©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Jun 15, 2023; 14(6): 656-679
Published online Jun 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i6.656
Published online Jun 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i6.656
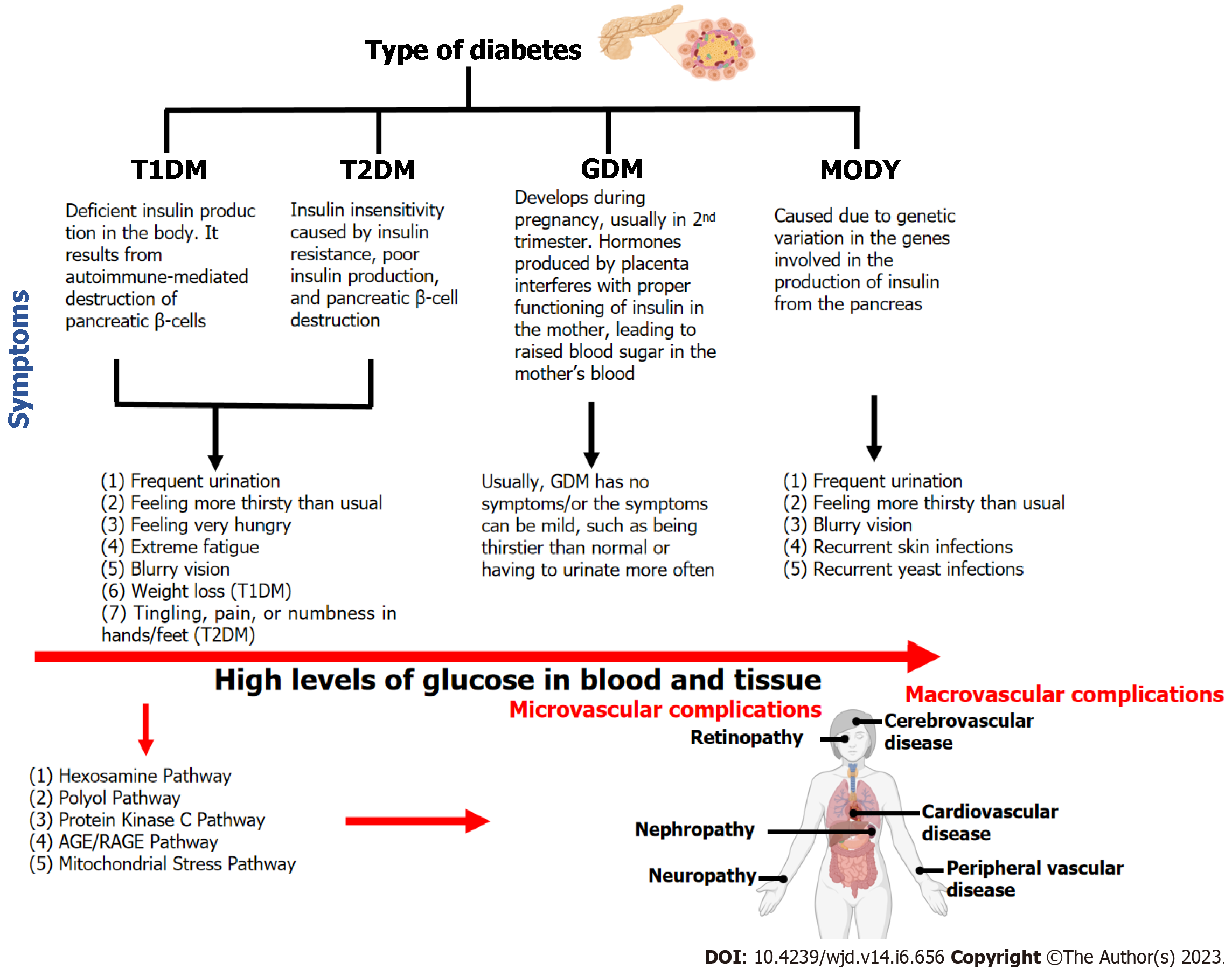
Figure 1 Types of diabetes and their symptoms.
Hyperglycemia and potential metabolic pathways in the pathogenesis of diabetic complications (microvascular and macrovascular) are also indicated. AGE: Advanced glycation end-products; RAGE: Receptor for advanced glycation end-products; T1DM: Type 1 diabetes mellitus; T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus; GDM: Gestational diabetes mellitus; MODY: Maturity-onset diabetes of young.
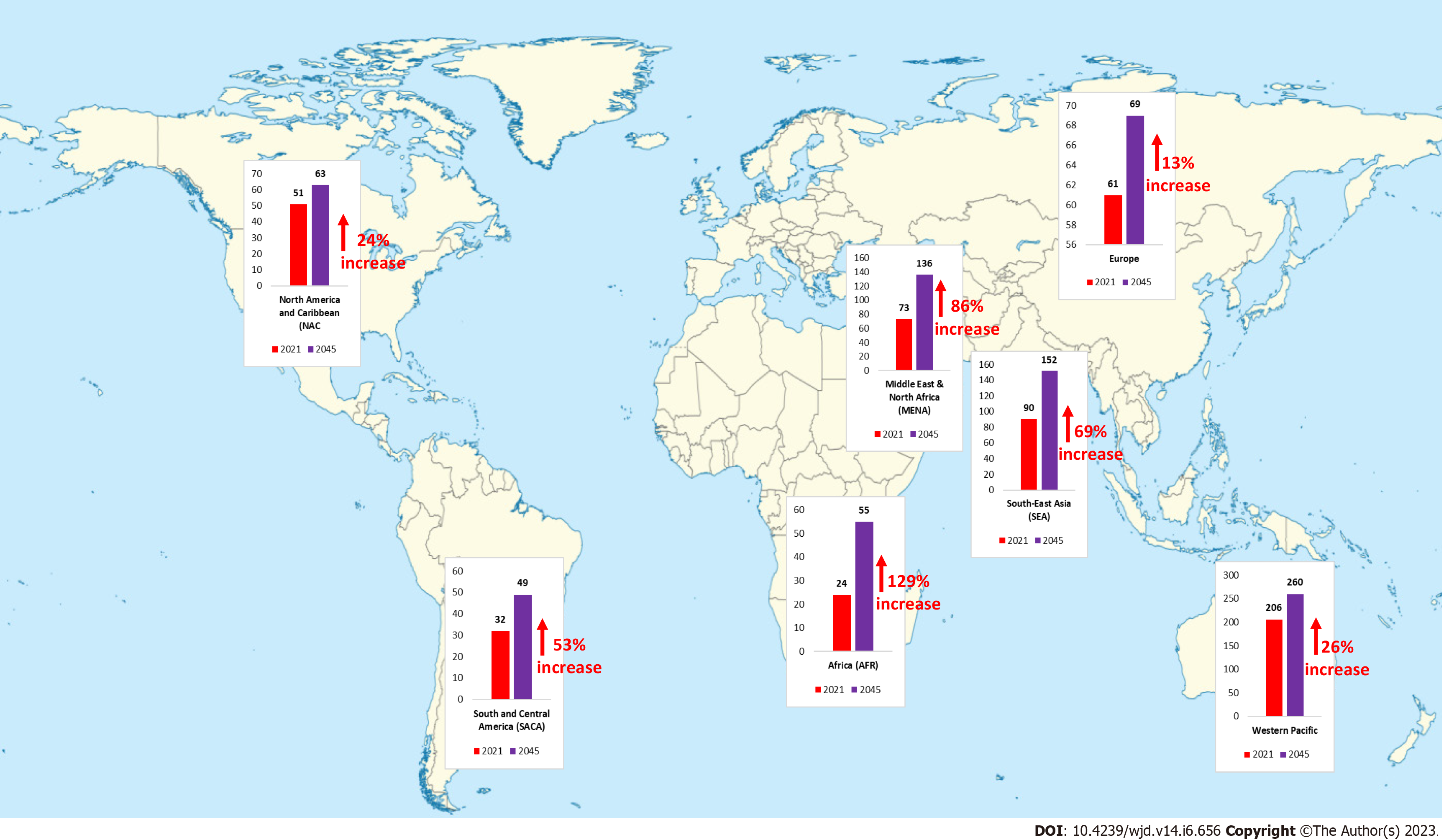
Figure 2 Predicted percentage increase in the global prevalence of diabetes mellitus from 2021 to 2045[24].
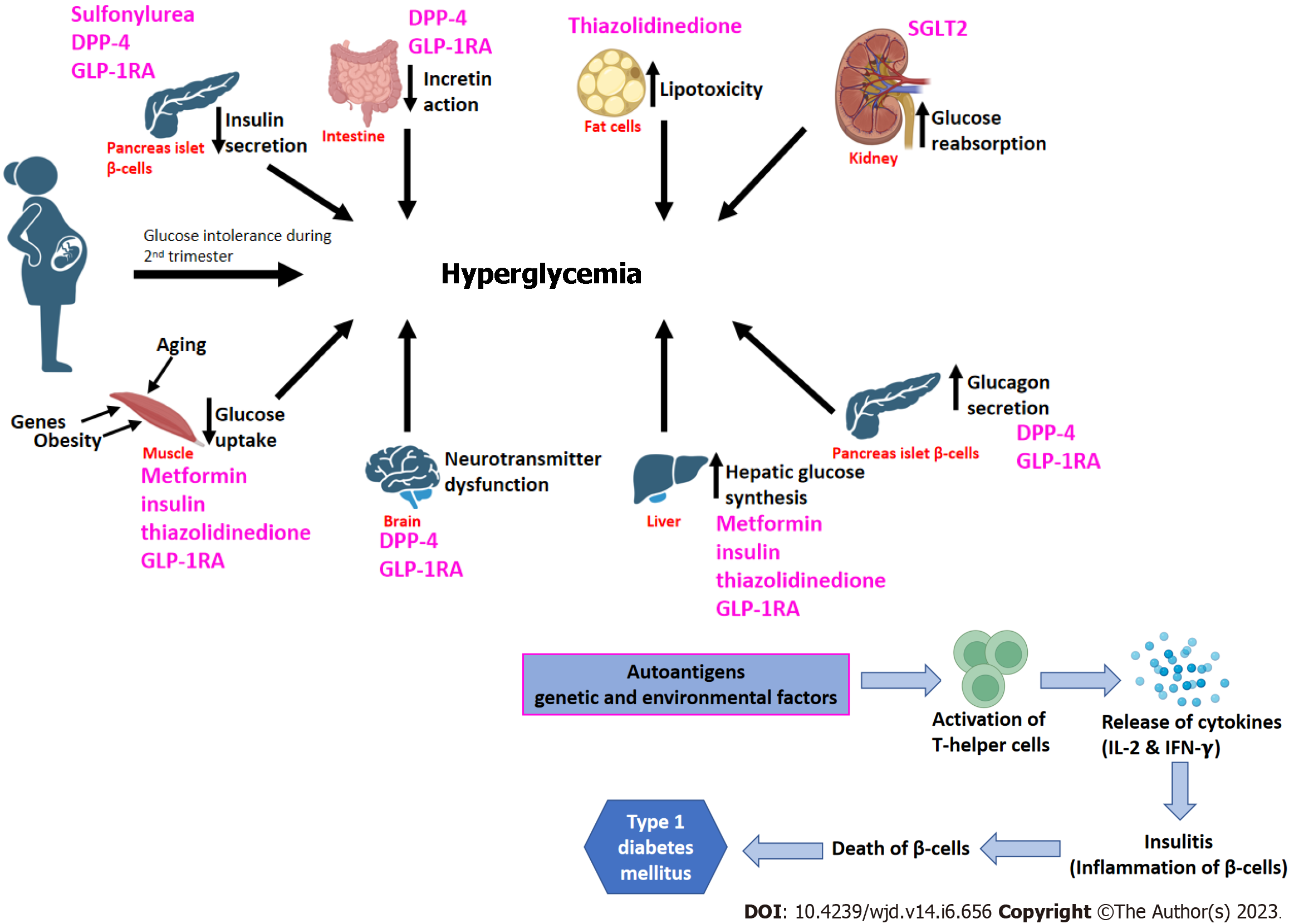
Figure 3 Pathogenesis of gestational diabetes mellitus, type 2 diabetes mellitus-ominous octet, and type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Pharmacological glycemic management targets have also been shown here. DPP-4: Dipeptidyl peptide-4 inhibitor; GLP-1RA: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist; SGLT2: Sodium-Glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor; IL-2: Interleukin-2; IFN-γ: Interferon gamma.
- Citation: Goyal S, Rani J, Bhat MA, Vanita V. Genetics of diabetes. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(6): 656-679
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i6/656.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i6.656