©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jun 15, 2025; 17(6): 106617
Published online Jun 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i6.106617
Published online Jun 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i6.106617
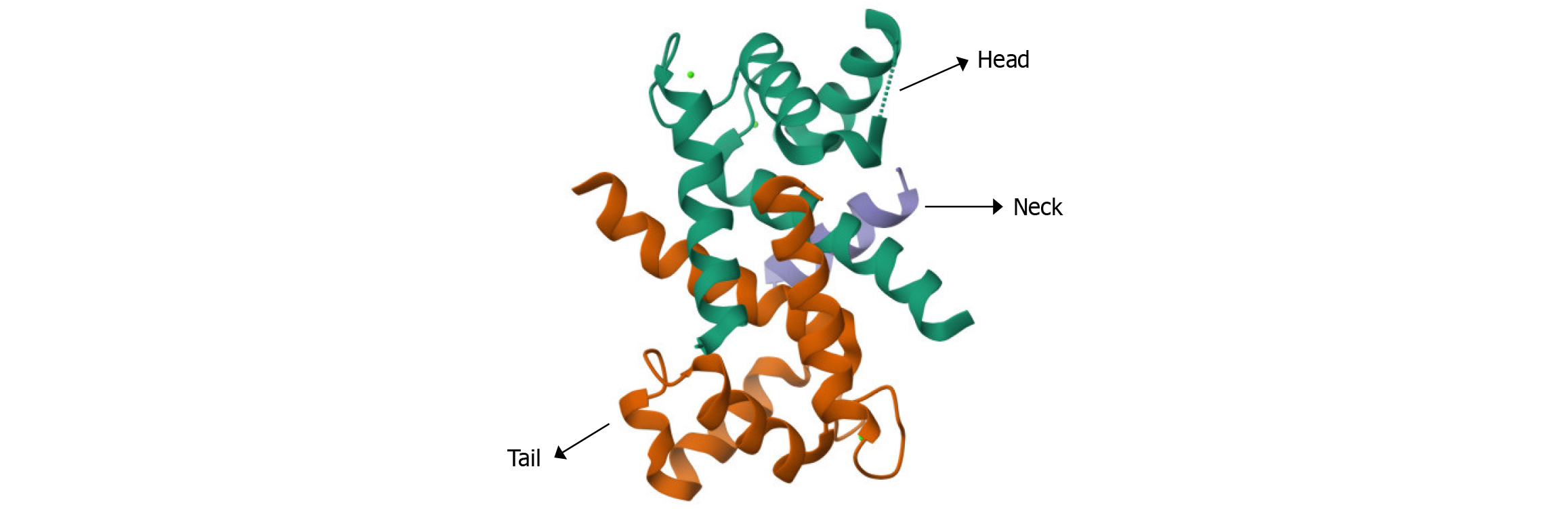
Figure 1
Spatial structure of myosin heavy chain 9 protein.
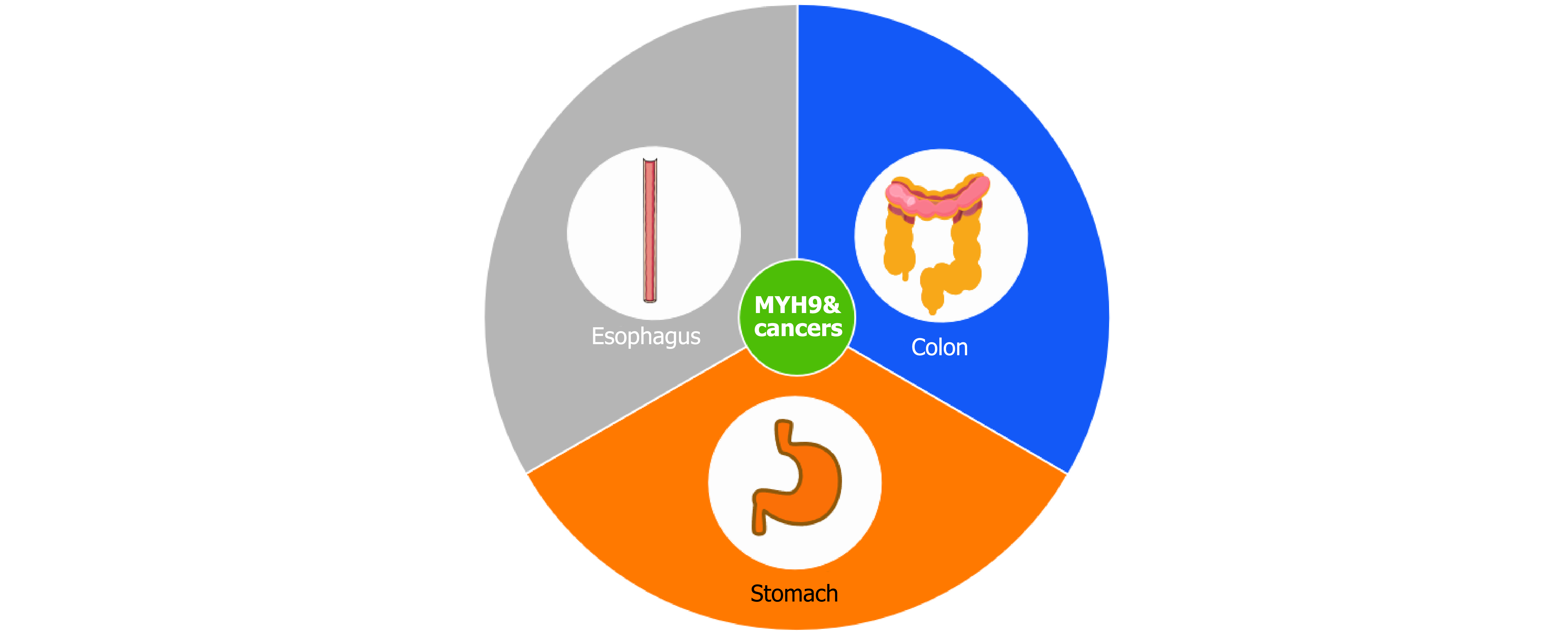
Figure 2 Expression of myosin heavy chain 9 in esophageal cancer, gastric cancer, and colorectal cancer.
MYH9: Myosin heavy chain 9.
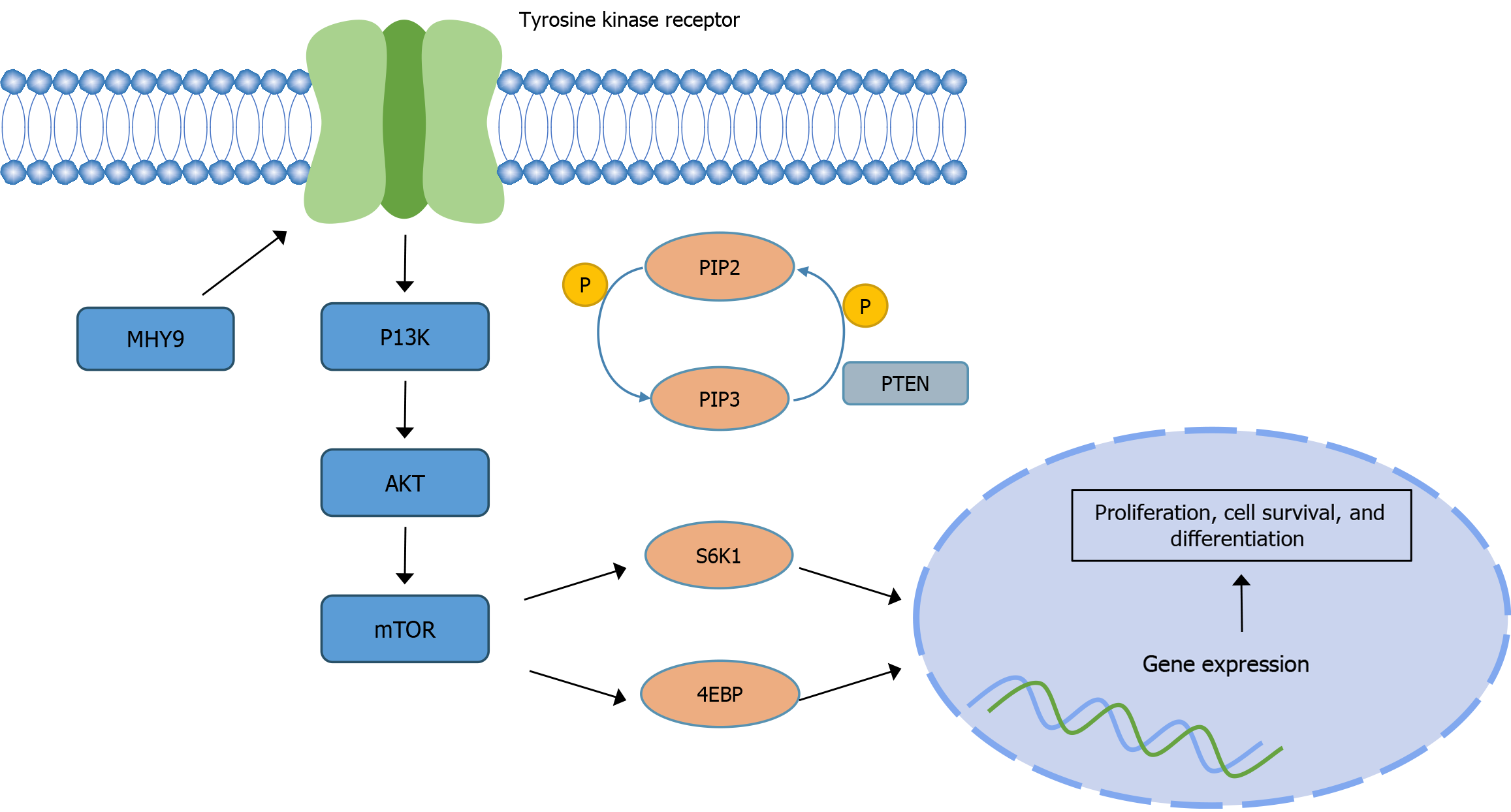
Figure 3 Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway is involved in cell growth, differentiation, and tumorigenesis.
When the ligand binds to the membrane receptor, the receptor and myosin heavy chain 9 activate phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, which then catalyzes the formation of phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate from phosphatidylinositol 4,5-biphosphate on the inner surface of the membrane. As the second messenger, phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate further activates protein kinase B. Protein kinase B can activate the downstream mammalian target of rapamycin pathway, which can phosphorylate and activate S6 kinase 1 and 4E-binding protein, and finally participate in gene expression. PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; AKT: Protein kinase B; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin. MYH9: Myosin heavy chain 9; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; AKT: Protein kinase B; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; PIP2: Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-biphosphate; PIP3: Phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate; S6K1: S6 kinase 1; 4EBP: 4E-binding protein; PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homolog.
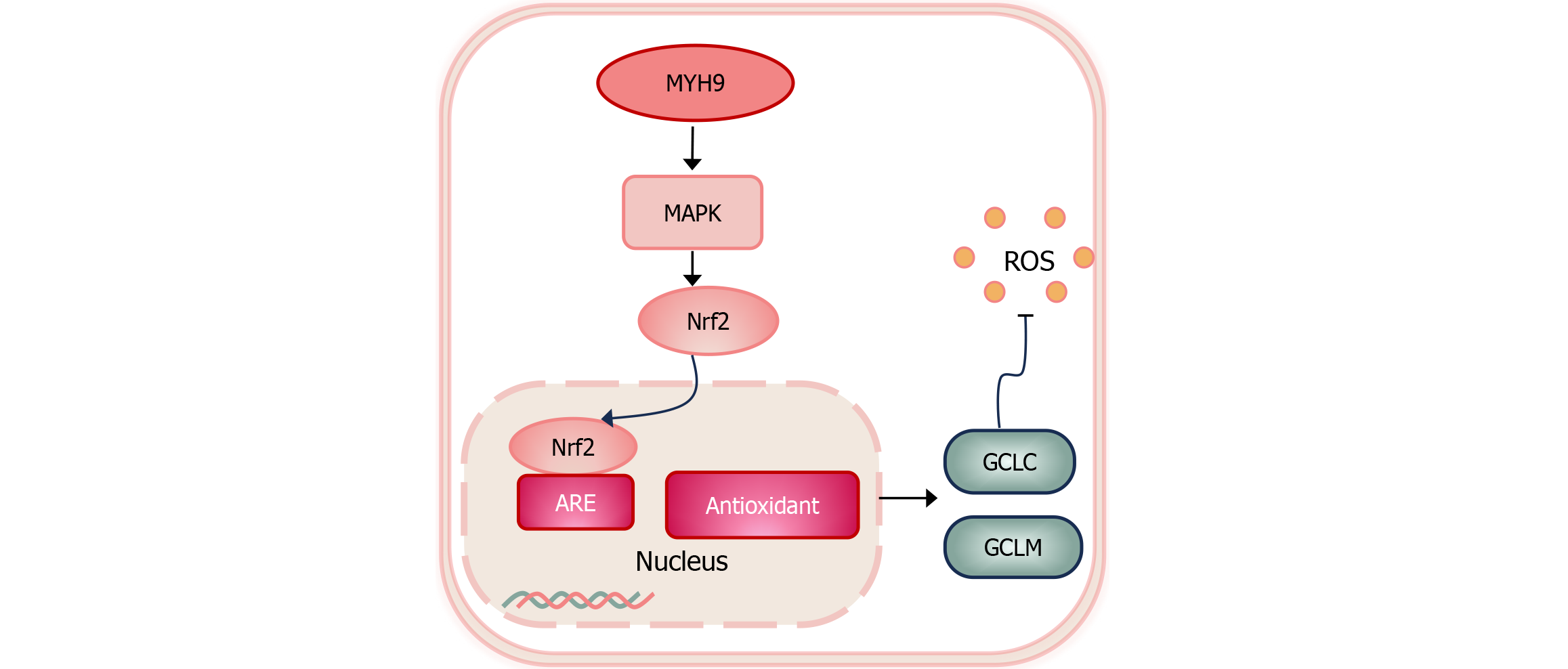
Figure 4 Myosin heavy chain 9 activates pan-mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling molecules, including extracellular signal-regulated kinase, p38, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase.
This activation leads to the induction of nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2 transcriptional activity, the upregulation of the antioxidant enzymes, and the reduction of cellular reactive oxygen species levels. The antioxidant enzyme, such as glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit, further confers cell invasion and radioresistance, resulting in aggressive cancer and poor prognosis. MYH9: Myosin heavy chain 9; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinases; Nrf2: Nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2; ARE: Antioxidant response element; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; GCLC: Glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit; GCLM: Glutamate-cysteine ligase modifier subunit.
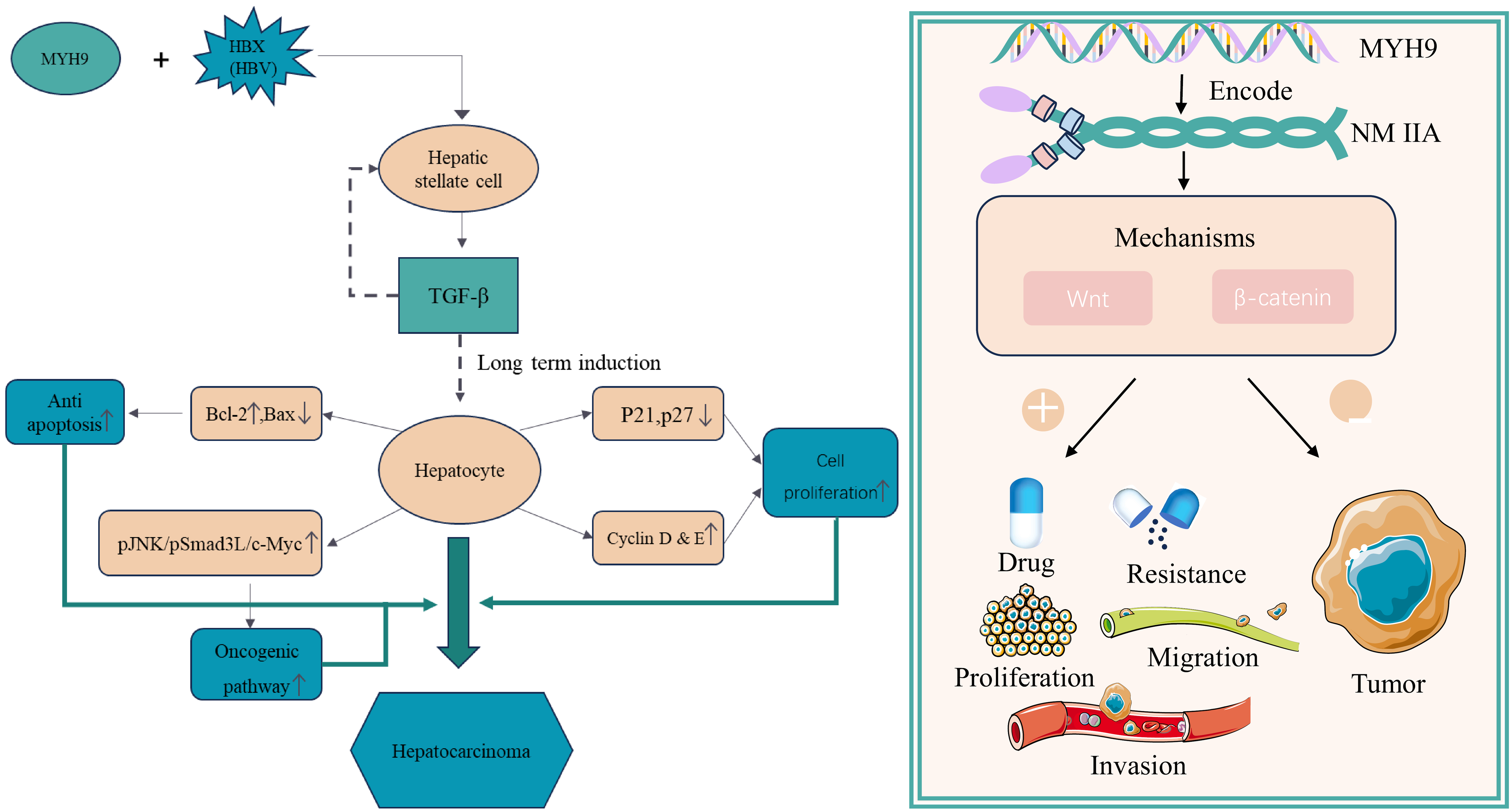
Figure 5 Myosin heavy chain 9 activates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway to enhance the proliferation and survival of cancer cells.
Myosin heavy chain 9 activates the transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathway and promotes tumor cell invasion and metastasis by interacting with the X protein encoded by the hepatitis B virus. MYH9: Myosin heavy chain 9; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-beta; JNK: C-Jun N-terminal kinase.
- Citation: Zeng XF, Wang YW, Ou Y, Liu L. Role of myosin heavy chain 9 in gastrointestinal tumorigenesis: A comprehensive review. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(6): 106617
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i6/106617.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i6.106617