©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Diabetes. Nov 15, 2020; 11(11): 527-539
Published online Nov 15, 2020. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v11.i11.527
Published online Nov 15, 2020. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v11.i11.527
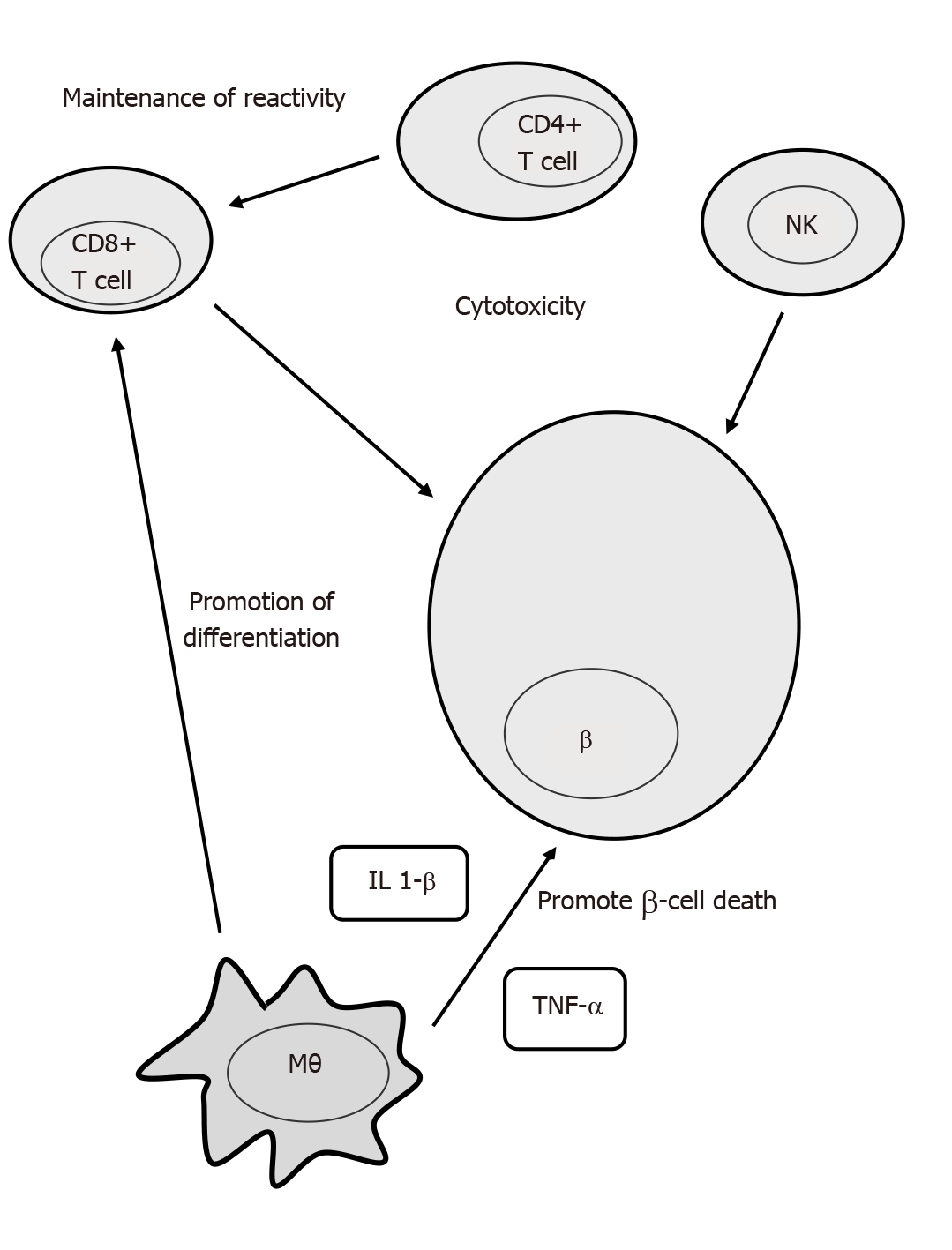
Figure 1 Pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes-cellular crosstalk.
CD: Celiac disease; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; IL 1-β: Interleukin 1-β; NK: Natural killer cell.
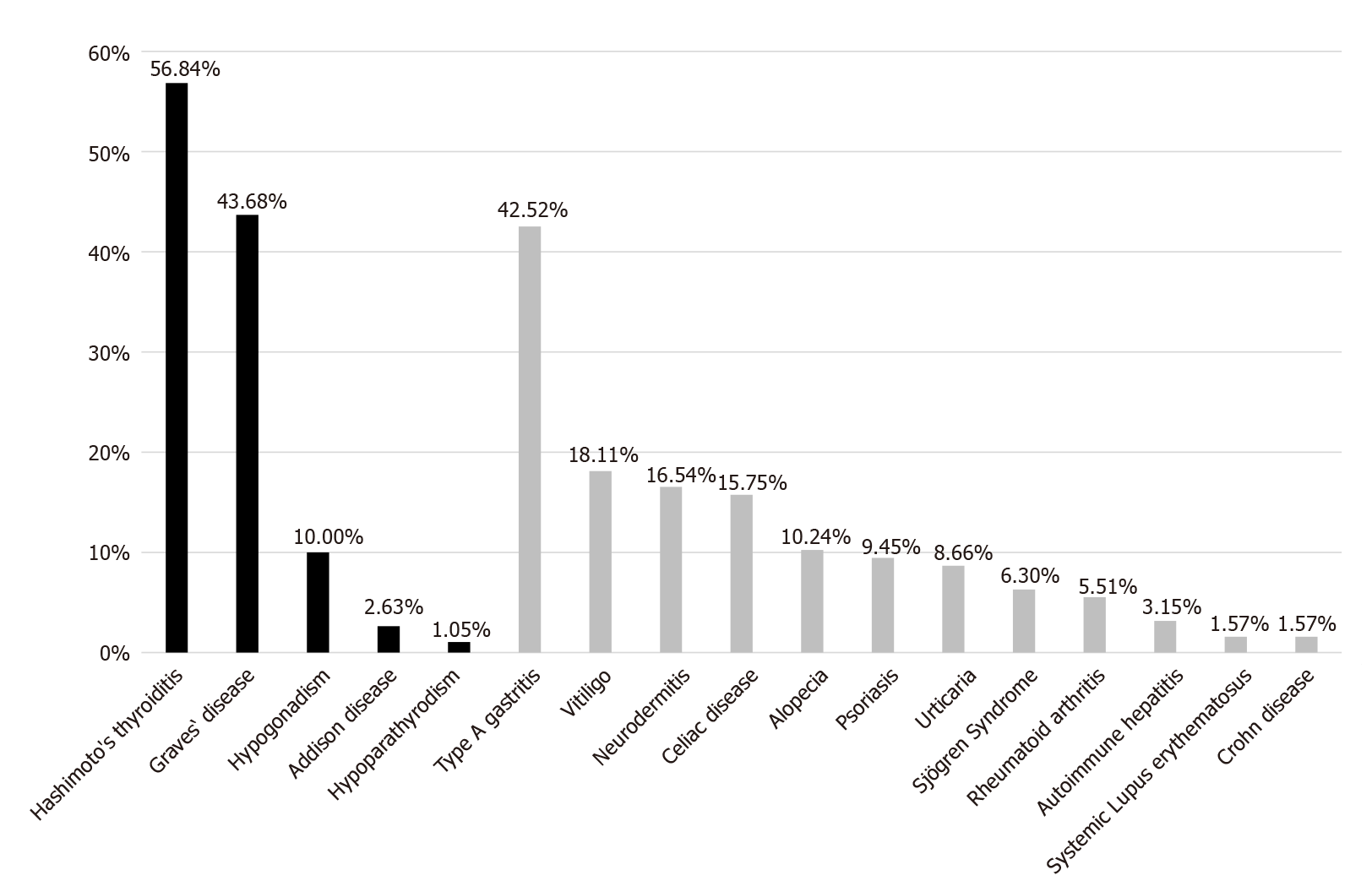
Figure 2 Associated autoimmune disorders in type 1 diabetes.
The prevalence of associated glandular (black) and non-glandular (light grey) autoimmune diseases in patients with type 1 diabetes + autoimmune diseases, followed at the Johannes Gutenberg University Medical Center.
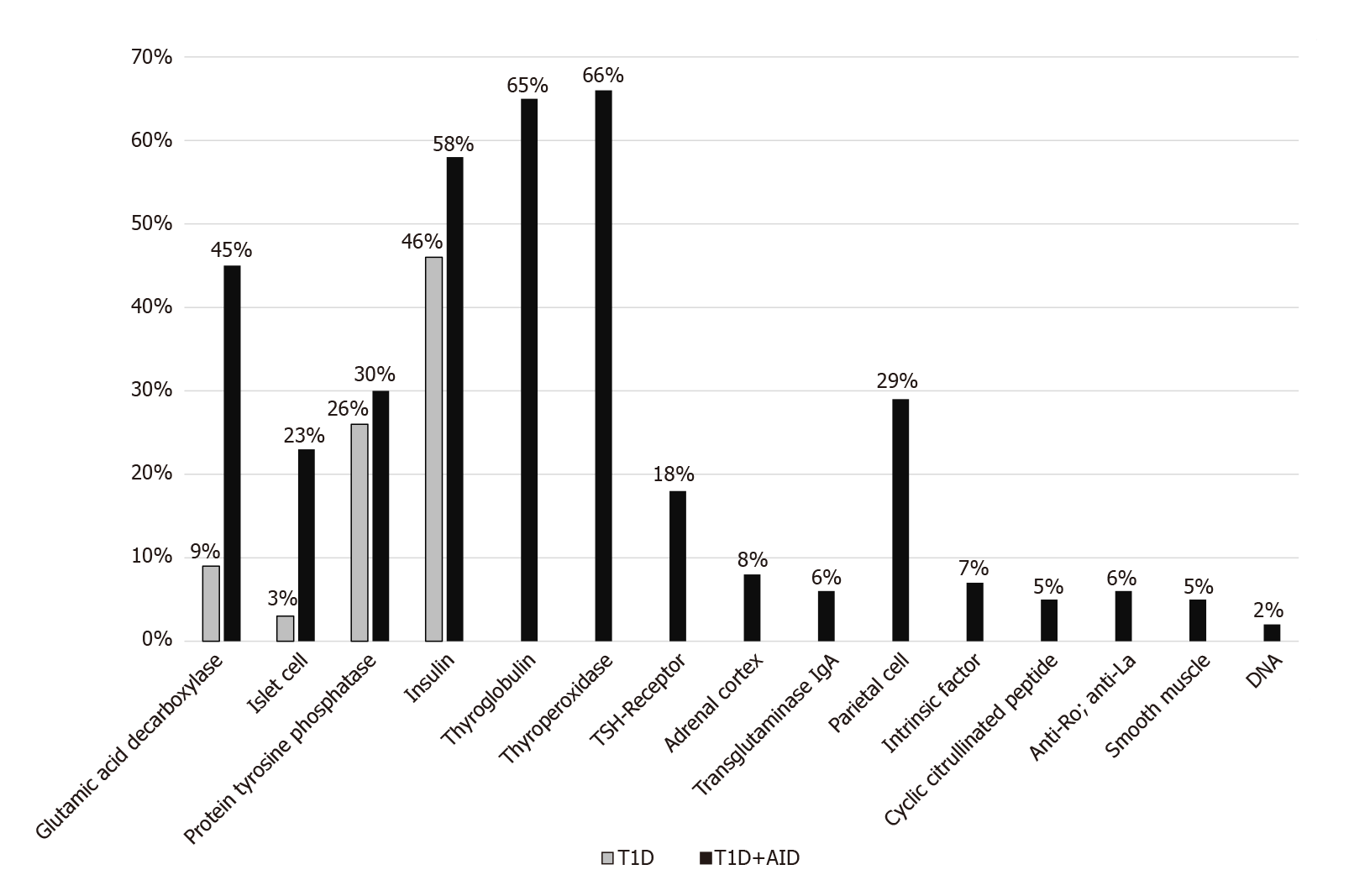
Figure 3 Prevalence of autoantibodies in type 1 diabetes.
The prevalence of autoantibodies in patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D) (light grey) and in patients with T1D + autoimmune diseases (black), followed at the Johannes Gutenberg University Medical Center. T1D: Type 1 diabetes; AID: Autoimmune diseases.
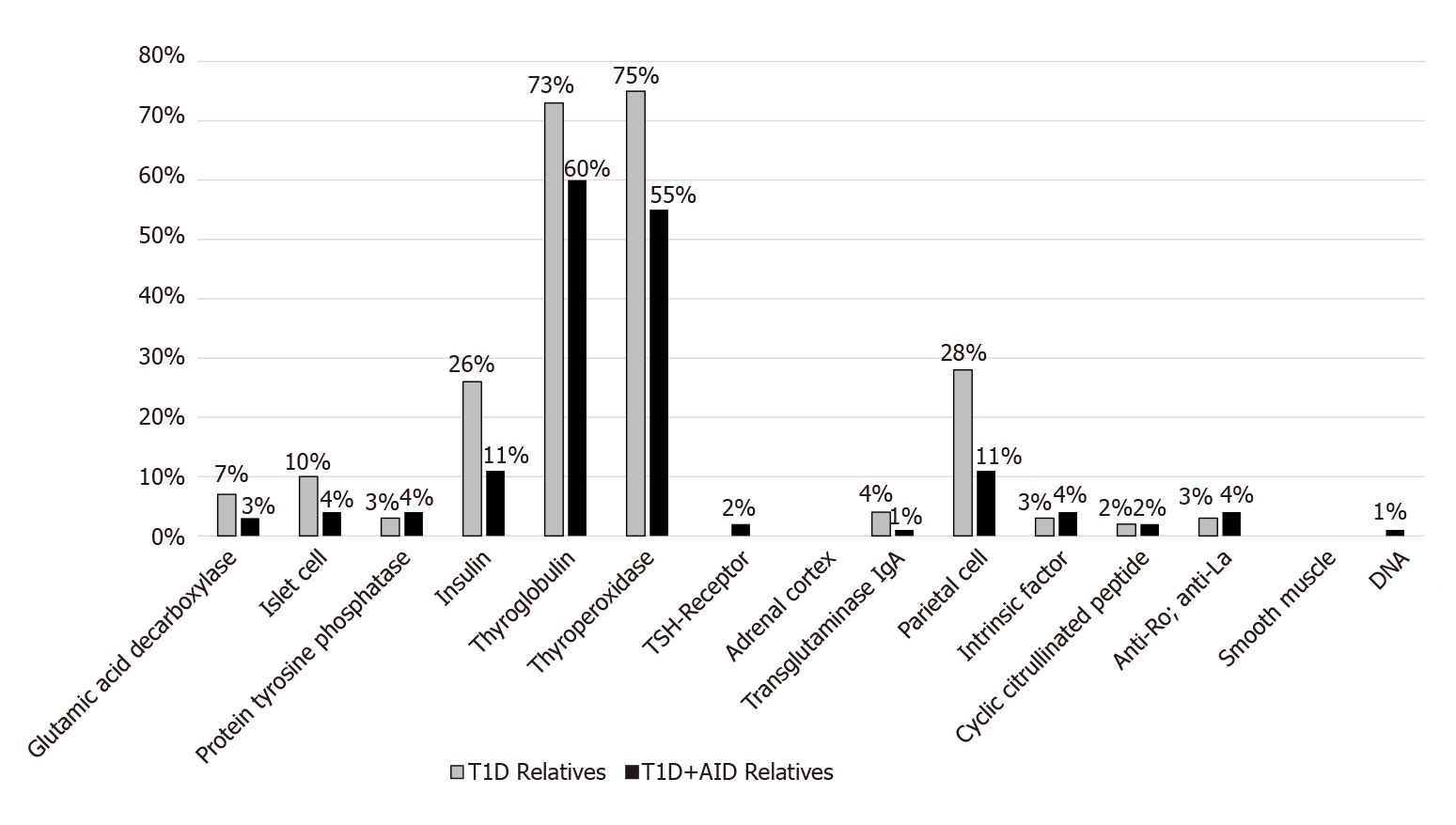
Figure 4 Autoantibodies in relatives.
Prevalence of autoantibodies in the relatives of patients with type 1 diabetes only (T1D) (light grey) and in the relatives of those with T1D + autoimmune diseases (AID, black). T1D: Type 1 diabetes; AID: Autoimmune diseases.
- Citation: Frommer L, Kahaly GJ. Type 1 diabetes and associated autoimmune diseases. World J Diabetes 2020; 11(11): 527-539
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v11/i11/527.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v11.i11.527