©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Dec 15, 2025; 16(12): 112423
Published online Dec 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i12.112423
Published online Dec 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i12.112423
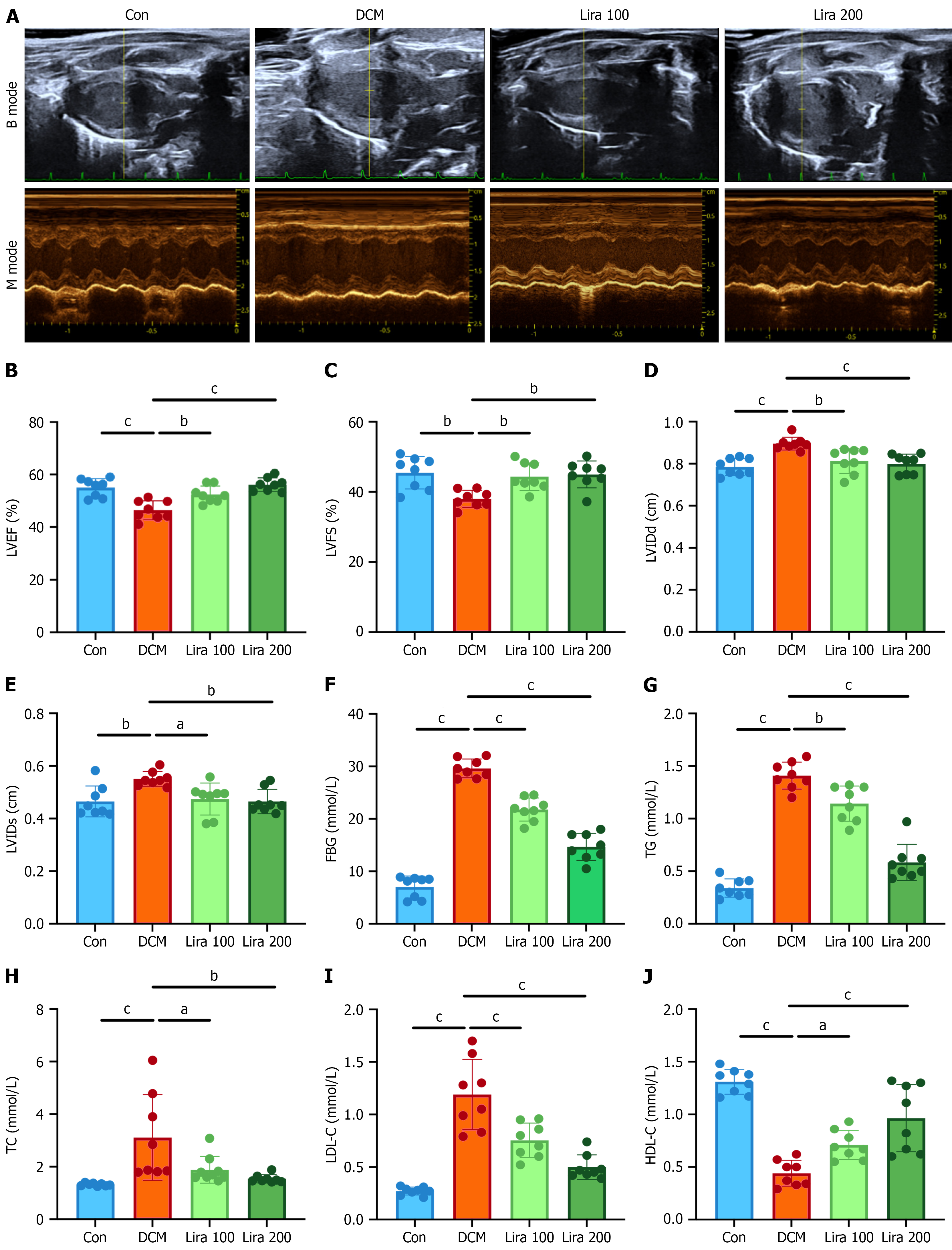
Figure 1 Liraglutide improves cardiac function and biochemical profiles in streptozotocin-induced diabetic cardiomyopathy rats.
A: Representative echocardiographic images for four groups of rats at the end of the experiment. B mode represents a two-dimensional echocardiogram showing left ventricular (LV) long-axis view. M mode represents M-mode echocardiogram showing LV dimensions; B-E: Quantification of LV ejection fraction, LV fractional shortening, LV internal diastolic dimension, LV internal diameter in systole in four groups of rats, n = 8 per group; F: Serum level of fasting blood glucose in the four groups of rats, n = 8 per group; G-J: Serum levels of triglyceride, total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in the four groups of rats, n = 8 per group. Values are presented as the mean ± SD, n = 8. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; CP < 0.001. Con: Control group; DCM: Diabetic cardiomyopathy; LVEF: Left ventricular ejection fraction; LVFS: Left ventricular fractional shortening; LVIDd: Left ventricular internal end-diastolic diameter; LVIDs: Left ventricular internal dimension systole; FBG: Fasting blood glucose; TG: Triglyceride; TC: Total cholesterol; LDL-C: Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HDL-C: High-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
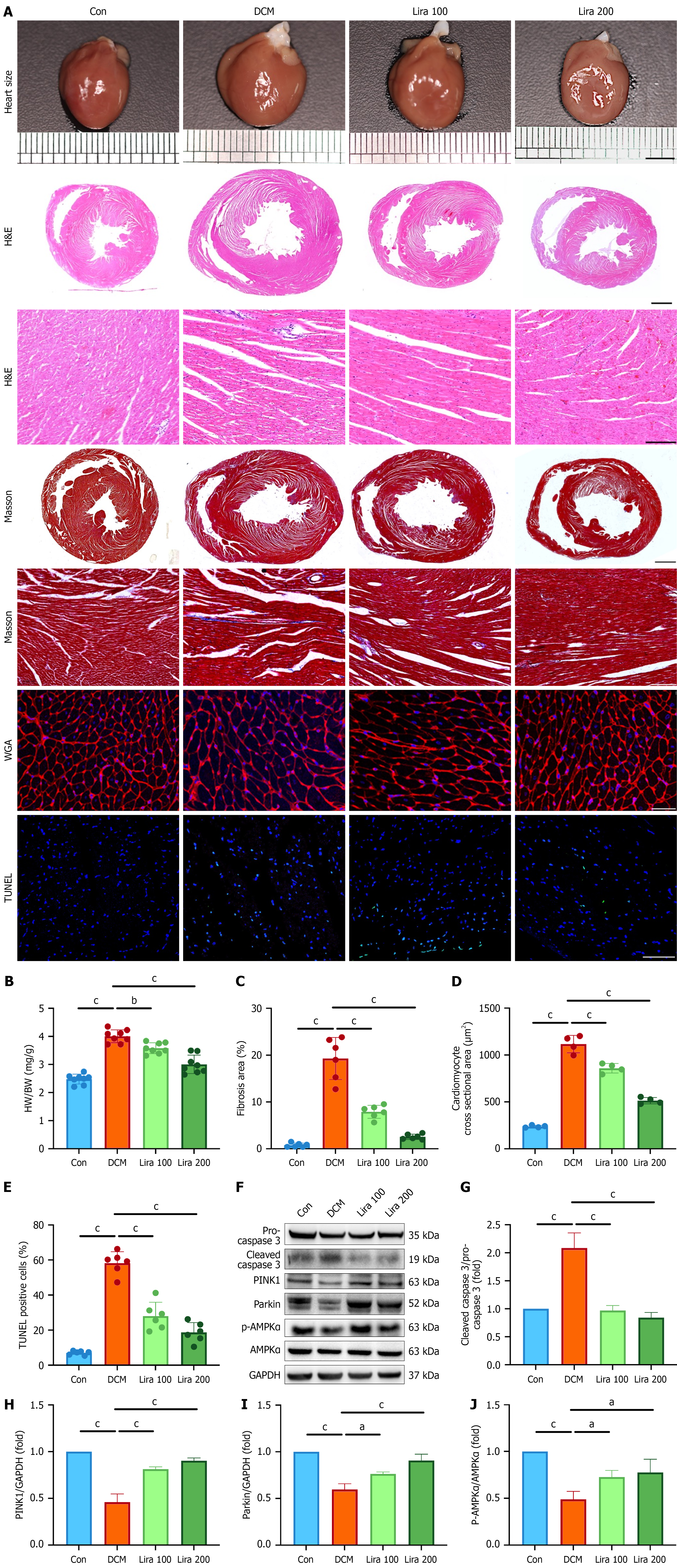
Figure 2 Liraglutide alleviates myocardial injury in diabetic cardiomyopathy rats.
A: Representative images of the hearts from four groups of rats (the first row, scale bar = 5mm), haematoxylin and eosin staining (n = 6 per group, scale bar = 2000 μm as indicated in upper panel, scale bar = 200 μm as indicated in low panel), Masson’s trichrome staining (n = 6 per group, scale bar = 2000 μm as indicated in upper panel, scale bar = 200 μm as indicated in low panel). Wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) staining (n = 6 per group, scale bar = 50 μm), and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining (n = 4 per group, scale bar = 75 μm); B: The ratio of heart weight to body weight in four groups of rats (n = 8 per group); C: Quantification of Masson’s trichrome staining (n = 6 per group); D: Quantification of WGA staining (n = 6 per group); E: Quantification of TUNEL staining (n = 6 per group); F: Representative Western blotting images of pro-caspase 3, cleaved caspase 3, PTEN-induced putative kinase 1 (PINK1), Parkin, p-AMPKα and AMPKα in the hearts of the four groups of rats; G-J: Quantification of the protein expression including pro-caspase 3, cleaved caspase 3, PINK1, Parkin, p-AMPKα and AMPKα in F. Values are presented as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; CP < 0.001. Con: Control group; DCM: Diabetic cardiomyopathy; H&E: Haematoxylin and eosin; WGA: Wheat germ agglutinin; HW: Heart weight; BW: Body weight.
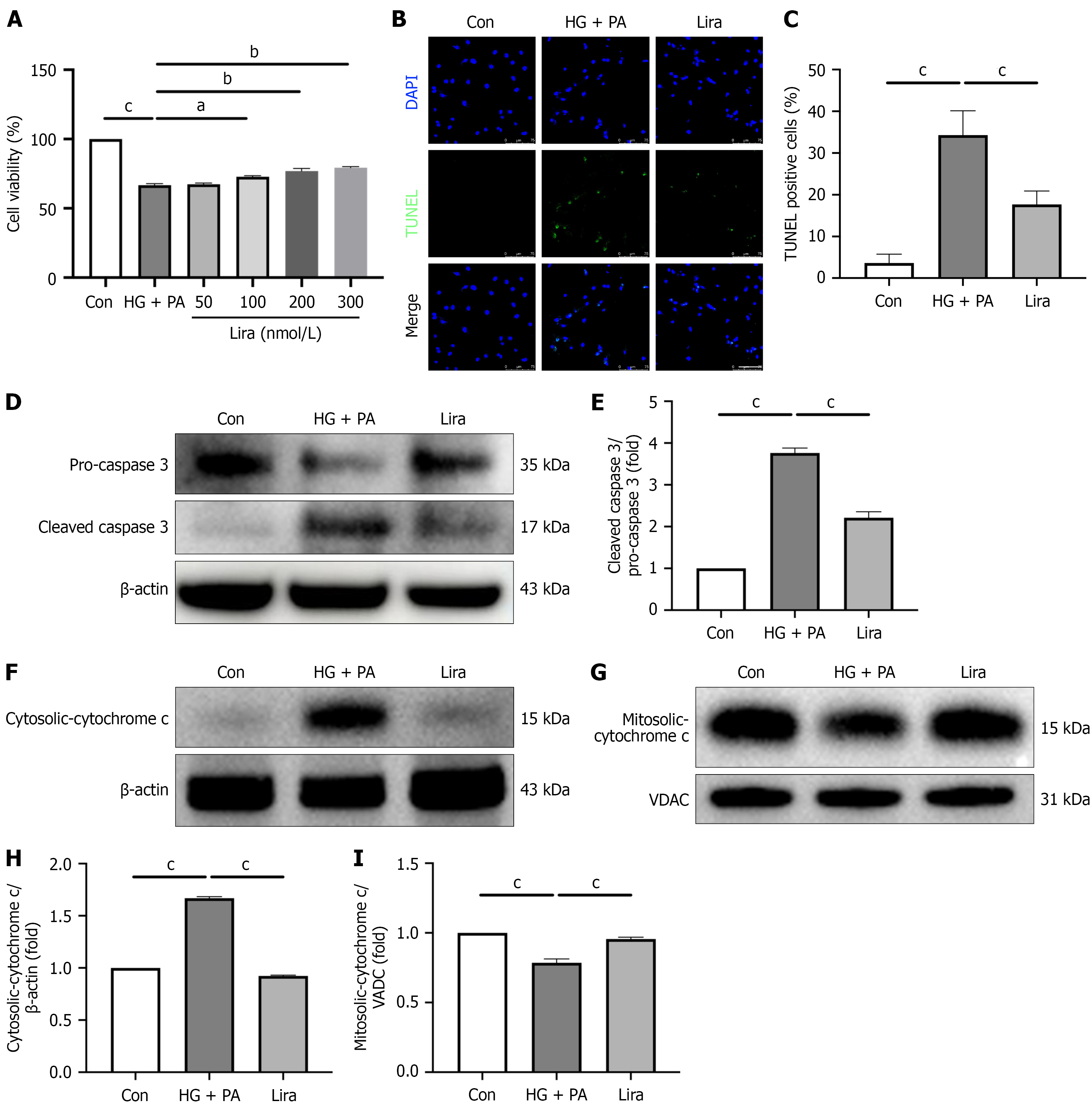
Figure 3 Liraglutide ameliorate cardiomyocyte apoptosis induced by high glucose + palmitic acid.
A: Representative CCK8 images for optimum treatment dose of liraglutide (Lira: 200 nmol/L); B and C: Representative and quantitative analysis images of cell terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase mediated dUTP nick end labeling staining for the three groups (scale bar: 50 μm); D, F and G: Representative Western blotting images of pro-caspase 3 and cleaved caspase 3, cytosolic-cytochrome C and mitosolic-cytochrome C in the three groups [control group (Con), high glucose (HG) + palmitic acid (PA; 25 mmol/L D-glucose plus 250 μmol/L palmitate), Lira (HG + PA with 200 nmol/L liraglutide)]; E, H and I: Quantification of the expression of the proteins including cleaved caspase 3, cytosolic-cytochrome C and mitosolic-cytochrome C. Values are presented as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. Con: Control group; HG: High glucose; PA: Palmitic acid.
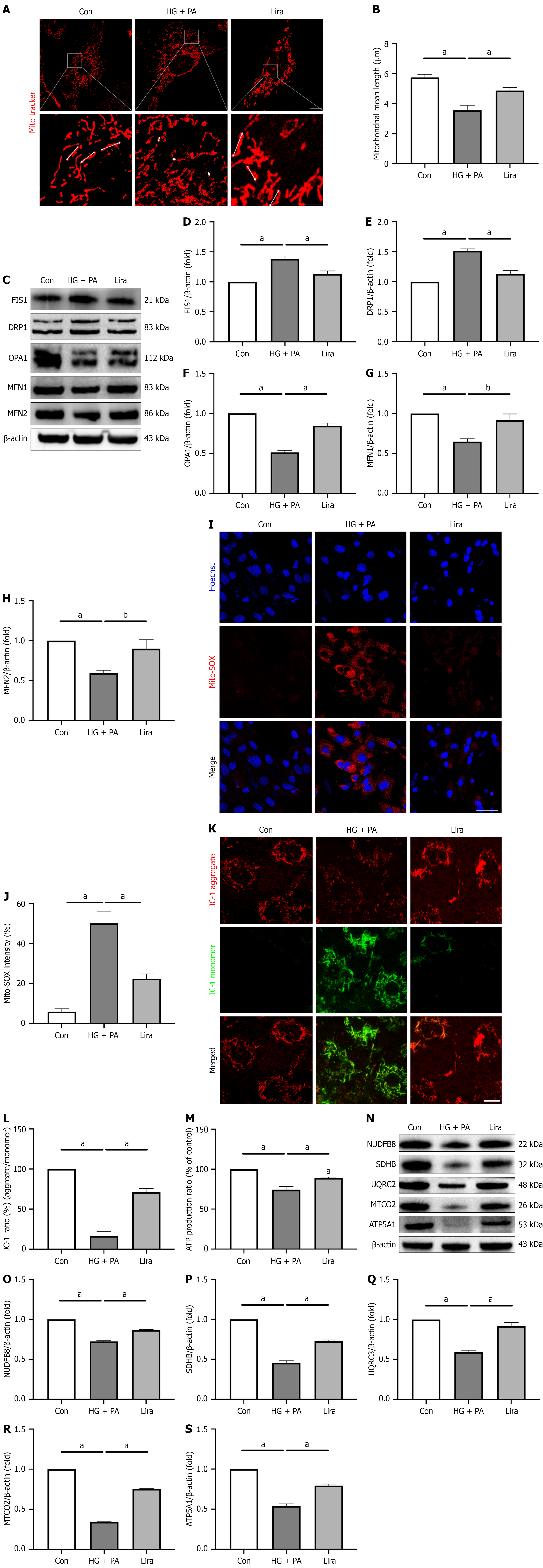
Figure 4 Liraglutide rescues mitochondrial damage in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes induced by high glucose + palmitic acid.
A: Re
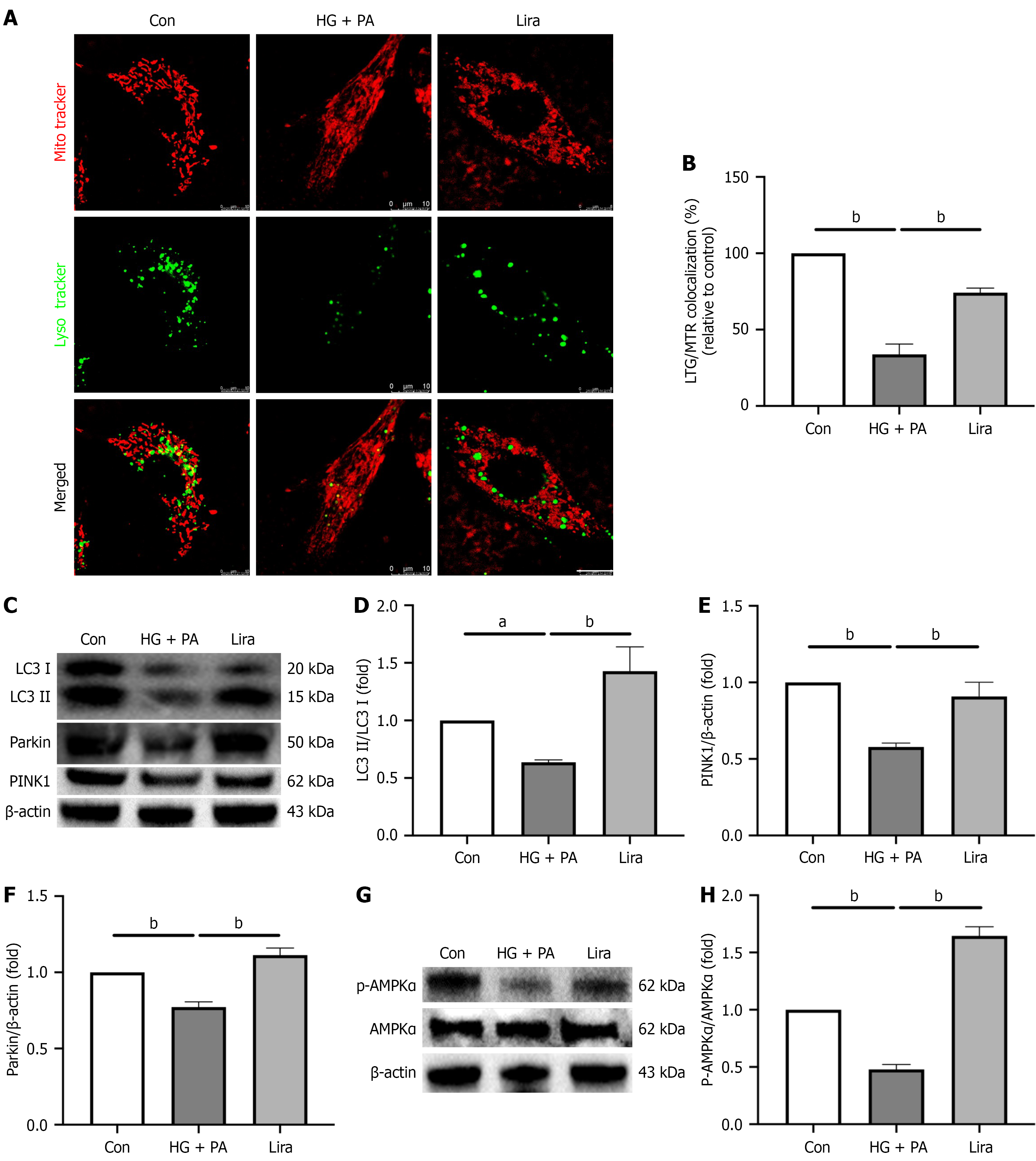
Figure 5 Liraglutide attenuates mitophagy by activating AMPK-Parkin pathway in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes induced by high glucose + palmitic acid.
A: Representative colocalization images of lysosomes (LysoTracker Green) and mitochondria (Mito Tracker Red; scale bar: 10 µm); B: Percentage of cells with lysosome (LysoTracker Green) and mitochondria (Mito Tracker Red) colocalization; C: Representative western blotting images of LC3 I, LC3 II, PTEN-induced putative kinase 1 (PINK1) and Pakin in the four groups; D-F: Quantification of the expression of the proteins including LC3 I and LC3 II, PINK1 and Pakin in C; G: Representative western blotting images of p-AMPKα and AMPKα in the four groups; H: Quantification of the expression levels of p-AMPKα and AMPKα in G. Values are presented as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.001. Con: Control group; HG: High glucose; PA: Palmitic acid.
Figure 6 Liraglutide attenuates mitochondrial damage and cardiomyocytes apoptosis via AMPK-Parkin pathway mediated mitophagy in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes induced by high glucose + palmitic acid.
A: Mito-SOX Red staining representing mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (mitoROS) levels in the four groups (scale bar: 25 μm); B: Quantification of mitoROS production as measured with mito-SOX Red staining in B; C: Representative fluorescence staining images of JC-1 aggregates (red) and JC-1 monomer (scale bar: 25 μm); D: Relative fluorescence intensity of aggregate/monomeric JC-1 in D; E: Representative images Mito Tracker Red of the four groups (scale bar = 25 μm as indicated in upper panel, scale bar = 5 μm as indicated in low panel); F: Quantification of the mitochondrial mean length (white double arrow); G: Transmission electron microscopic images showing mitochondria in cardiomyocytes. Normal mitochondria were denoted by white arrows, while the damaged mitochondria (edema, cristae rupture and vacuolized) were indicated by yellow arrows (scale bar: 1 µm); H and I: Fraction of swollen mitochondria and mitochondrial loss of cristae in the four groups; J and K: Representative and quantitative analysis images of cell terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase mediated dUTP nick end labeling staining for the three groups (scale bar: 50 μm); L-N: Representative western blotting images of pro-caspase 3, cleaved caspase 3, cytosolic-cytochrome C and mytosolic-cytochrome C in the the four groups; O-Q: Quantification of the expression of the proteins including pro-caspase 3, cleaved caspase3, cytosolic-cytochrome C and mytosolic-cytochrome C in L, N and P; R: Representative colocalization images of lysosomes (LysoTracker Green) and mitochondria (Mito Tracker Red; scale bar: 10 µm); S: The percentage of cells with lysosome (LysoTracker Green) and mitochondria (MitoTracker Red) colocalization; T: Representative Western blotting images of LC3 I, LC3 II and Pakin in the four groups; U and V: Quantification of the expression of the proteins including LC3I, LC3II and Pakin in T. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. Con: Control group; HG: High glucose; PA: Palmitic acid.
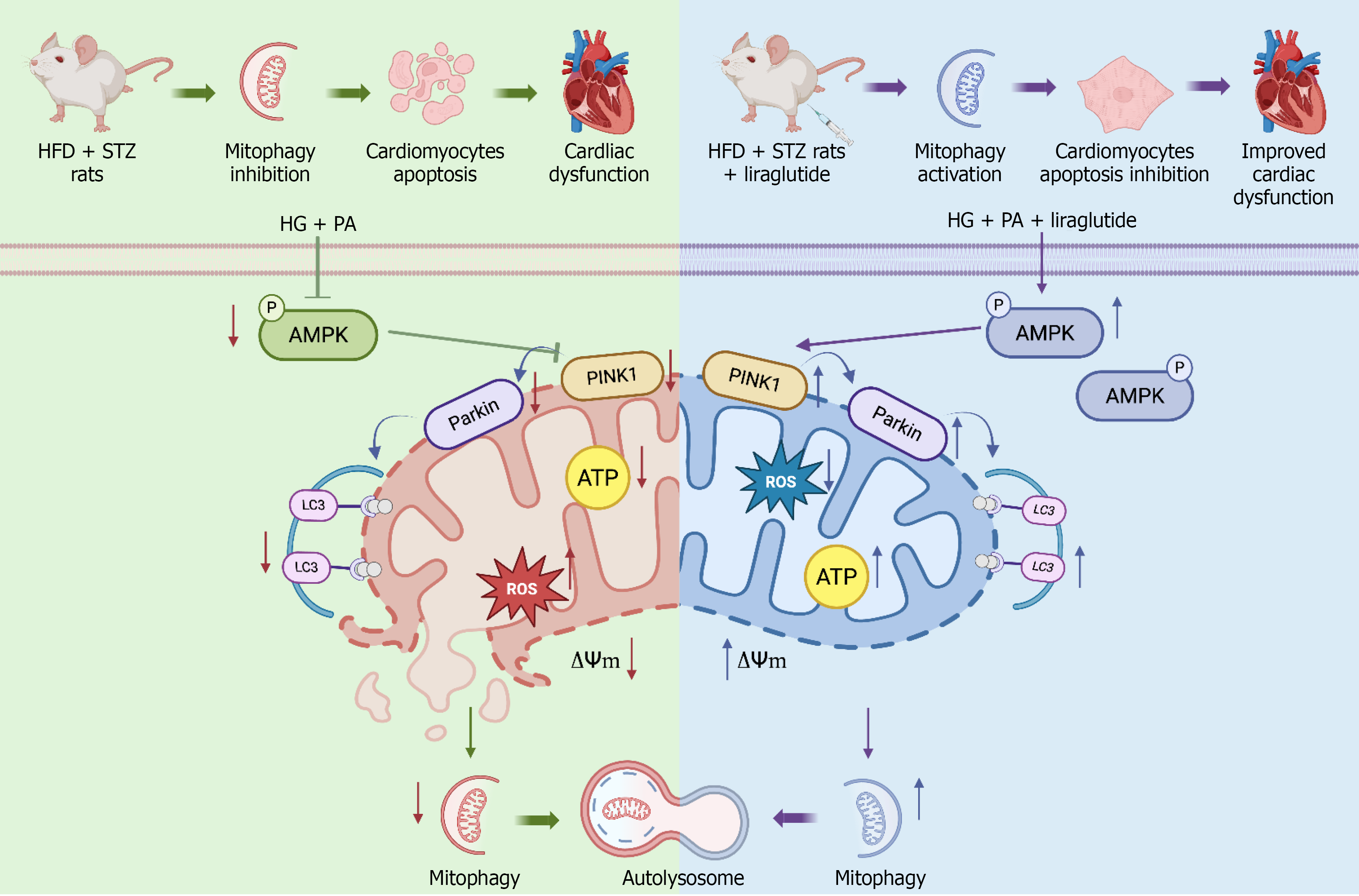
Figure 7 The molecular mechanism of the improvement of liraglutide in diabetic cardiomyopathy.
Graphic summary demonstrating liraglutide could be a novel AMPK-Parkin activator to ameliorate myocardial dysfunction in high-fat diet and streptozotocin induced rat. In diabetes, liraglutide increases phosphorylation of AMPK, upregulates the expression of PTEN-induced putative kinase 1 and Parkin, and then, recruits and phosphorylates more Parkin, activates mitophagy, and improves mitochondrial function (mitochondrial membrane potential recovery, mitochondrial reactive oxygen species level decrease and ATP content increase). HFD: High-fat diet; STZ: Streptozotocin; HG: High glucose; PA: Palmitic acid; ∆Ψm: Mitochondrial membrane potential. Created in BioRender (Supplementary material).
- Citation: Zhu YX, Zhang W, Qu HL, Zhang Y, Zhou RQ, Li P, Wang F, Zhang Y, Liu HH, Li S, Dong Q, Dou KF, Guo YL, Li JJ, Xu RX. Liraglutide alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats by enhancing mitophagy mediated by the AMPK-Parkin signaling pathway. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(12): 112423
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i12/112423.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i12.112423