©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. Jun 15, 2024; 15(6): 1367-1373
Published online Jun 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i6.1367
Published online Jun 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i6.1367
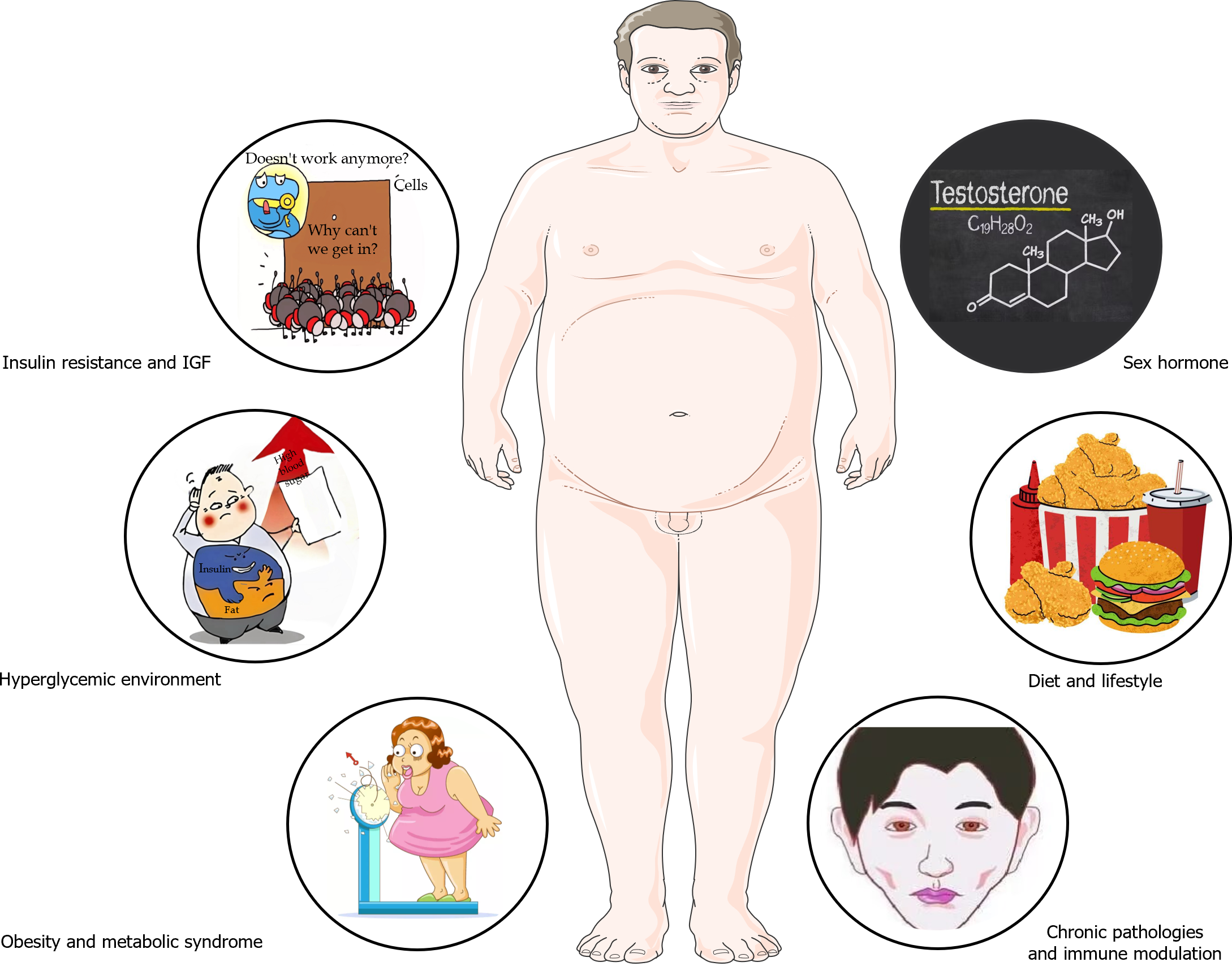
Figure 1 Possible biological mechanisms of diabetes mellitus leading to prostate cancer.
Insulin-like growth factor-1 can encourage cellular proliferation and hinder cell apoptosis, potentially elevating the risk of various cancers, including prostate cancer (PCa). Elevated blood glucose can accelerate cell oxidation and chronic inflammation, both of which are linked to cancer progression. Diabetes mellitus (DM) often coexists with obesity and metabolic syndrome, conditions that are associated with systematic inflammation and hormone imbalance, potentially increasing the risk of PCa. DM can also influence the levels of sex hormones, including testosterone. Altered testosterone levels can influence the risk of PCa. The diet and lifestyle of diabetics may also contribute to an elevated risk of PCa. Additionally, the disease itself and the immune function changes caused by long-term DM may play a role in the development of PCa. IGF: Insulin-like growth factor.
- Citation: Li J, Li ZP, Xu SS, Wang W. Unraveling the biological link between diabetes mellitus and prostate cancer: Insights and implications. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(6): 1367-1373
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i6/1367.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i6.1367