©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Dec 15, 2025; 17(12): 110736
Published online Dec 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i12.110736
Published online Dec 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i12.110736
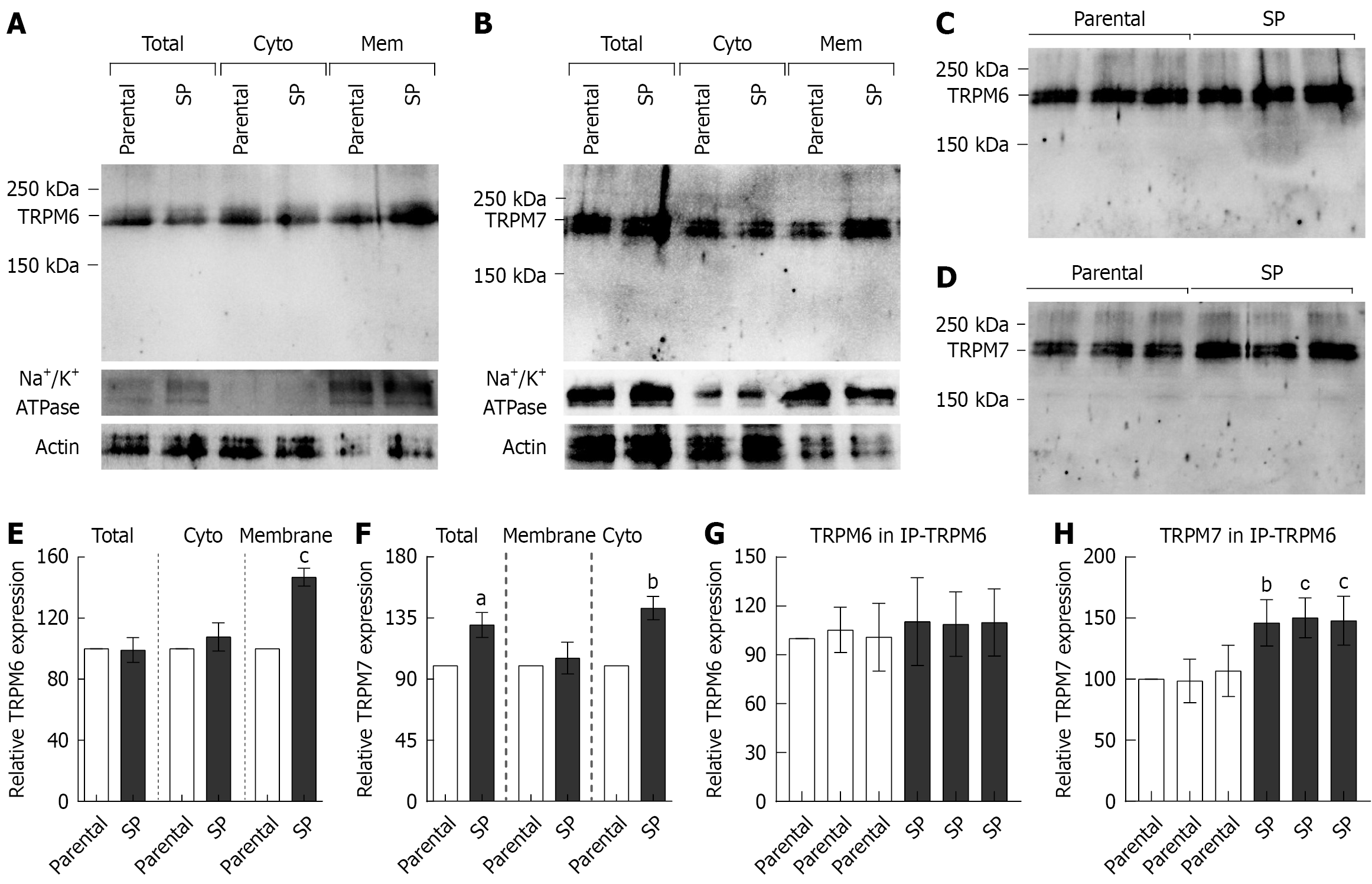
Figure 1 Expression and subcellular localization of transient receptor potential melastatin 6 and transient receptor potential melastatin 7 in parental and spheroid-derived HT-29 cells.
A: The western blot analysis of transient receptor potential melastatin (TRPM) 6; B: The western blot analysis of TRPM7; C: TRPM6 in immunoprecipitation of TRPM6 (IP-TRPM6); D: TRPM7 in IP-TRPM6 of parental HT-29 monolayers and spheroid-derived cells; E: The densitometric analysis of TRPM6; F: The densitometric analysis of TRPM7; G: TRPM6 in IP-TRPM6; H: TRPM7 in IP-TRPM6 of parental HT-29 monolayers and spheroid-derived cells. Total: Total cell; Cyto: Cytosol; Mem: Membrane; SP: Spheroid; TRPM: Transient receptor potential melastatin; IP-TRPM6: Immu
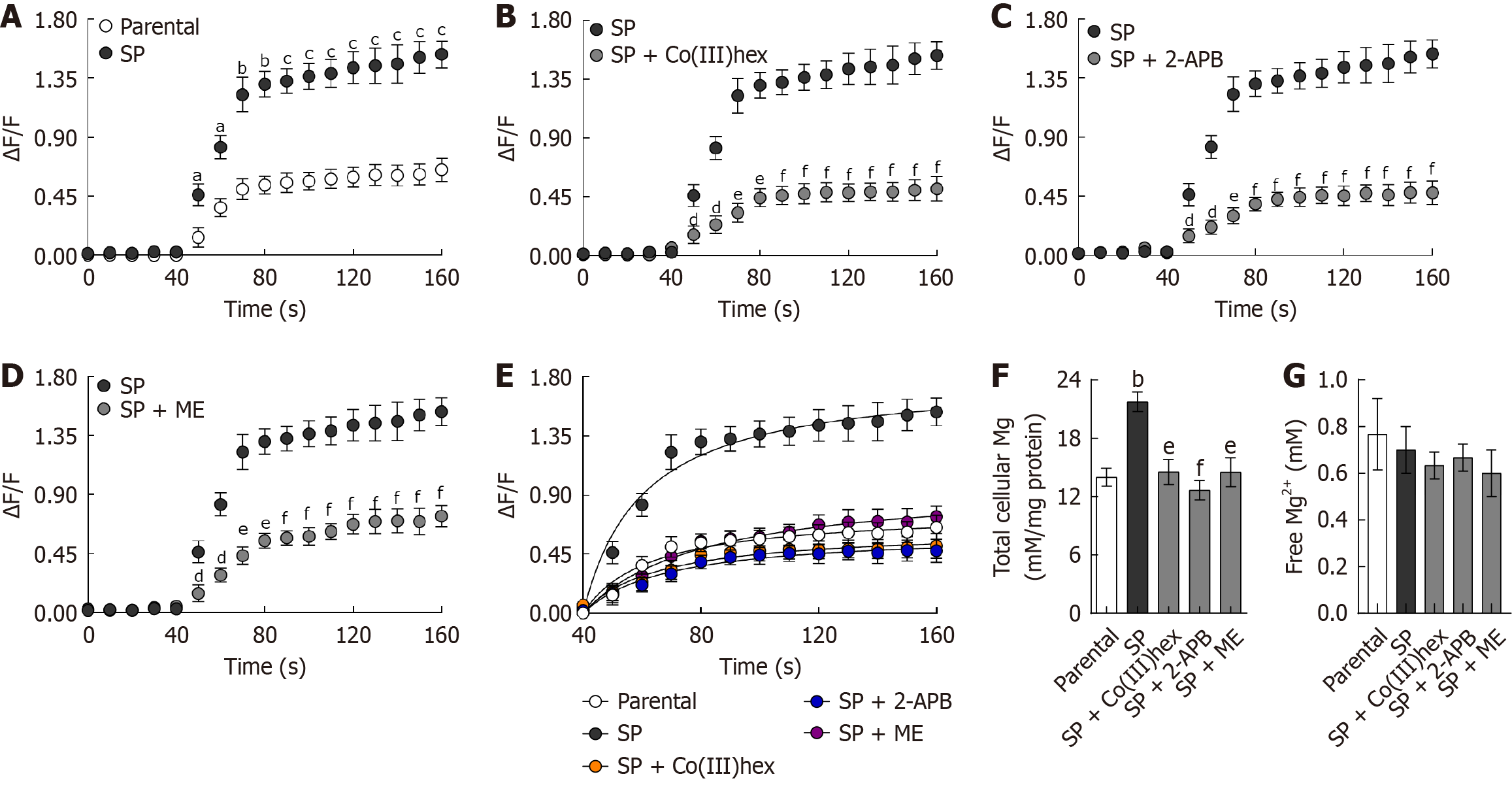
Figure 2 Mg2+ influx and total Mg content in cancer spheroids.
A: Mg2+ influx in parental HT-29 cells compared with spheroid (SP)-derived HT-29 cells; B: Mg2+ influx in SP cells with or without the Mg2+ channel inhibitor Co(III)hexamine; C: Mg2+ influx in SP cells with or without the transient receptor potential melastatin 6/7 inhibitor 2-aminoethyl diphenylborinate; D: Mg2+ influx in SP cells with or without the transient receptor potential melastatin 6 inhibitor Mesendogen; E: Michaelis-Menten kinetic analysis of ΔF/F values between 40 and 160 seconds in parental HT-29 vs SP cells, SP vs SP with Co(III)hexamine, SP vs SP with 2-aminoethyl diphenylborinate, and SP vs SP with Mesendogen; F: Total intracellular Mg2+ content; G: Free intracellular Mg2+ level. SP: Spheroid; Co(III)hex: Co(III)hexamine; 2-APB: 2-aminoethyl diphenylborinate; ME: Mesendogen. aP < 0.05 vs parental HT-29 cells, bP < 0.01 vs parental HT-29 cells, cP < 0.001 vs parental HT-29 cells, dP < 0.05 vs spheroid group, eP < 0.01 vs spheroid group, and fP < 0.001 vs spheroid group.
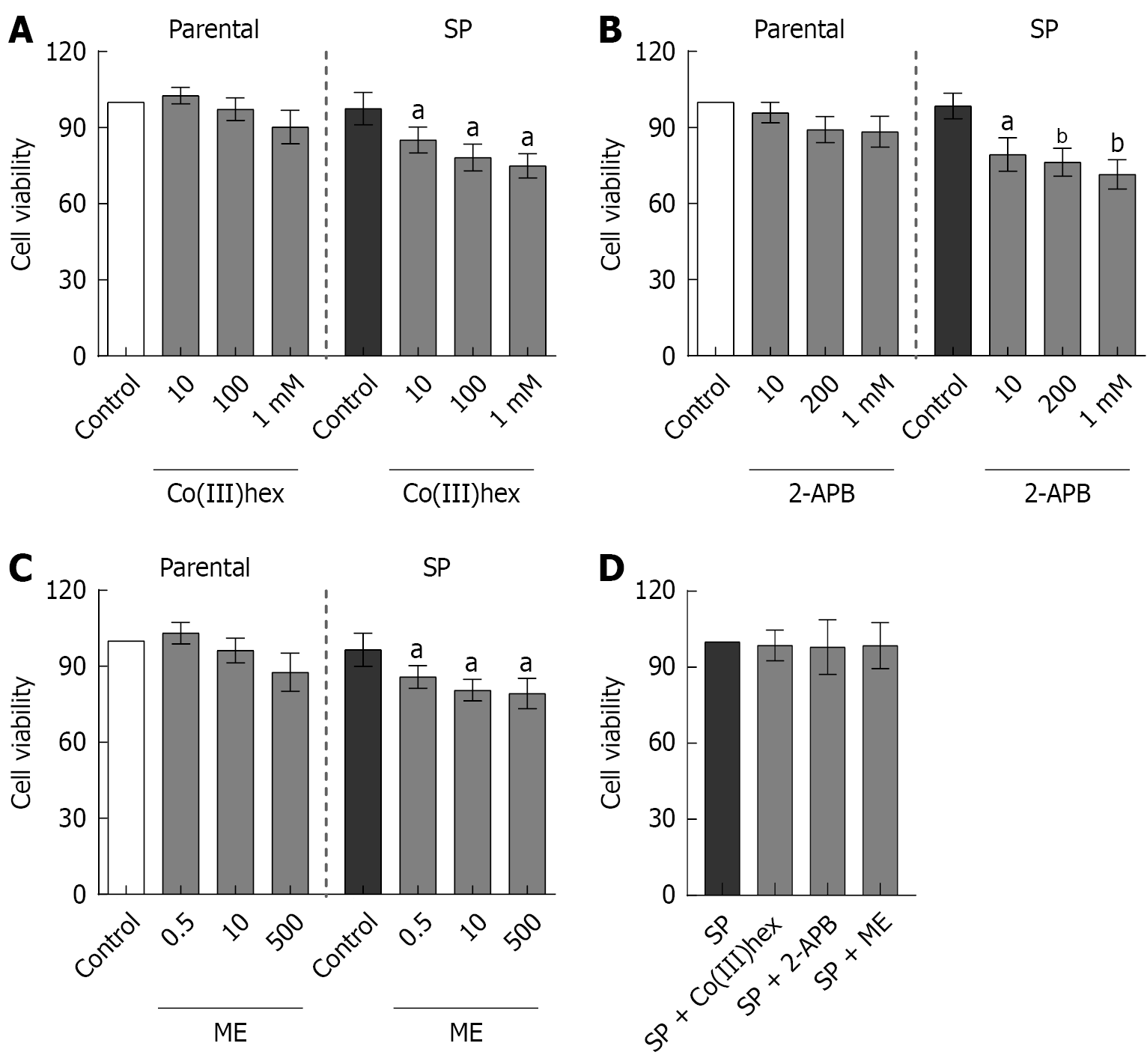
Figure 3 Effects of transient receptor potential melastatin inhibitors on the viability of spheroid-derived cells.
A: Cell viability of parental and spheroid (SP)-derived HT-29 cells treated with the Mg2+ channel inhibitor Co(III)hexamine; B: Cell viability of parental and SP cells treated with the transient receptor potential melastatin 6/7 inhibitor 2-aminoethyl diphenylborinate; C: Cell viability of parental and SP cells treated with the transient receptor potential melastatin 6 inhibitor Mesendogen; D: Cell viability of SP cells with or without Co(III)hexamine, 2-aminoethyl diphenylborinate, or Mesendogen treatment for 12 hours. SP: Spheroid; Co(III)hex: Co(III)hexamine; 2-APB: 2-aminoethyl diphenylborinate; ME: Mesendogen. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs the control spheroid group (n = 6).
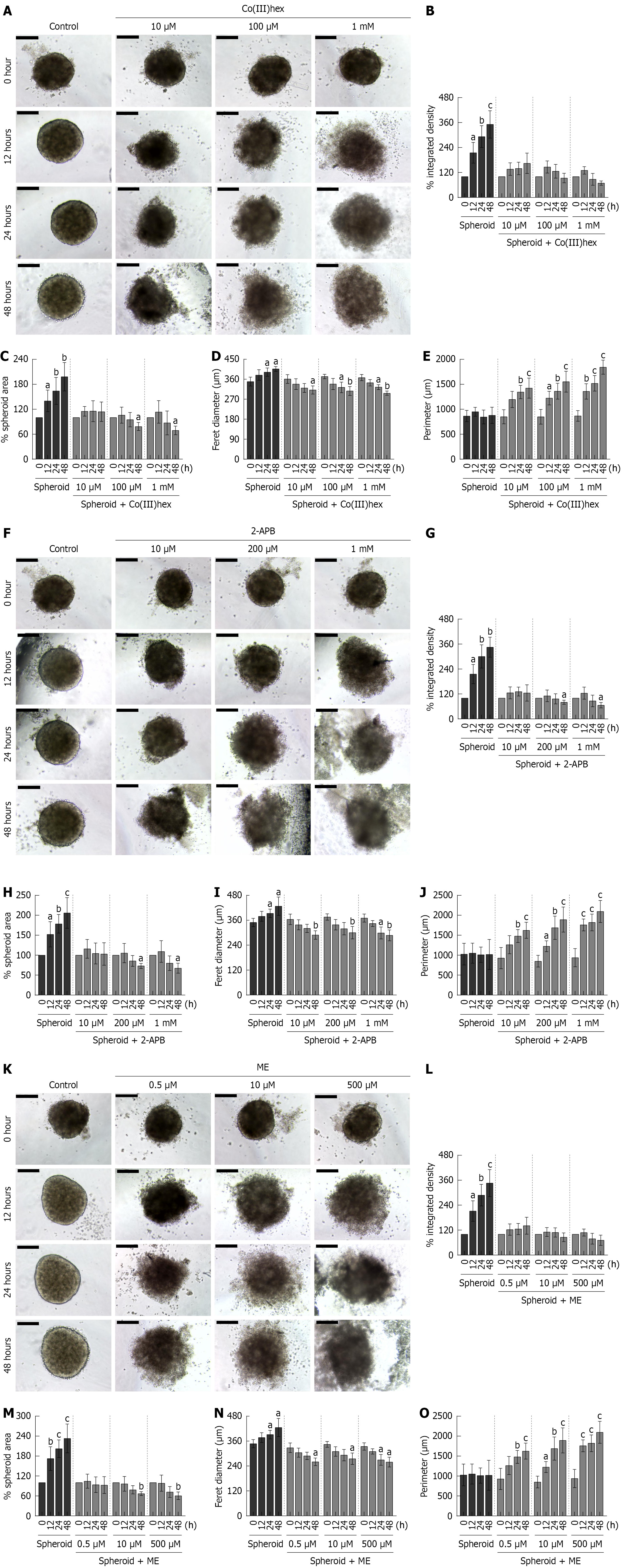
Figure 4 Transient receptor potential melastatin inhibitors affect spheroid stability.
A-E: Cancer spheroids treated with or without Co(III)hexamine, representative images, percent integrated density, percent spheroid area, Feret diameter, perimeter; F-J: Cancer spheroids treated with or without 2-aminoethyl diphenylborinate, representative images, percent integrated density, percent spheroid area, Feret diameter, perimeter; K-O: Cancer spheroids treated with or without Mesendogen, representative images, percent integrated density, percent spheroid area, Feret diameter, perimeter. Scale bar = 200 μm. SP: Spheroid; Co(III)hex: Co(III)hexamine; 2-APB: 2-aminoethyl diphenylborinate; ME: Mesendogen. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs the same grout at time 0 hour (n = 6).
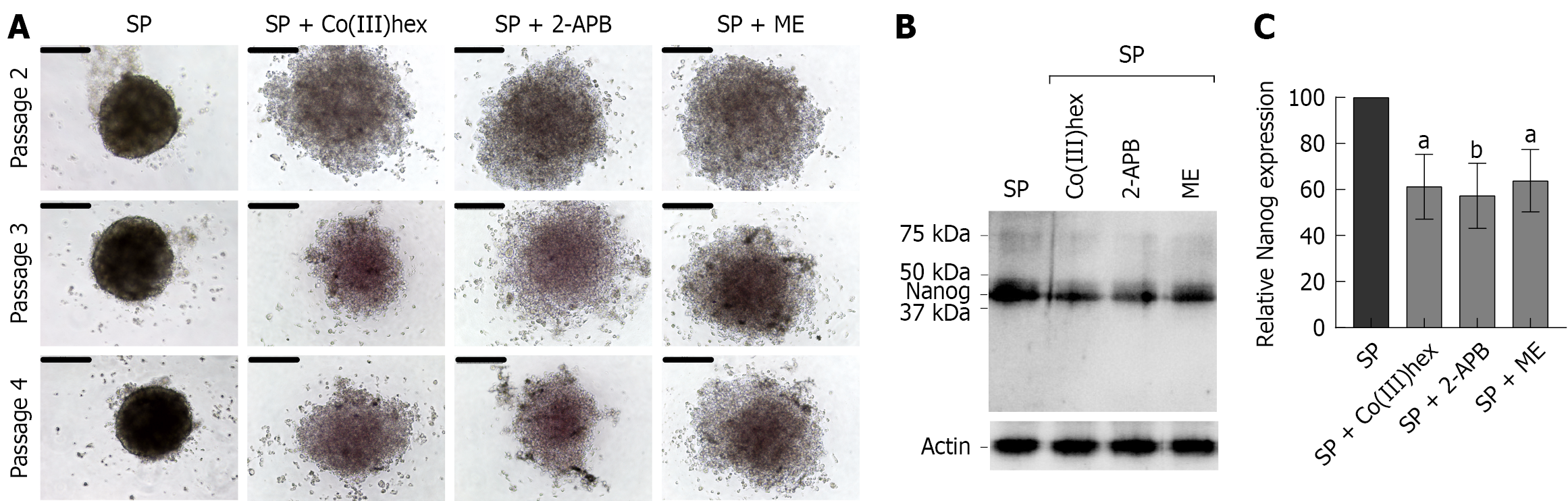
Figure 5 Secondary sphere formation assay.
A: Serial spheroid formation was assessed by repeated passaging of cancer spheroid (SP)-derived cells treated with or without 100 μmol/L Co(III)hexamine, 200 μmol/L 2-aminoethyl diphenylborinate, or 10 μmol/L Mesendogen. Scale bar = 200 μm; B: The western blot analysis; C: Densitometric analysis of Nanog in SP cells treated with or without 100 μmol/L Co(III)hexamine, 200 μmol/L 2-aminoethyl diphenylborinate, or 10 μmol/L Mesendogen. SP: Spheroid; Co(III)hex: Co(III)hexamine; 2-APB: 2-aminoethyl diphenylborinate; ME: Mesendogen. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs the control spheroid group (n = 6).
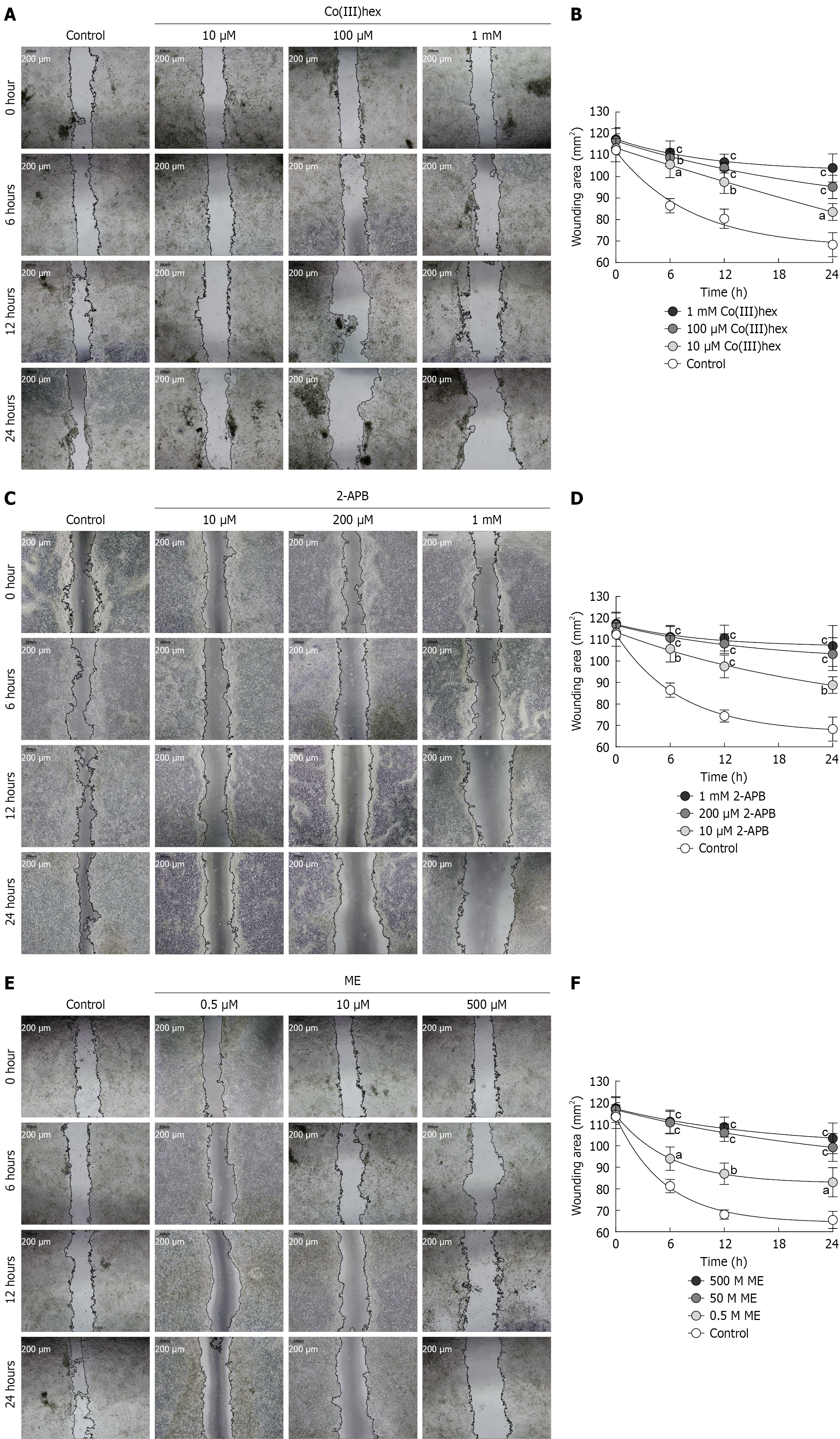
Figure 6 Effects of Mg2+ channel inhibitors on migration of spheroid-derived HT-29 cells.
A and B: Wounding area of spheroid (SP)-derived HT-29 cells treated with or without Co(III)hexamine; C and D: Wounding area of SP-derived HT-29 cells treated with or without 2-aminoethyl diphenylborinate; E and F: Wounding area of SP-derived HT-29 cells treated with or without Mesendogen. Scale bar = 200 μm. Co(III)hex: Co(III)hexamine; 2-APB: 2-aminoethyl diphenylborinate; ME: Mesendogen. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs the corresponding control group at same time point (n = 6).
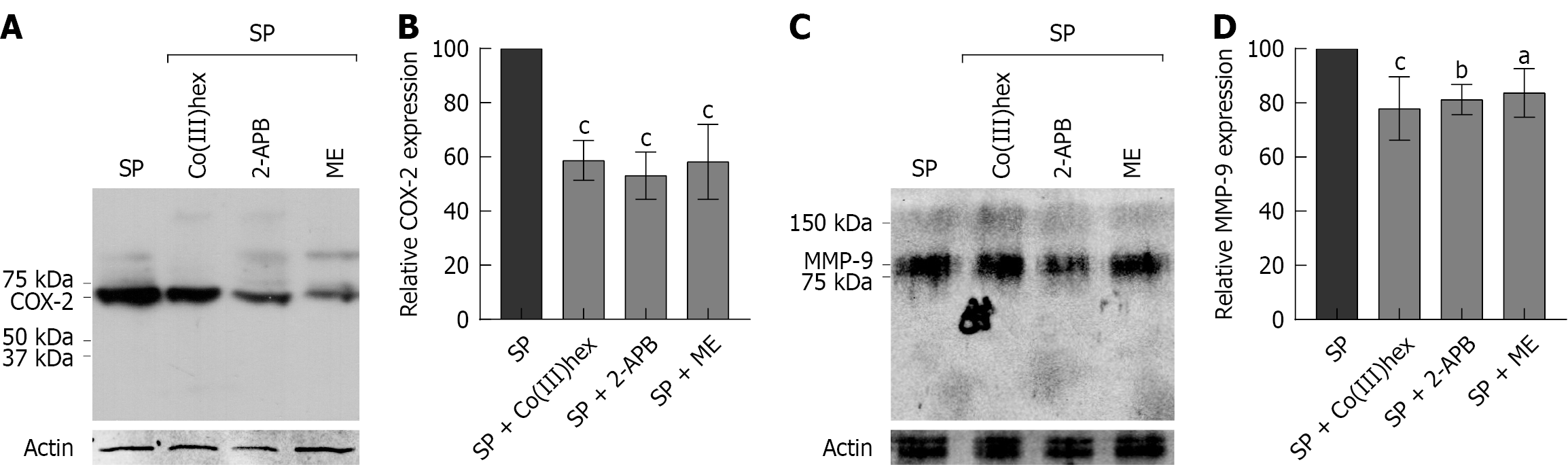
Figure 7 Effects of Mg2+ channel inhibitors on the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and matrix metalloproteinase-9.
A and B: The western blot analysis and densitometric analysis of cyclooxygenase-2 in spheroid cells treated with or without 100 μmol/L Co(III)hexamine, 200 μmol/L 2-aminoethyl diphenylborinate, or 10 μmol/L Mesendogen; C and D: The western blot analysis and densitometric analysis of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in spheroid cells treated with or without 100 μmol/L Co(III)hexamine, 200 μmol/L 2-aminoethyl diphenylborinate, or 10 μmol/L Mesendogen. SP: Spheroid; Co(III)hex: Co(III)hexamine; 2-APB: 2-aminoethyl diphenylborinate; ME: Mesendogen; COX-2: Cyclooxygenase-2; MMP-9: Matrix metalloproteinase-9. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs the control spheroid group (n = 6).
- Citation: Kampuang N, Chamniansawat S, Pongkorpsakol P, Treveeravoot S, Thongon N. Transient receptor potential melastatin 6 and transient receptor potential melastatin 6/7 antagonists suppress colon adenocarcinoma HT-29 cells. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(12): 110736
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i12/110736.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i12.110736