin-releasing peptide was upregulated, as assessed using real-time PCR with specific primers.
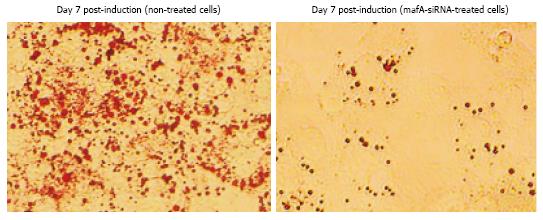
Figure 4 Comparison between histological changes and the Oil-Red-O staining of stop-mafA-siRNA- and mafA-siRNA-treated cells.
Mouse 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes were induced to differentiate, and Mafa SiRNA was transfected using a transfection reagent. The morphological appearances of the pre-adipocyte culture before induction and 7 d after induction were then compared. The morphology of the 3T3-L1 cells was directly observed, and lipid droplets were stained using Oil Red O. Oil Red O staining was compared between untreated and Mafa-siRNA-treated cells. Intracellular lipid staining was not observed in the Mafa-siRNA-treated cells.
- Citation: Tsuchiya M, Misaka R, Nitta K, Tsuchiya K. Transcriptional factors, Mafs and their biological roles. World J Diabetes 2015; 6(1): 175-183
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v6/i1/175.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v6.i1.175