©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Jun 15, 2025; 16(6): 99602
Published online Jun 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.99602
Published online Jun 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.99602
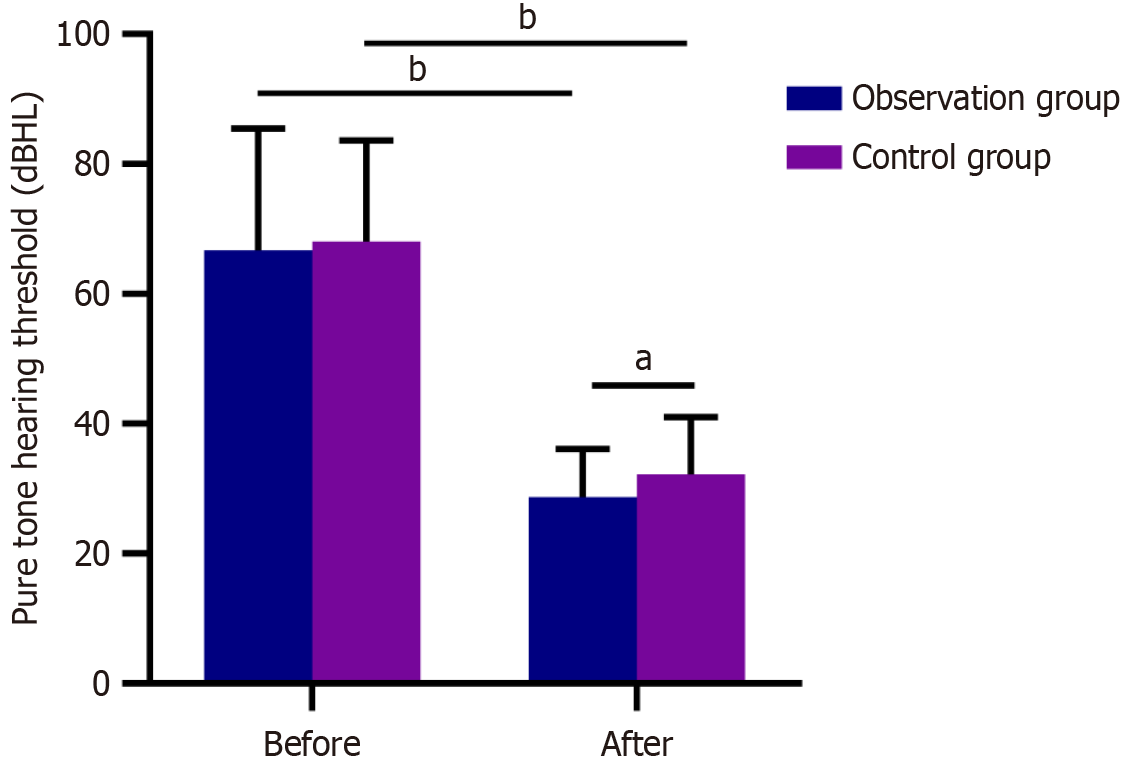
Figure 1 Comparison of hearing recovery.
Before treatment, the pure-tone audiometry thresholds of the observation and control groups were comparable (P = 0.823); following treatment, the pure-tone audiometry threshold of the observation group was markedly lower than that of the control group (P = 0.019). aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01 in the inter-group comparison.
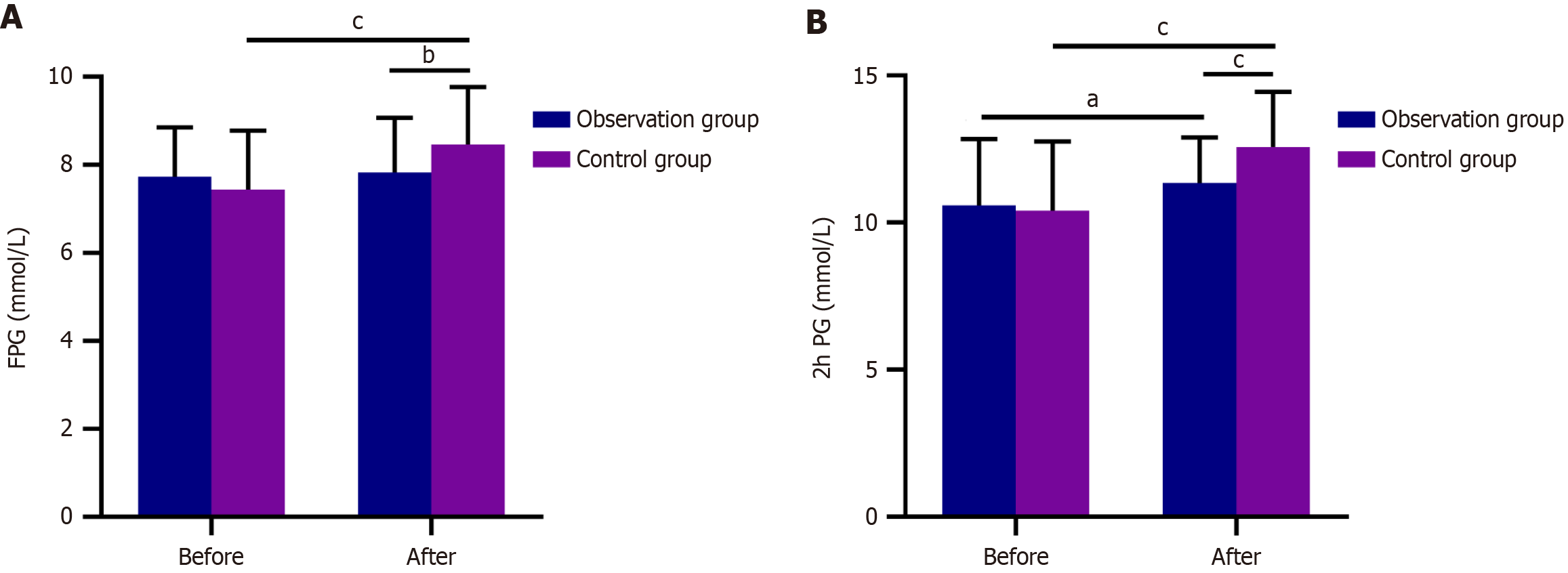
Figure 2 Comparison of blood glucose levels.
A: There was no significant difference in fasting plasma glucose (FPG) between the two groups before treatment (P = 0.181), but the FPG in the observation group was significantly lower than that in the control group after treatment (P = 0.006); B: Before treatment, there was no significant difference in 2-hour postprandial blood glucose (2hPBG) between the two groups (P = 0.669); the observation group showed statistically lower 2hPBG than the control group after treatment (P < 0.001). aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001 in the inter-group comparison; 2hPBG: 2-hour postprandial blood glucose; FPG: Fasting plasma glucose.
- Citation: Long J, Zuo HW. Retroauricular subperiosteal vs systemic intravenous glucocorticoid administration on efficacy and blood glucose in diabetic patients with sudden deafness. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(6): 99602
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i6/99602.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.99602