©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Feb 15, 2026; 18(2): 114782
Published online Feb 15, 2026. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v18.i2.114782
Published online Feb 15, 2026. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v18.i2.114782
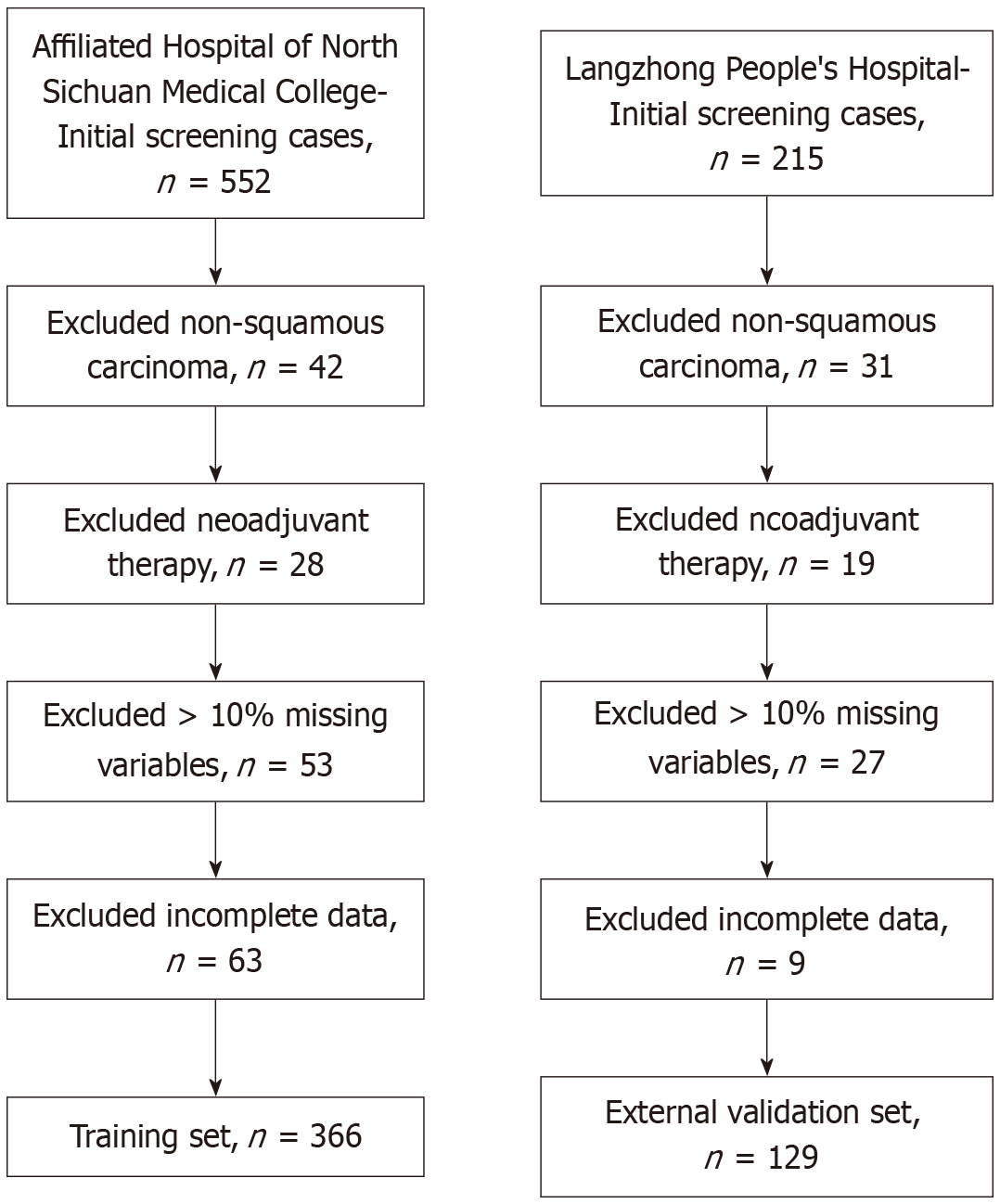
Figure 1
Flowchart of patients included in the analysis.
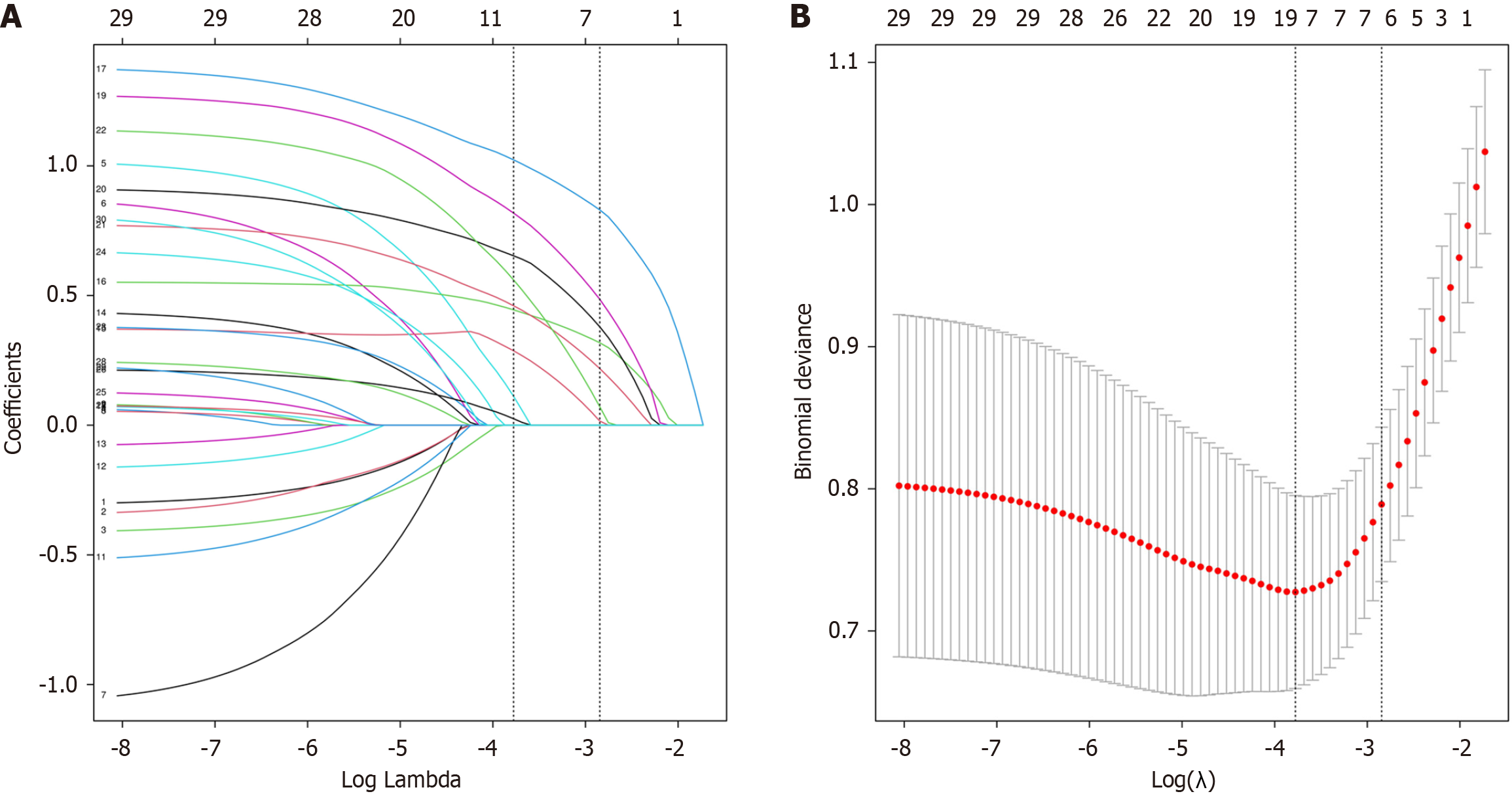
Figure 2 Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression analysis for feature selection.
A: Coefficient paths of 30 variables vs log(λ). Vertical lines indicate key λ values: 0.023 (9 variables, minimal mean squared error) and 0.058 (7 core variables under 1-SE rule); B: Cross-validation curve shows deviance vs log(λ) with error bands. λ = 0.023 gives minimum deviance; λ = 0.058 provides optimal parsimony. Together, these demonstrate regularization’s control of model complexity and prediction performance.
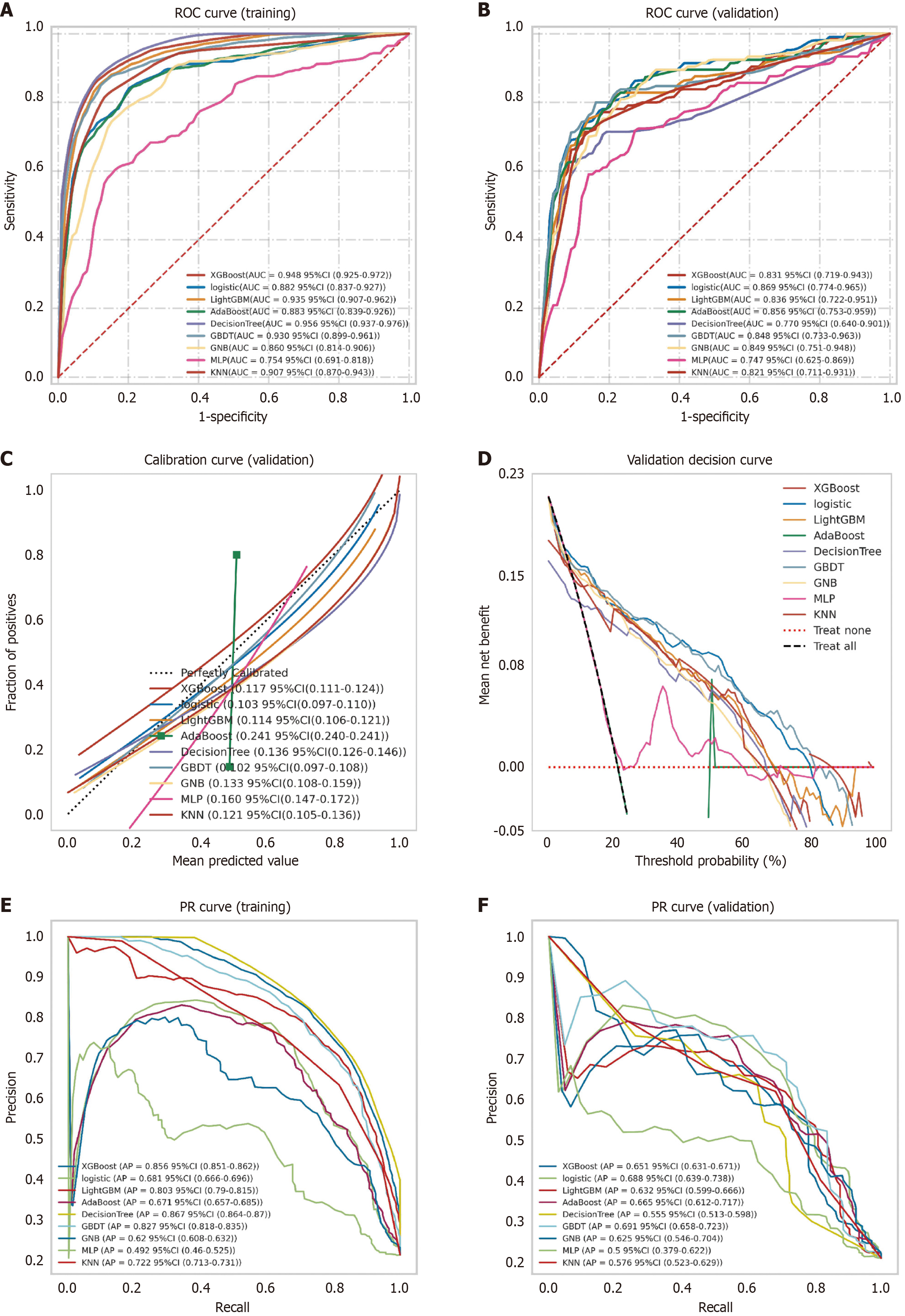
Figure 3 Comprehensive performance evaluation of machine learning models.
A: Receiver operating characteristic curve and area under the curve values for the training set; B: Receiver operating characteristic curve and area under the curve values for the validation set using five 7:3 random splits; C: Calibration curve shows predicted vs observed probabilities. Dashed diagonal indicates ideal reference. Solid lines show model performance. Better calibration is indicated by closer fit to diagonal and lower Brier scores (in parentheses); D: Decision curve analysis compares models. Black dashed line: All patients undergo non-curative resection; red dashed line: No intervention; E: Precision-recall curve and average precision (AP) for training set; F: Precision-recall curve and AP for validation set (Y-axis: Precision; X-axis: Recall). The logistic regression model showed consistently superior performance. Superiority is determined either by complete curve encapsulation or higher AP values for intersecting curves. Models are color-coded with mean and 95% confidence intervals. ROC: Receiver operating characteristic; AUC: Area under the curve; CI: Confidence interval; PR: Precision-recall.
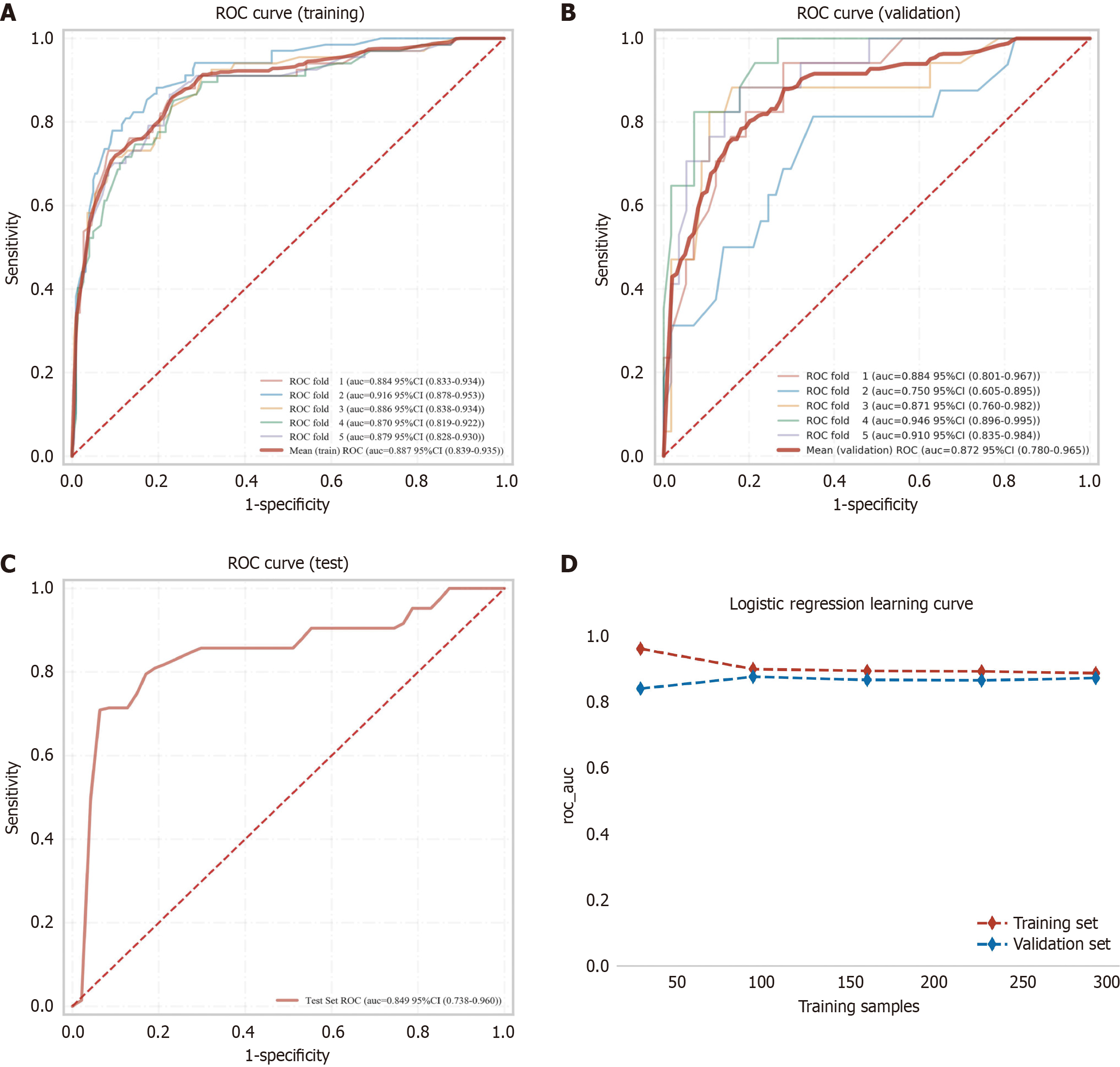
Figure 4 Performance evaluation of the logistic regression model across the training, validation, and external test sets.
A: Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and area under the curve (AUC) value for the training set; B: ROC curve and AUC values for the validation set, constructed through random selection of 30% of training cases with 5-fold cross-validation. Five solid lines represent individual validation fold outcomes; C: ROC curve and AUC value for the independent external test set; D: Learning curves show performance progression, with training and validation sets represented by red and blue dashed lines, respectively. ROC: Receiver operating characteristic; CI: Confidence interval.
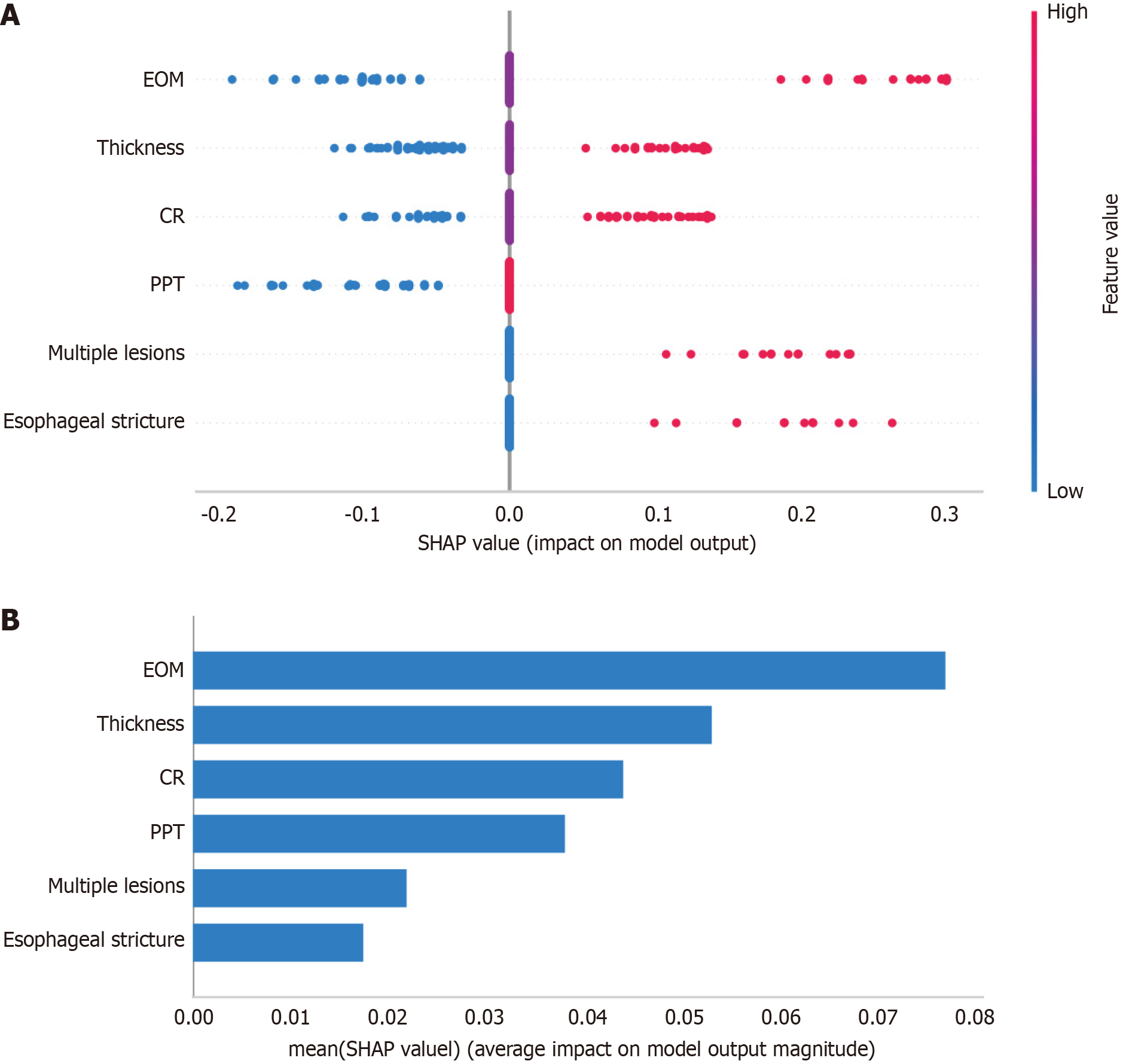
Figure 5 SHapley Additive exPlanations interpretability analysis for the non-curative resection prediction model.
A: Feature contribution summary. The horizontal axis indicates the Shapley Additive exPlanations value (log-odds impact on prediction); the vertical axis lists clinical predictors. Red and blue dots indicate high and low feature values, respectively; B: Predictor importance ranking. Bar length reflects the mean |SHapley Additive exPlanations| value, quantifying each predictor’s contribution to model decisions. SHAP: SHapley Additive exPlanations; CR: Circumferential ratio; EOM: Endoscopic ultrasound or magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging; PPT: Postoperative pathological type.
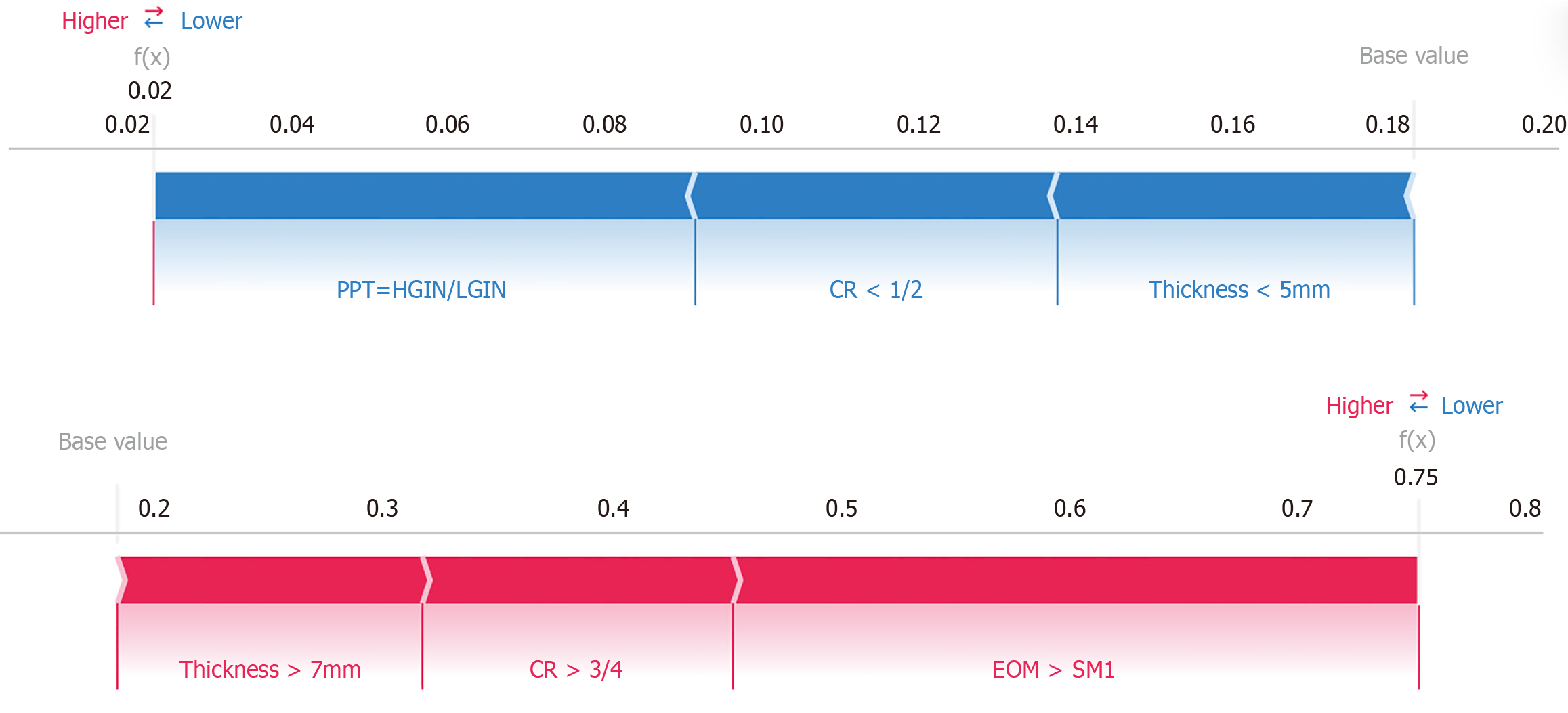
Figure 6 Two case examples illustrating SHapley Additive exPlanations-based interpretation of the logistic regression model.
CR: Circumferential ratio; EOM: Endoscopic ultrasound or magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging; PPT: Postoperative pathological type; HGIN/LGIN: High-grade intraepithelial neoplasia/Low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia.
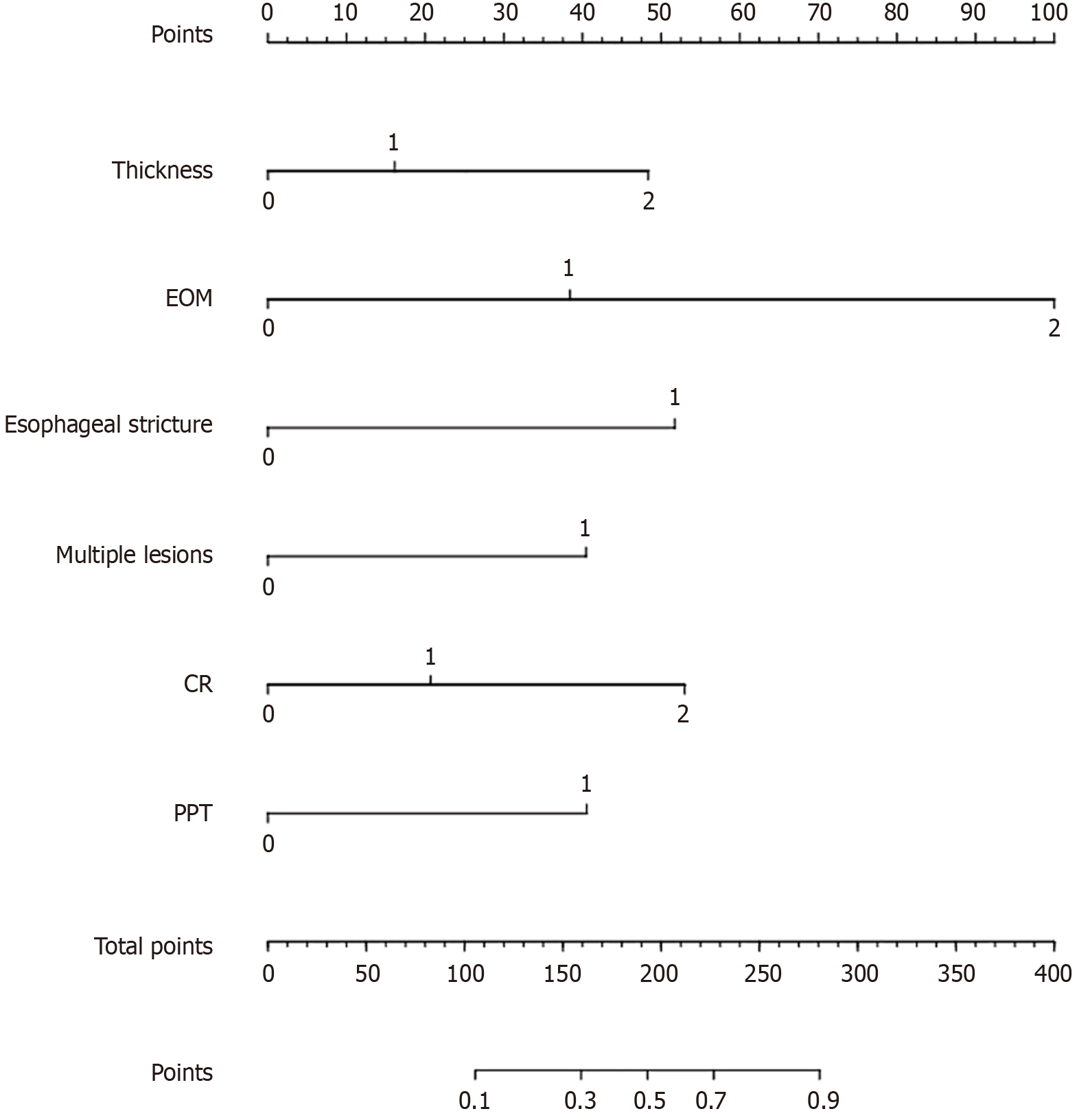
Figure 7 Nomogram of the machine learning prediction model for non-curative resection in superficial esophageal cancer.
CR: Circum
- Citation: Luo ZC, Guo HY, Tang X, Chen XR, Zhang CY, Cui YT, Zuo J, Li HR, Hou XM, Chen H, Song SB, Wang XF. Predicting the magnitude of risk for non-curative endoscopic submucosal dissection in superficial esophageal cancer using explainable artificial intelligence. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2026; 18(2): 114782
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v18/i2/114782.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v18.i2.114782