©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jan 15, 2026; 18(1): 112896
Published online Jan 15, 2026. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v18.i1.112896
Published online Jan 15, 2026. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v18.i1.112896
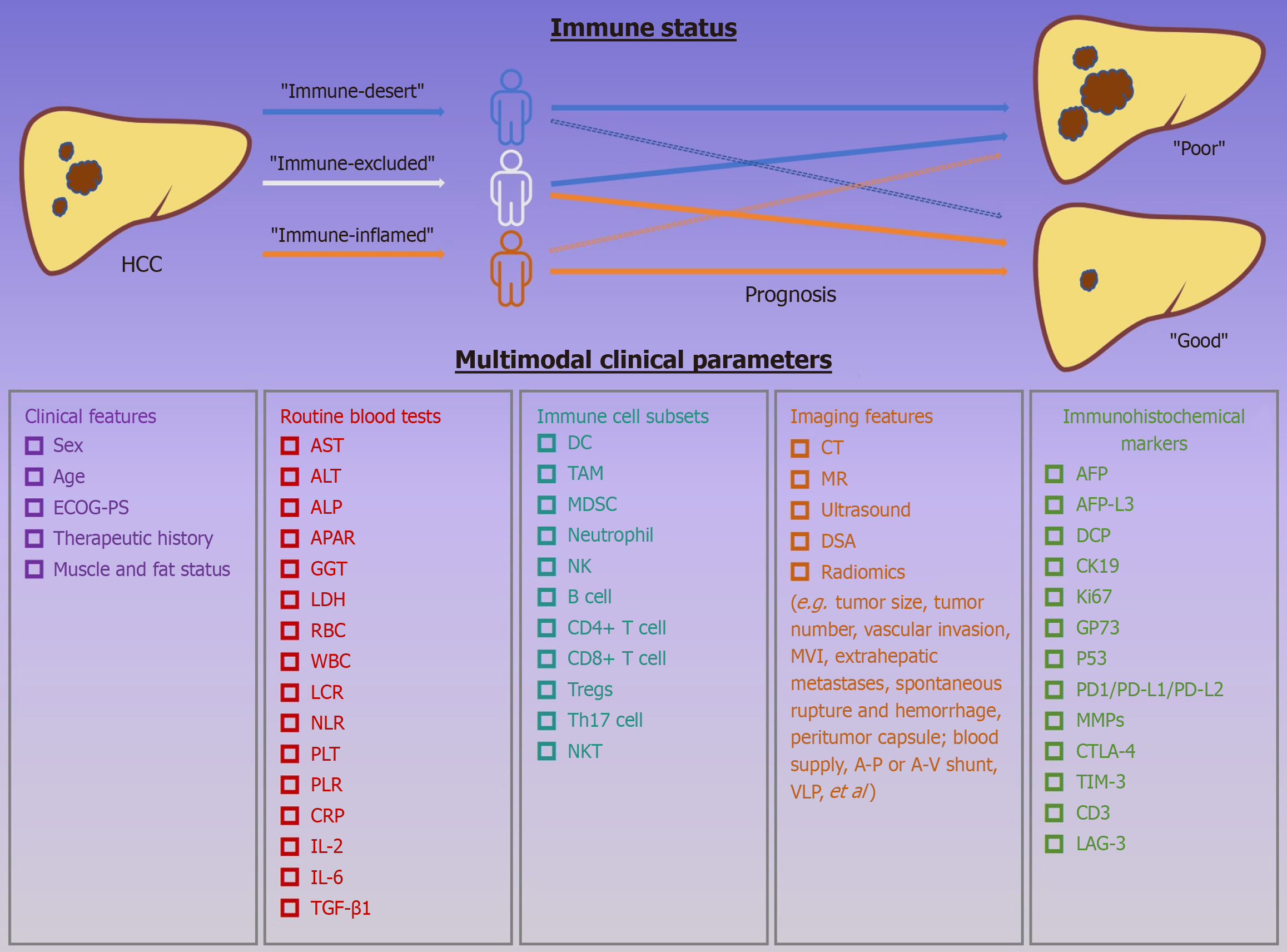
Figure 1 Exploring the relationship between immune status and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma with multimodal clinical pa
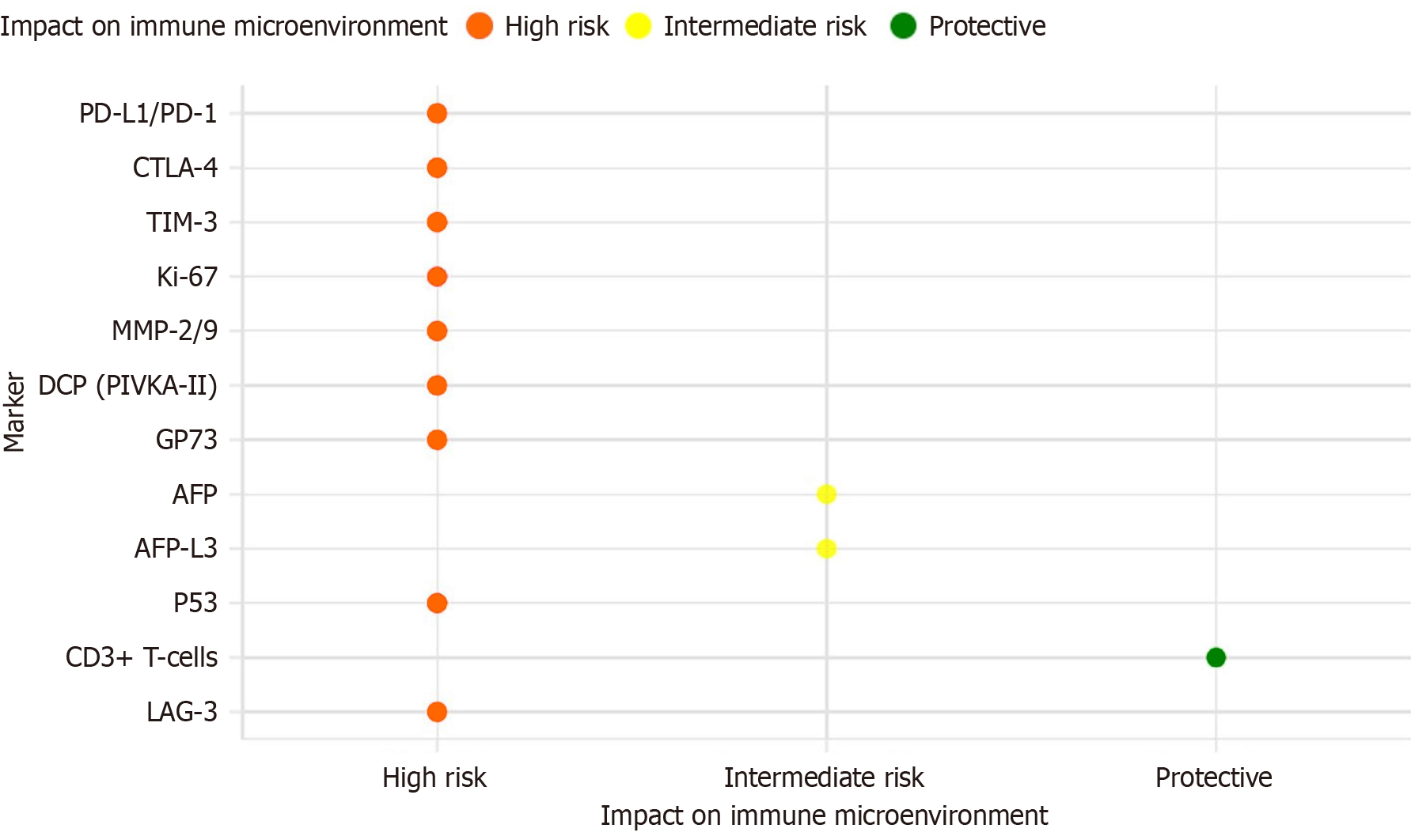
Figure 2 Evaluation of immunohistochemical markers in prognostic risk stratification for hepatocellular carcinoma.
By analyzing the expression patterns of key immune checkpoints and biomarkers in the tumor microenvironment, the prognostic risks of HCC were classified into three categories: High risk, intermediate risk, and protective factors. PD-L1: Programmed death-ligand 1; PD-1: Programmed cell death protein 1; TIM-3: T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin-domain containing-3; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase; DCP: Des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin; GP73: Golgi protein 73; AFP: Alpha-fetoprotein; AFP-L3: Alpha-fetoprotein L3 fraction; LAG-3: Lymphocyte-activation gene 3.
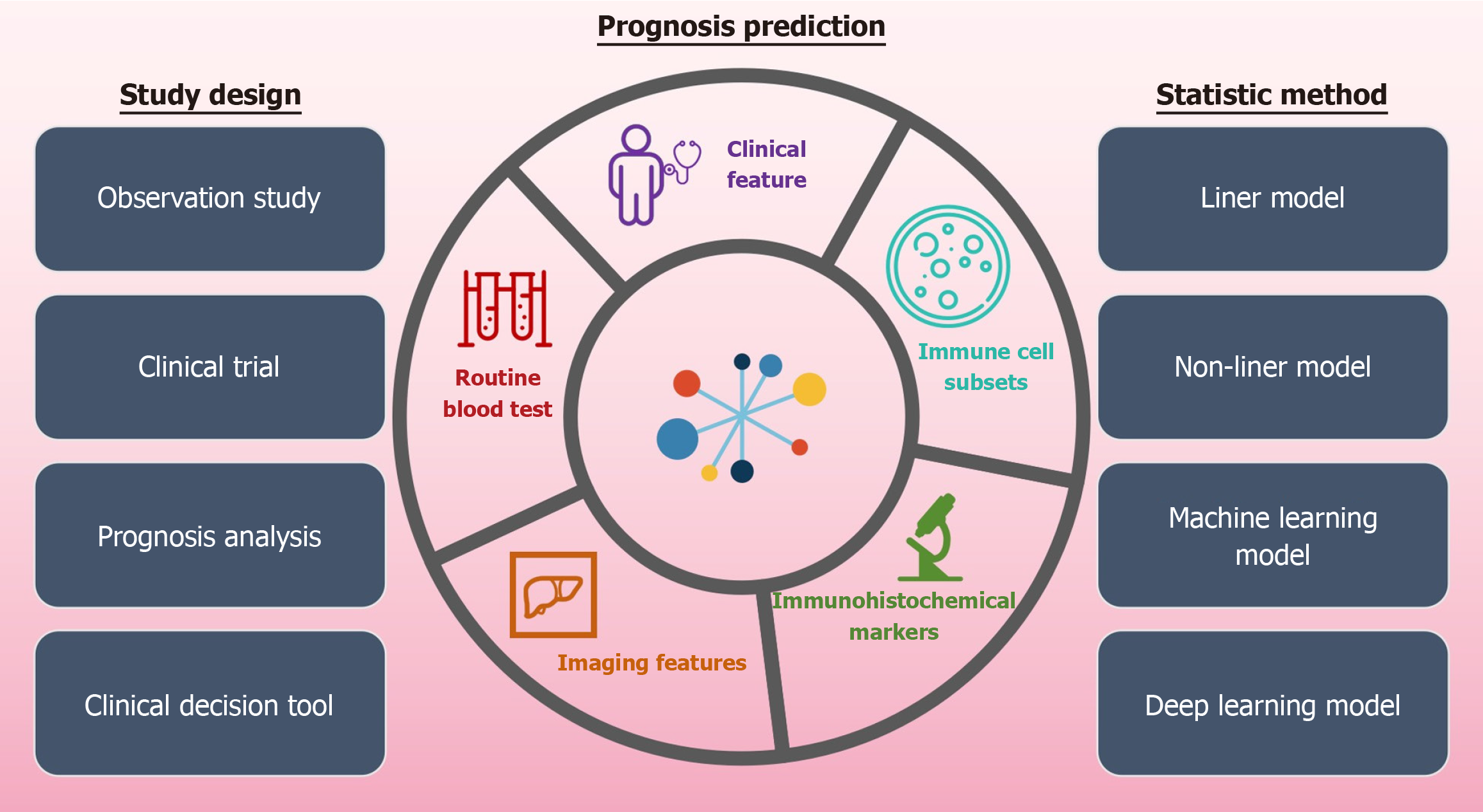
Figure 3 Future prospects of study design and statistic method for prognostic prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma patients based on analysis of multimodal clinical parameters.
Based on the multimodal clinical parameters, follow-up studies will center on four key areas: Observation studies, clinical trials, prognosis analyses, and clinical decision tools. Diverse statistical methods, covering linear and nonlinear models as well as machine learning and deep learning models, can be applied for achieving comprehensive and in-depth research results.
- Citation: Zhang YZ, Tang YZ, He YX, Pan ST, Dai HC, Liu Y, Zhou HF. Multimodal clinical parameters-based immune status associated with the prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2026; 18(1): 112896
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v18/i1/112896.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v18.i1.112896