©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Feb 15, 2026; 18(2): 115562
Published online Feb 15, 2026. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v18.i2.115562
Published online Feb 15, 2026. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v18.i2.115562
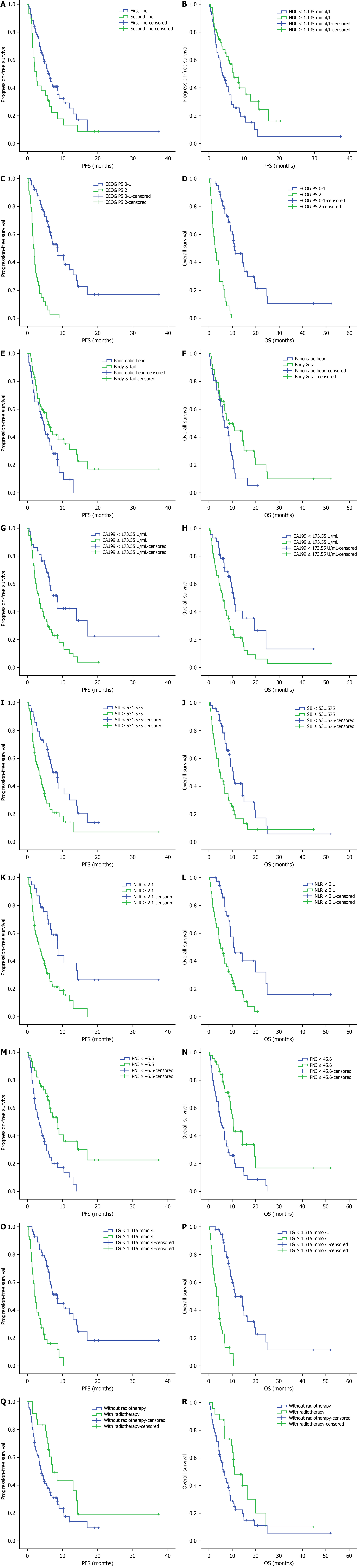
Figure 1 Kaplan-Meier curves for progression-free survival and overall survival in patients with pancreatic cancer treated with programmed death-1 inhibitors.
A: Correlation between the number of prior systemic therapy lines and progression-free survival (PFS); B: Correlation between high-density lipoprotein levels and PFS; C: Correlation between Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (ECOG PS) and PFS; D: Correlation between ECOG PS and overall survival (OS); E: Correlation between primary tumor location and PFS; F: Correlation between primary tumor location and OS; G: Correlation between carbohydrate antigen (CA199) levels and PFS; H: Correlation between CA199 levels and OS; I: Correlation between systemic immune-inflammation (SII) index and PFS; J: Correlation between SII index and OS; K: Correlation between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte (NLR) ratio and PFS; L: Correlation between NLR ratio and OS; M: Correlation between prognostic nutritional index (PNI) and PFS; N: Correlation between PNI and OS; O: Correlation between triglyceride (TG) levels and PFS; P: Correlation between TG levels and OS; Q: Correlation between radiotherapy and PFS; R: Correlation between radiotherapy and OS. HDL: High-density lipoprotein; PFS: Progression-free survival; ECOG PS: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status; OS: Overall survival; CA199: Carbohydrate antigen; SII: Systemic immune-inflammation; NLR: Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte; PNI: Prognostic nutritional index; TG: Triglyceride.
- Citation: Lu YY, Chen P, Lu Y. Clinical characteristics of programmed death-1 inhibitors for older patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2026; 18(2): 115562
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v18/i2/115562.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v18.i2.115562