©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. Jun 15, 2024; 15(6): 1280-1290
Published online Jun 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i6.1280
Published online Jun 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i6.1280
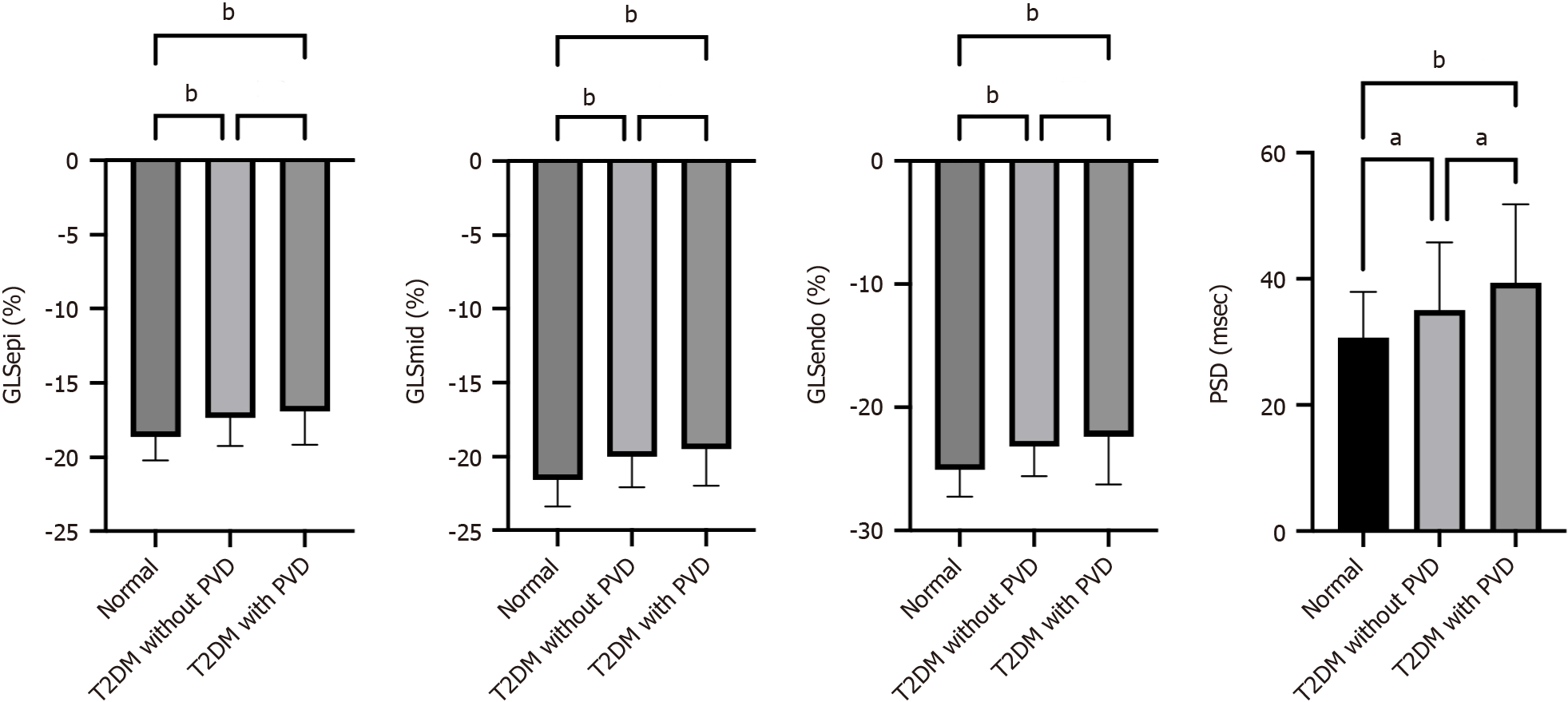
Figure 1 Line graph showing the differences in layer-specific global longitudinal strain and peak strain dispersion between normal controls, type 2 diabetes mellitus patients without peripheral vascular disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with peripheral vascular disease.
aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01. GLSEpi: Global longitudinal strain of the epimyocardium; GLSMid: Global longitudinal strain of the middle myocardium; GLSEndo: Global longitudinal strain of the endocardium; PSD: Peak strain dispersion; LDL-C: Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LVEF: Left ventricular ejection fraction; PVD: Peripheral vascular disease; T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
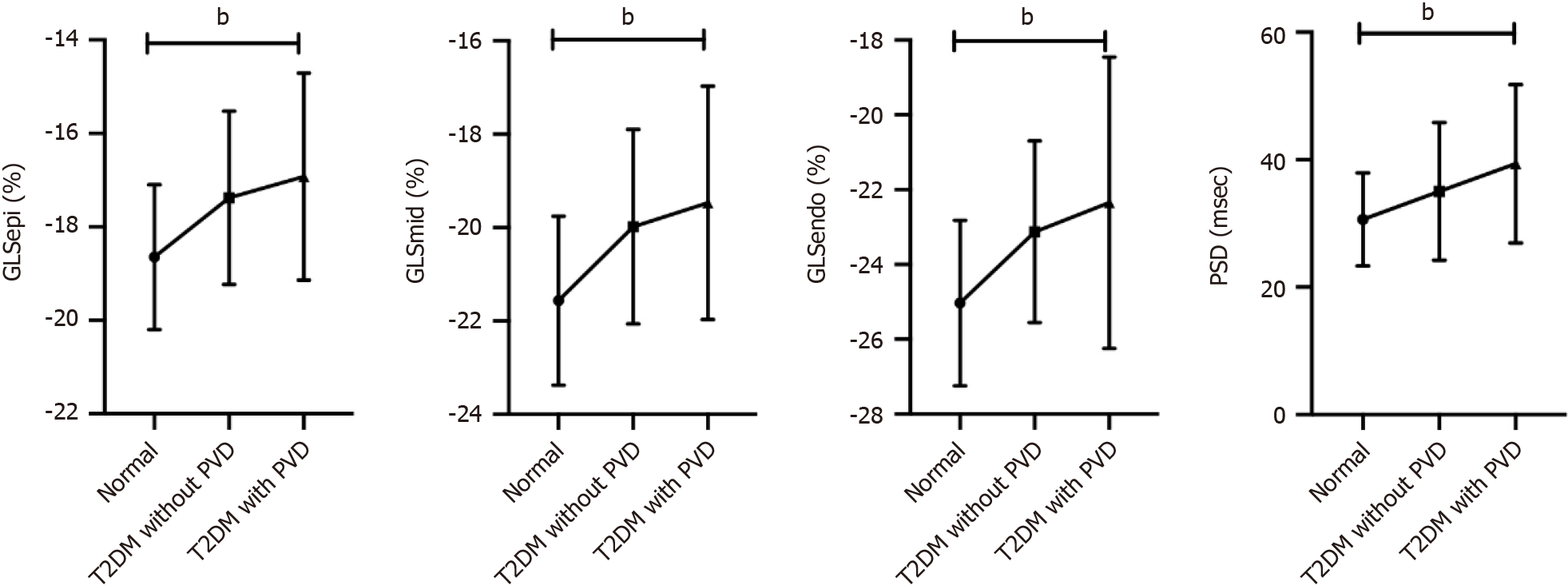
Figure 2 Trend analysis of layer-specific global longitudinal strain and peak strain dispersion between normal controls, type 2 diabetes mellitus patients without peripheral vascular disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with peripheral vascular disease.
bP < 0.01. GLSEpi: Global longitudinal strain of the epimyocardium; GLSMid: Global longitudinal strain of the middle myocardium; GLSEndo: Global longitudinal strain of the endocardium; PSD: Peak strain dispersion; LDL-C: Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LVEF: Left ventricular ejection fraction; PVD: Peripheral vascular disease; T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
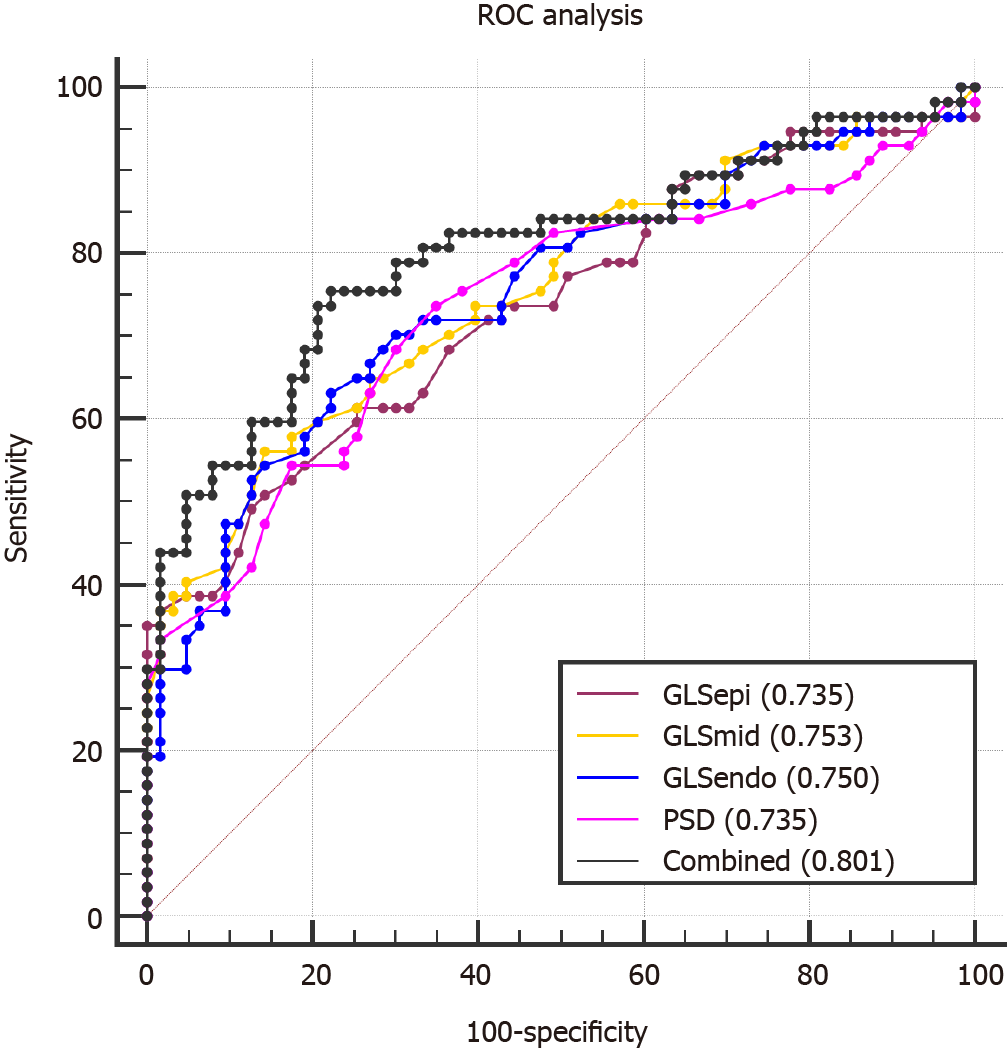
Figure 3 Receiver operating characteristic analysis for detecting the accuracy of left ventricular systolic dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with peripheral vascular disease.
GLSEpi: Global longitudinal strain of the epimyocardium; GLSMid: Global longitudinal strain of the middle myocardium; GLSEndo: Global longitudinal strain of the endocardium; PSD: Peak strain dispersion; LDL-C: Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LVEF: Left ventricular ejection fraction; PVD: Peripheral vascular disease; T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
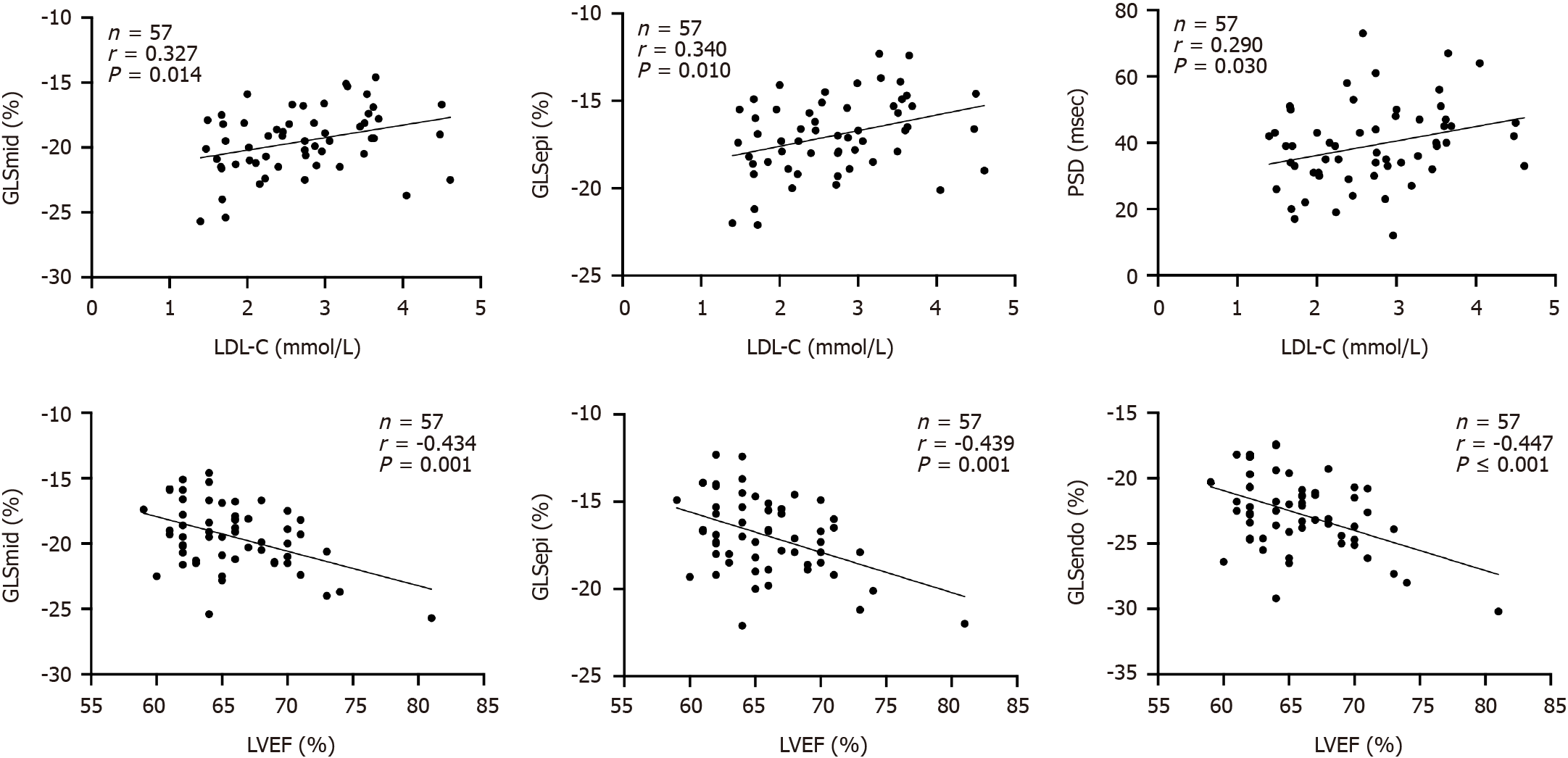
Figure 4 The correlation test showed that low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol was positively correlated with global longitudinal strain of the epimyocardium, global longitudinal strain of the middle myocardium and peak strain dispersion, while left ventricular ejection fraction was negatively correlated with global longitudinal strain of the epimyocardium and global longitudinal strain of the middle myocardium and global longitudinal strain of the endocardium.
GLSEpi: Global longitudinal strain of the epimyocardium; GLSMid: Global longitudinal strain of the middle myocardium; GLSEndo: Global longitudinal strain of the endocardium; PSD: Peak strain dispersion; LDL-C: Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LVEF: Left ventricular ejection fraction.
- Citation: Li GA, Huang J, Fan L. Evaluation of left ventricular systolic function in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with and without peripheral vascular disease. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(6): 1280-1290
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i6/1280.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i6.1280