©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Aug 15, 2024; 16(8): 3559-3584
Published online Aug 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i8.3559
Published online Aug 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i8.3559
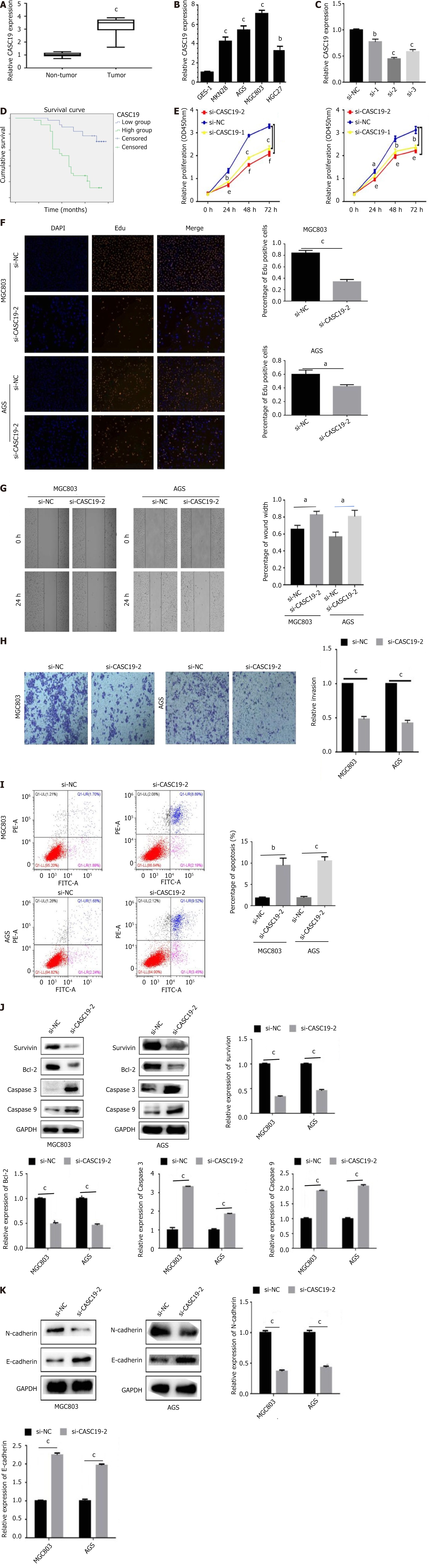
Figure 1 The clinical and biological function of CASC19 in gastric cancer.
A: The expression of CASC19 in cancer tissues and adjacent tissues of 72 gastric cancer patients were measured by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; B: The expression level of CASC19 in gastric cancer cell lines and GES-1 was measured; C: The transfection result of si-CASC19-1, si-CASC19-2, si-CASC19-3 into MGC803 cells and AGS cell lines; D: The K-M survival curve of high CASC19 group and low groups; E: The effect of si-CASC19-2 on cell proliferation was detected by cell counting kit-8; F: The effect of si-CASC19-2 on cell proliferation was detected by ethynyldeoxyuridine; G: The result of wound healing assay after inhibiting CASC19; H: The invasive ability of MGC803 and AGS cells after inhibiting CASC19 by transwell; I: The cell apoptosis result after knockdown of CASC19 by flow cytometry; J: The level of apoptosis-related proteins were detected by Western blot experiment; K: The level of epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related proteins was examined by western blot. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, eP < 0.01, fP < 0.001 was compared with the control group respectively. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
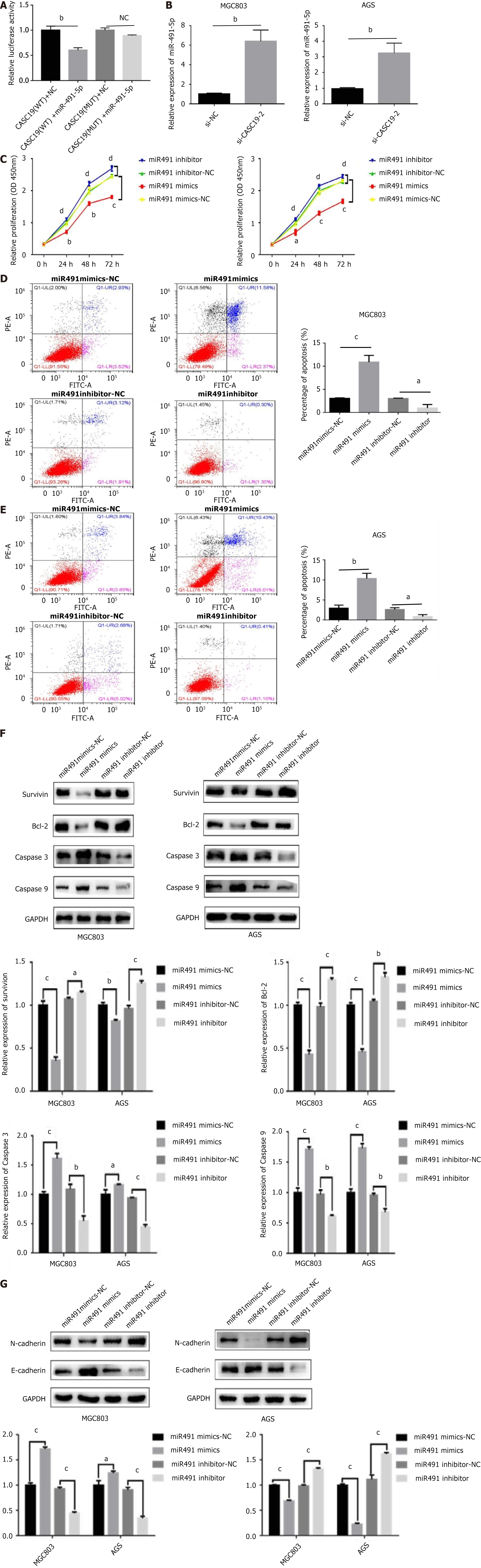
Figure 2 The effect of miR-491-5p in gastric cancer.
A: The targeting relationship between CASC19 and miR-491-5p by dual luciferase reporter experiments; B: The expression of miR-491-5p after knock down of CASC19; C: The effect of miR-491-5p on the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by cell counting kit-8 assay; D and E: The consequence of apoptosis result by miR-491-5p mimics and miR-491-5p inhibitor; F: The change of apoptosis-related proteins by miR-491-5p mimics and miR-491-5p inhibitor through western blot experiment; G: The change of epithelial-mesenchymal transition proteins by miR-491-5p mimics and miR-491-5p inhibitor through western blot experiment. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.05 was compared with the control group respectively. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
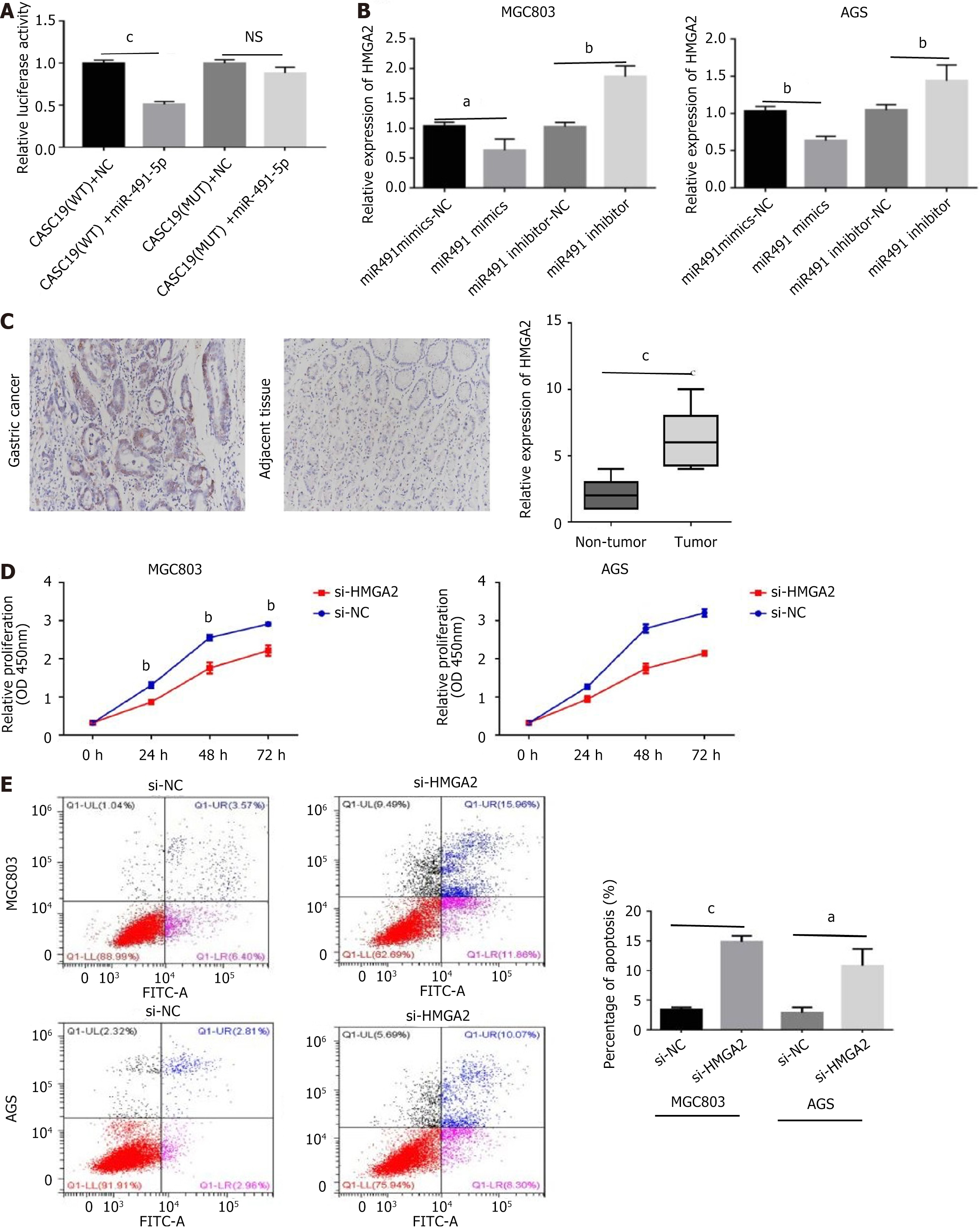
Figure 3 The role of HMGA2 in gastric cancer.
A: The targeting relationship between miR-491-5p and HMGA2 by the dual luciferase reporter experiment; B: The expression of HMGA2 affected by miR-491-5p mimics and miR-491-5p inhibitor through reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; C: The immunohistochemical staining of cancer and adjacent tissue; D: The effect of HMGA2 on cell proliferation was detected by cell counting kit-8 assay; E: Flow cytometry was used to explore the regulation of HMGA2 about apoptosis. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 was compared with the control group respectively. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
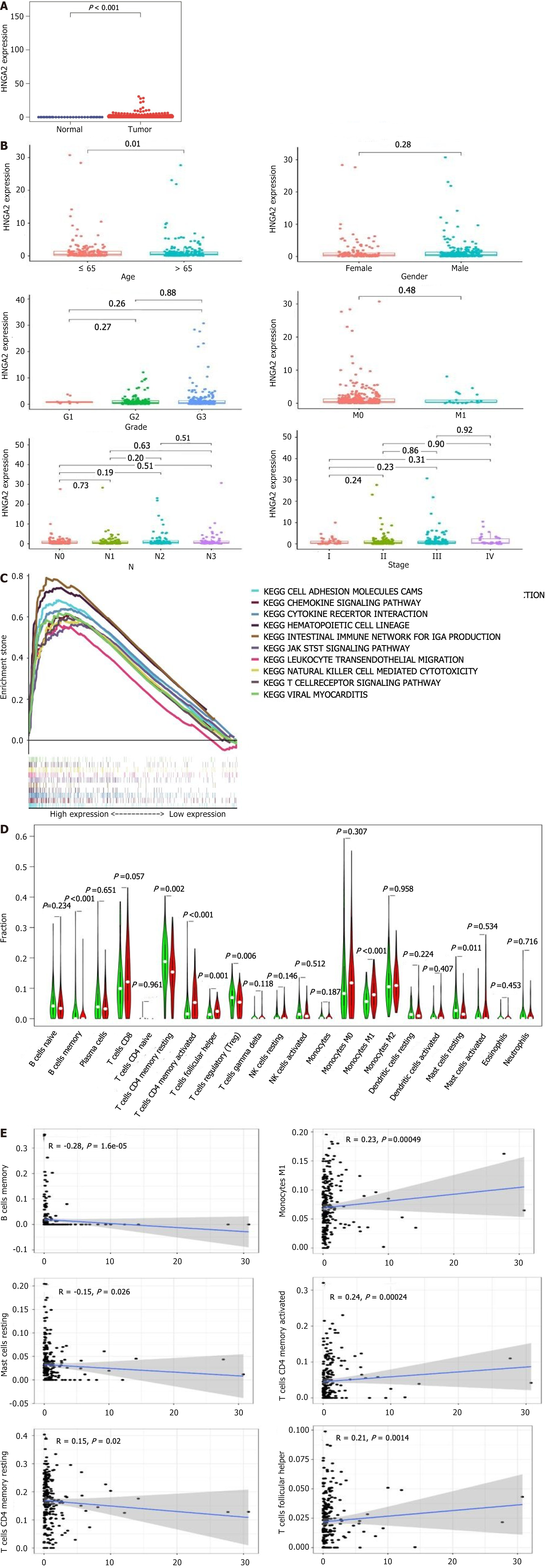
Figure 4 The value of HMGA2 in The Cancer Genome Atlas data.
A: The expression of HMGA2 in the gastric cancer tumor group and the normal group in the TCGA database; B: The relationship between HMGA2 and the clinical information of patients; C: The gene enrichment analysis of HMGA2; D and E: The correlation between HMGA2 and immune cell level was analyzed.
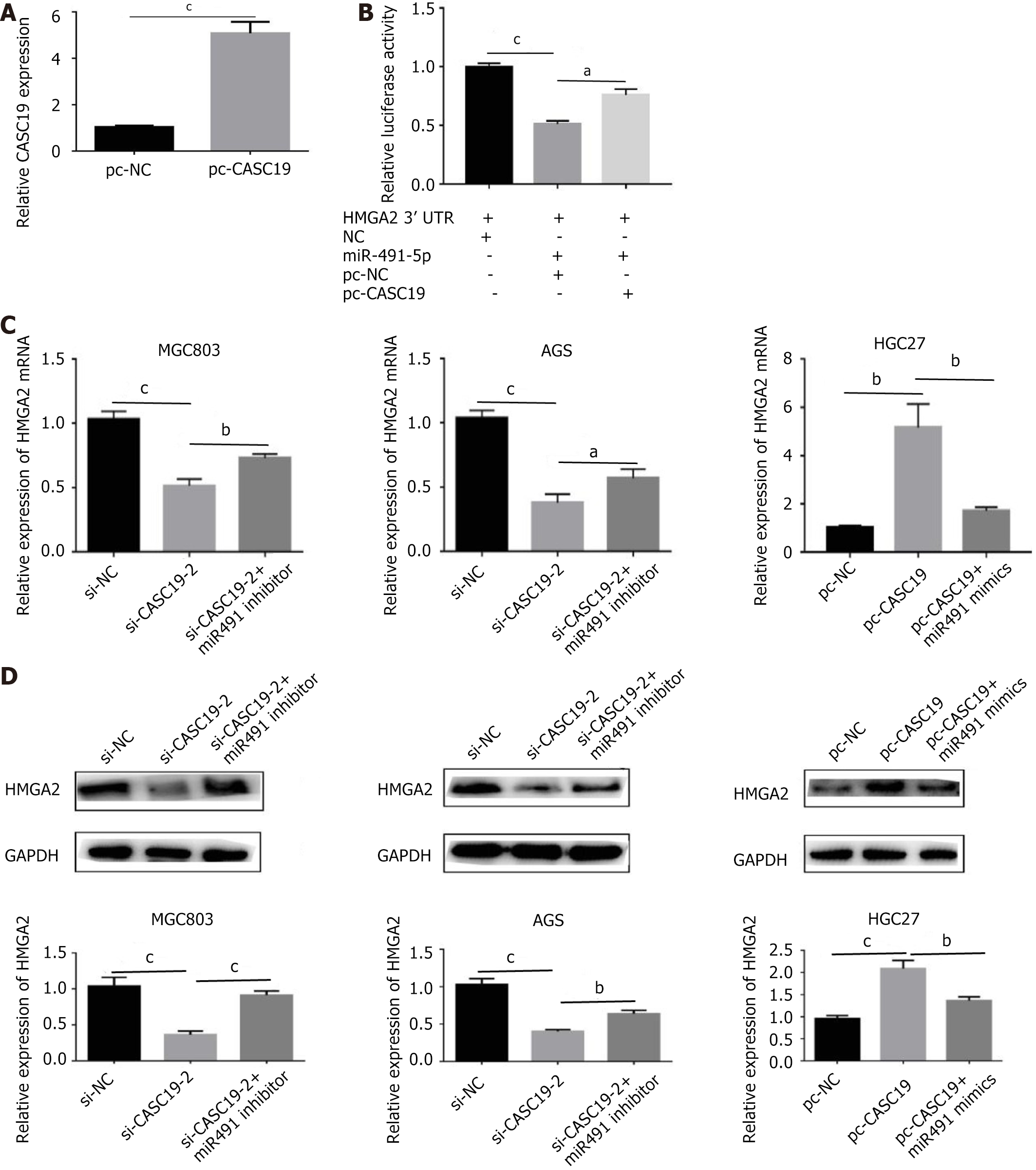
Figure 5 The regulatory relationship between CASC19, miR-491-5p and HMGA2 in vitro.
A: The CASC19 expression of pc-CASC19 (over-expression vector) in HGC27 cell lines; B: The relative inhibition of luciferase expression of the miR-491-5p containing HMGA2 3’UTR co-transfected with pc-CASC19 or pc-NC in 293T cells; C and D: The expression of HMGA2 detected by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and western blot, MGC803 and AGS were transfected with si-NC, si-CASC19-2, co-transfected with si-CASC19-2 and miR-491 inhibitor, respectively, the HGC27 cells were transfected with pc-NC, pc-CASC19, co-transfected with pc-CASC19 and miR-491 mimics, respectively. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 was compared with the control group respectively. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
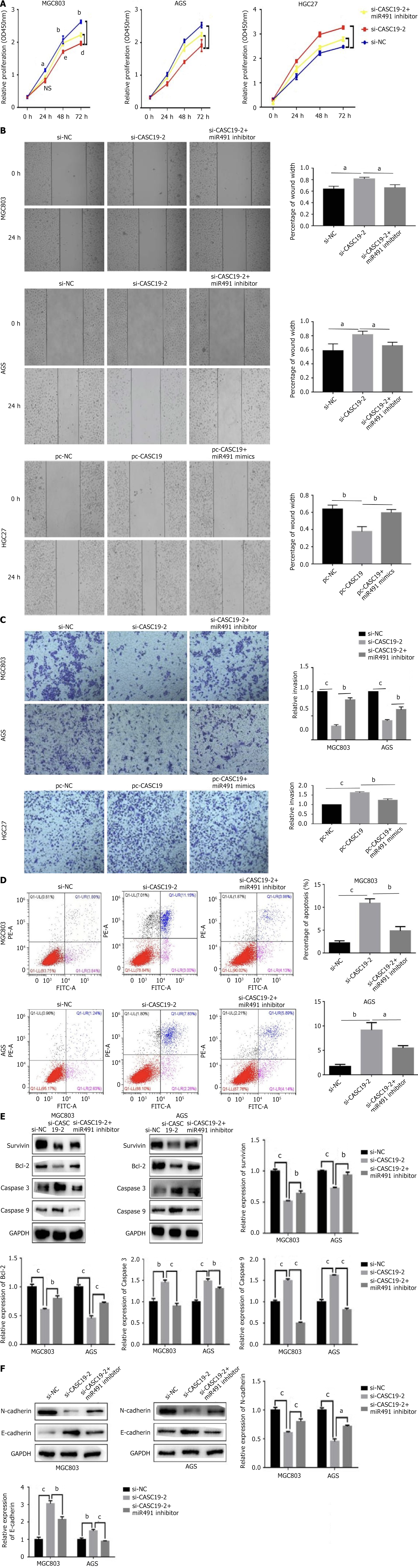
Figure 6 The ability of miR-491-5p to rescue CASC19 in gastric cancer cells.
A: The cell proliferation ability was detected by cell counting kit-8; B: The migration ability of cells was detected by wound healing assay; C: The invasion ability of cells was detected by transwell; D: Flow cytometry was used to detect cell apoptosis; E: The level of apoptosis-related proteins were detected by western blot experiment; F: The level of epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related proteins was detected by western blot experiment. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.05, eP < 0.01 was compared with the control group respectively, P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
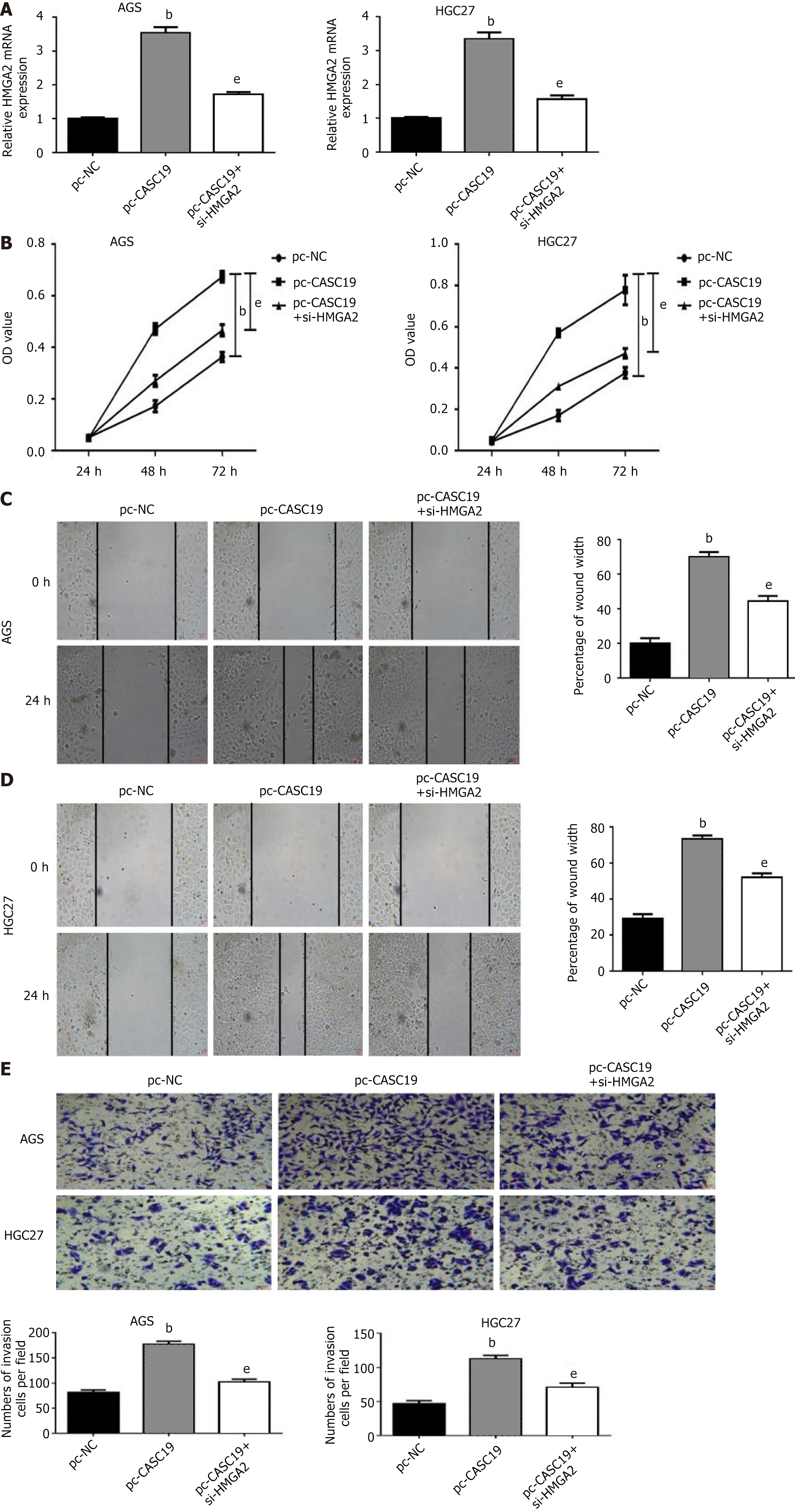
Figure 7 HMGA2 can rescue the biological behavior of CASC19 in gastric cancer cells.
A: Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction revealed the expression of HMGA2; B: Cell proliferation was detected by cell counting kit-8; C and D: The migration ability of AGS and HGC27 cells was detected by wounding assay; E: The invasive ability of the cells was detected by transwell. bP < 0.01, eP < 0.01 was compared with the control group respectively. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
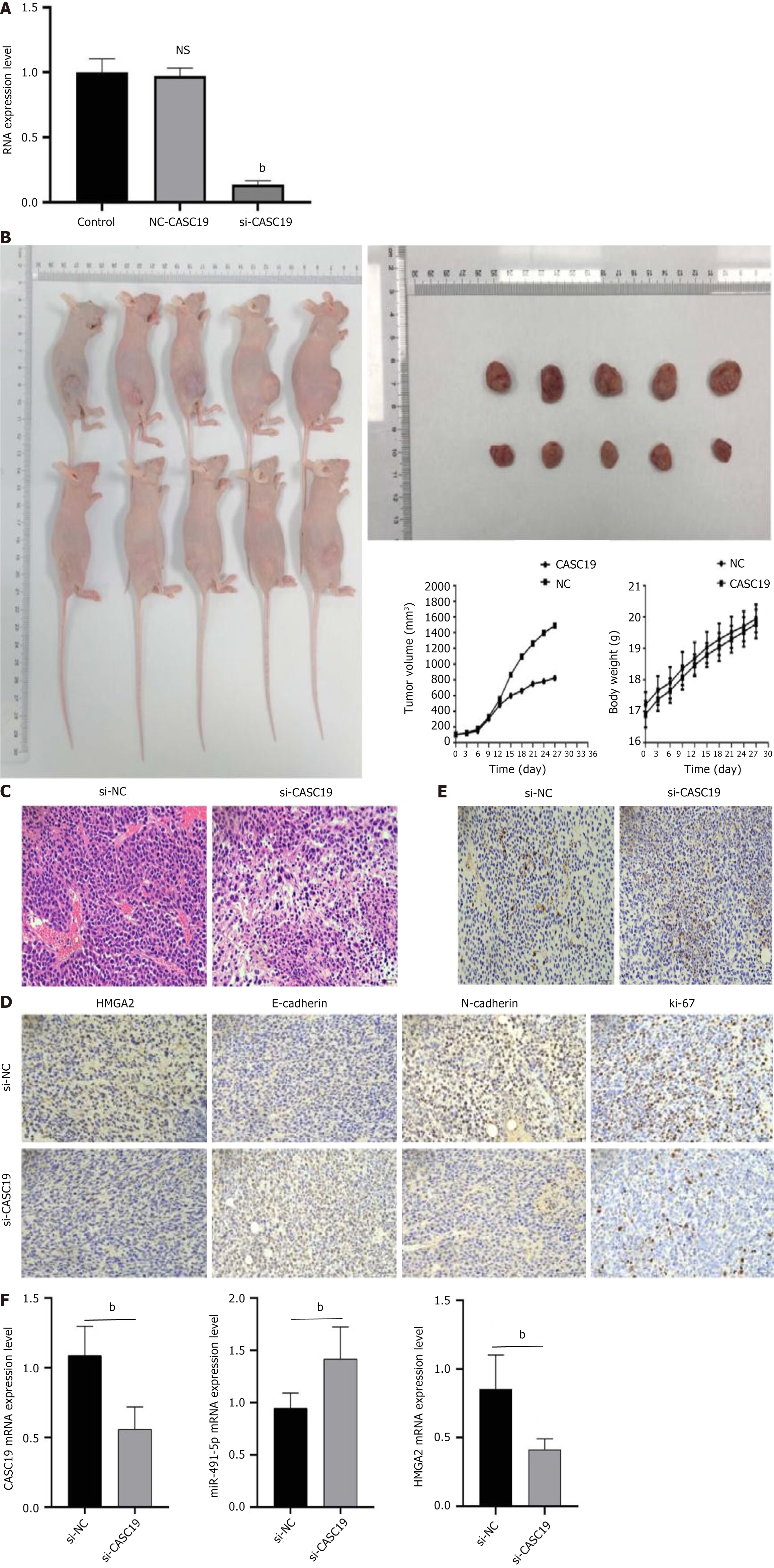
Figure 8 The oncogenic mechanism of CASC19 to gastric cancer in vivo.
A: The efficiency of lentivirus silencing CASC19 was verified by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR); B: The tumor growth rate of the CASC19 silencing lentivirus infection group was slower, and the tumor weight was significantly smaller than that of the negative control group; C: The hematoxylin and eosin staining of the tumor; D: Tumors were stained with TUNEL; E: The tumor was subjected to immunohistochemical staining; F: RT-PCR was performed on the tumor to examine the expression levels of CASC19, miR-491-5p, and HMGA2. bP < 0.05 was compared with the control group and P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
- Citation: Zhang LX, Luo PQ, Wei ZJ, Xu AM, Guo T. Expression and significant roles of the long non-coding RNA CASC19/miR-491-5p/HMGA2 axis in the development of gastric cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(8): 3559-3584
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i8/3559.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i8.3559