©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Sep 15, 2025; 16(9): 109053
Published online Sep 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i9.109053
Published online Sep 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i9.109053
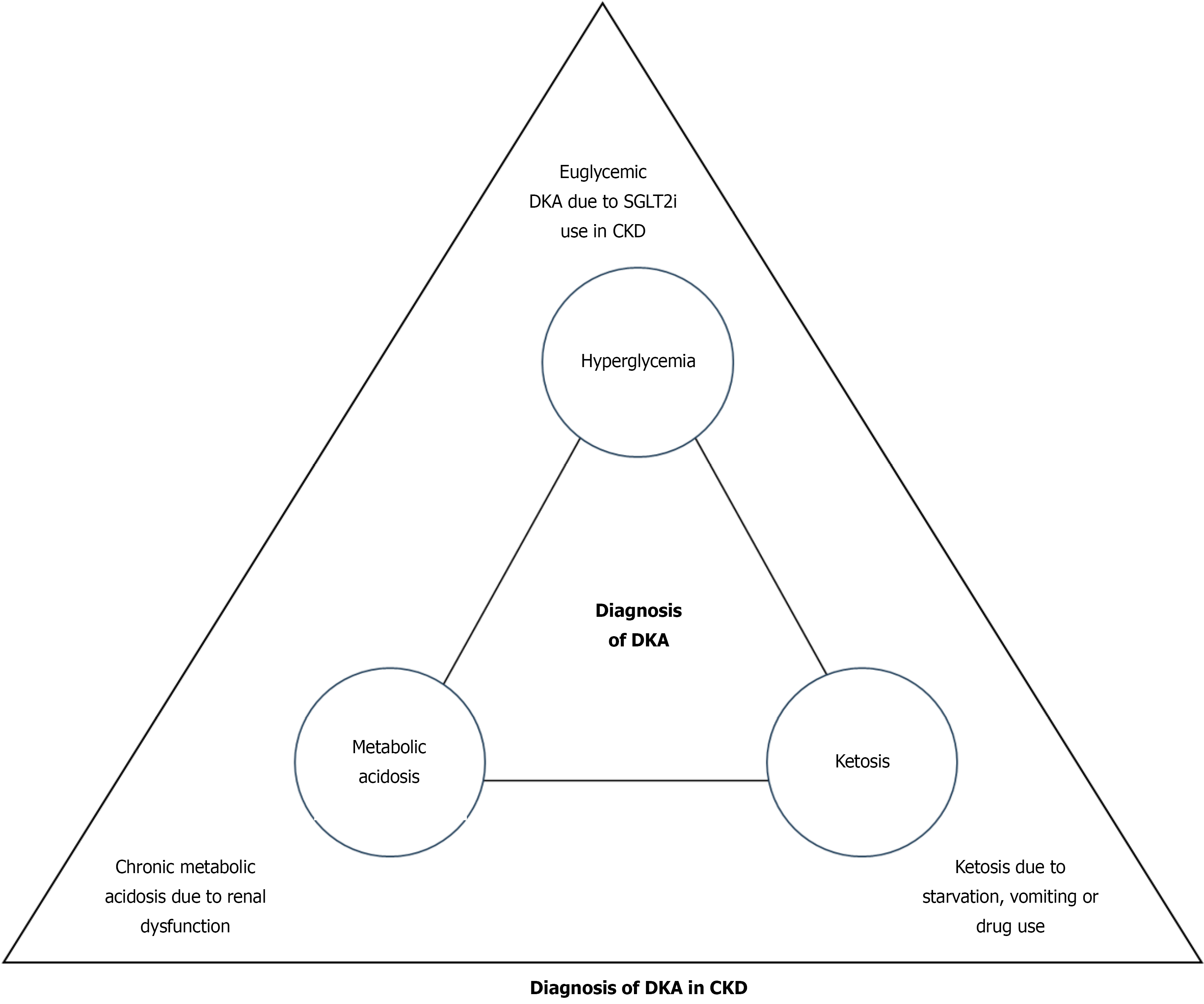
Figure 1 Dilemmas in diagnosis of diabetic ketoacidosis in chronic kidney disease.
CKD: Chronic kidney disease; DKA: Diabetic ketoacidosis; SGLT2i: Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors. Small triangle: Diagnosis in normal scenario; large triangle: Diagnosis in chronic kidney disease.
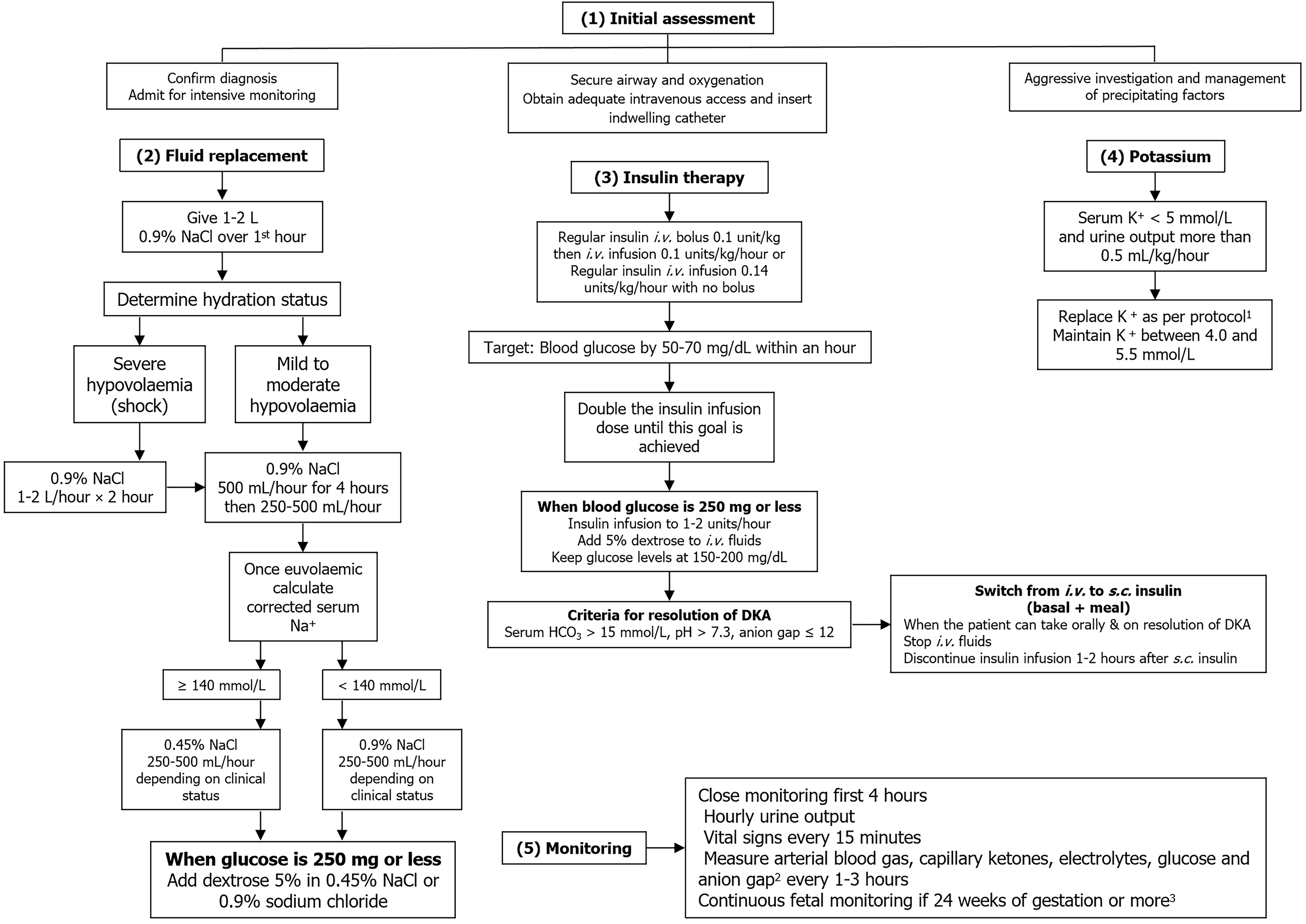
Figure 2 An algorithm for the management of diabetic ketoacidosis in pregnancy.
1Serum potassium level > 5.5 mmol/L: No replacement, 3.5-5 mmol/L: Potassium replacement 40 mmol/L, < 3.5 mmol/L: Potassium regimen needs review. 2Anion gap: [Na+] - [Cl- + HCO3-], corrected sodium = measured Na + 2[(plasma glucose in mg/dL - 100)/100]. 3No interventions on fetal behalf should be performed until stabilization of acute maternal condition has been achieved. s.c.: Subcutaneous; i.v.: Intravenous; DKA: Diabetic ketoacidosis.
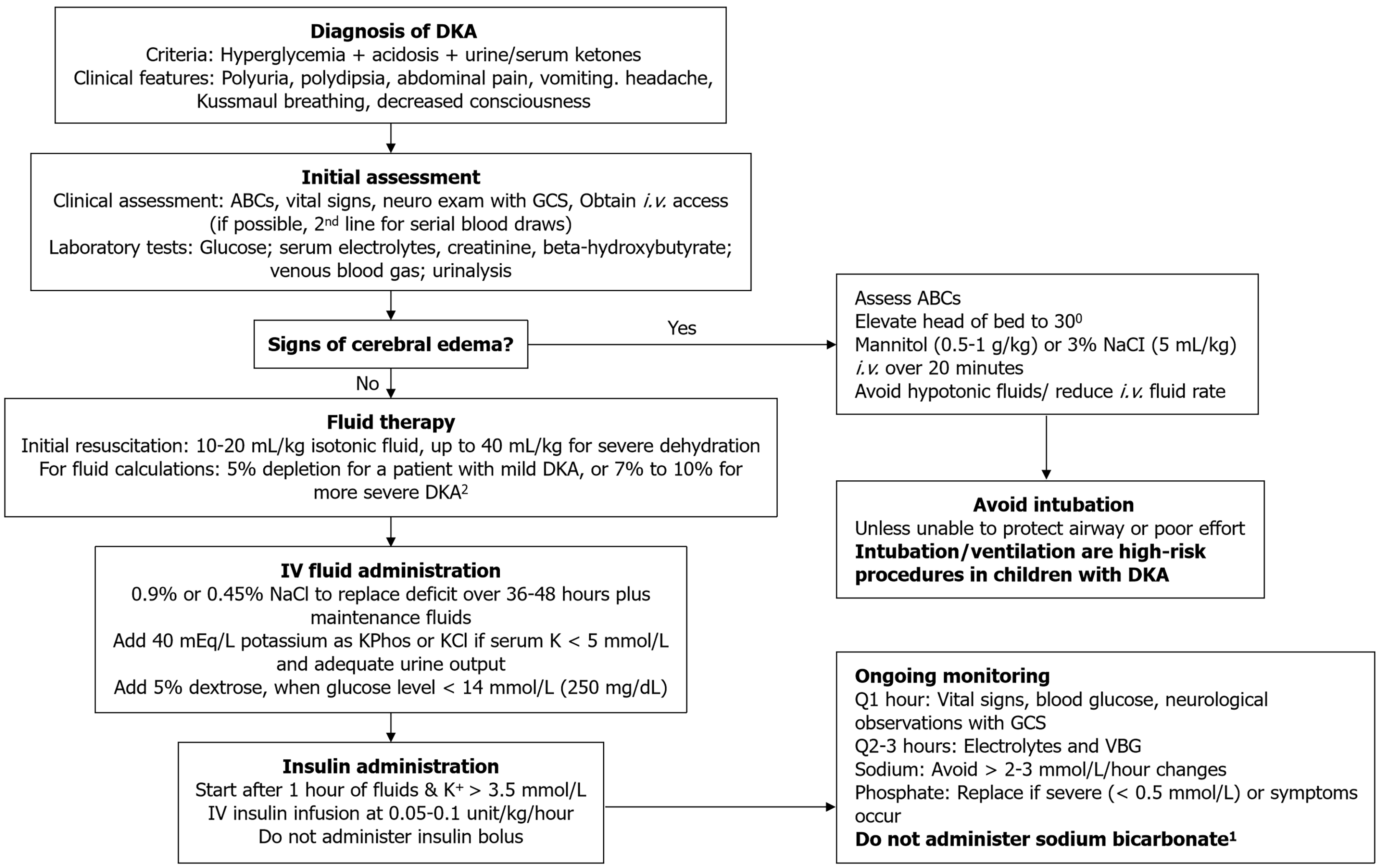
Figure 3 Diabetic ketoacidosis clinical algorithm for children.
1Consider for rare use such as life-threatening hyperkalemia or severe acidosis (pH < 6.9) with impaired cardiac contractility (The International Society for Paediatric and Adolescent Diabetes recommendation). 2The goal is repletion of the patient’s fluid deficit over the first 36 to 48 hours. ABC: Airway, breathing, circulation; DKA: Diabetic ketoacidosis; GCS: Glasgow Coma Scale; K: Potassium; Kacetate: Potassium acetate; KCl: Potassium chloride; NaCl: Sodium chloride; NS: Normal saline solution; VBG: Venous blood gas.
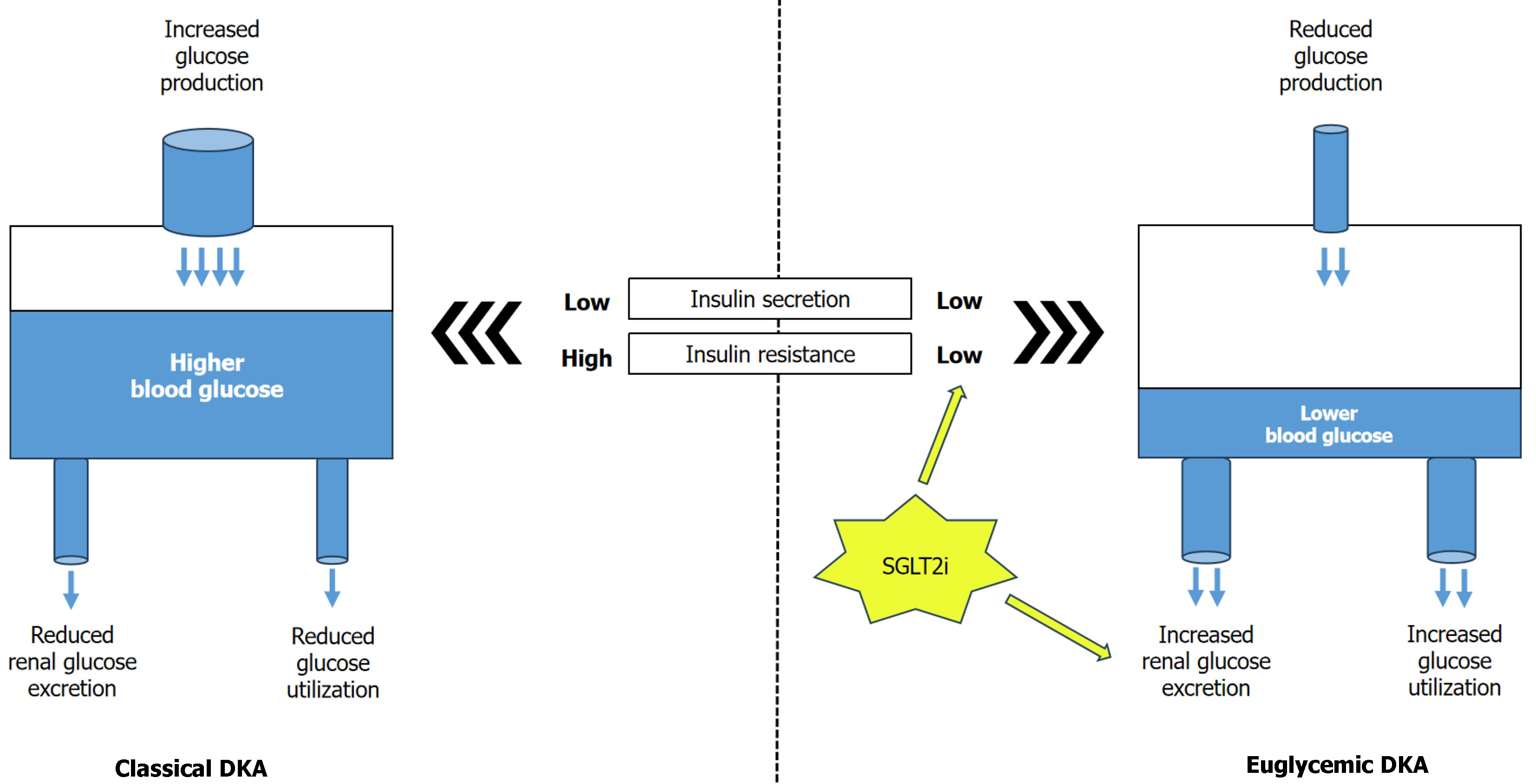
Figure 4 Schematic diagram showing pathophysiology of traditional diabetic ketoacidosis and euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis.
DKA: Diabetic ketoacidosis; SGLT2i: Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors.
- Citation: Ray S, Palui R. Managing diabetic ketoacidosis in special conditions: Difficulties and dilemmas. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(9): 109053
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i9/109053.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i9.109053