©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Apr 15, 2024; 16(4): 1500-1513
Published online Apr 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i4.1500
Published online Apr 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i4.1500
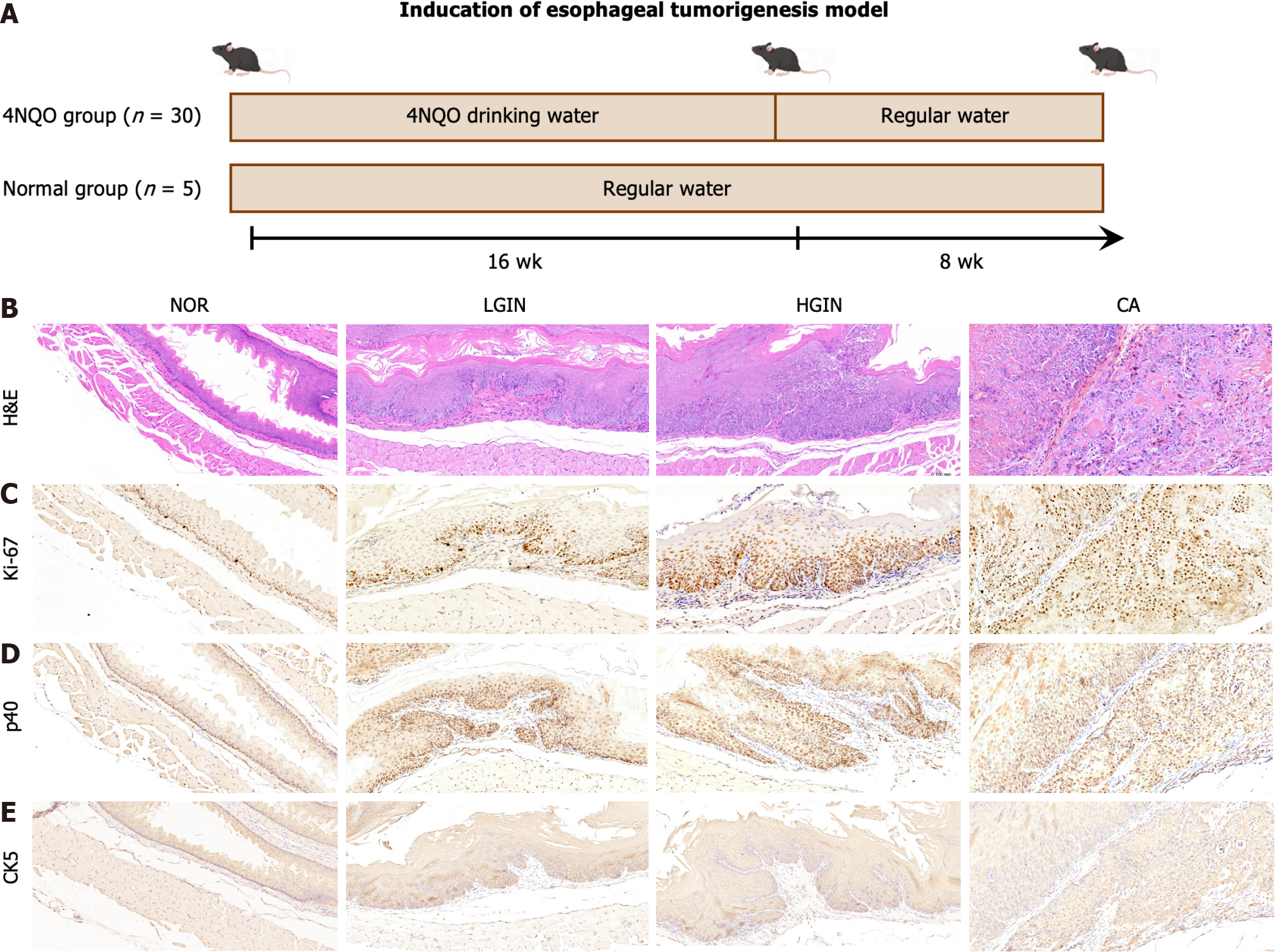
Figure 1 Development of esophageal tumor.
A: The scheme of the induction for esophageal tumorigenesis model; B-E: Hematoxylin-eosin staining and expression of Ki67, p40, and CK5 were showed at multi-stage of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma development including normal, low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia, high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia, and carcinoma. 4NQO: 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide; HE: Hematoxylin-eosin; LGIN: Low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia; HGIN: High-grade intraepithelial neoplasia; CA: Carcinoma; NOR: Normal.
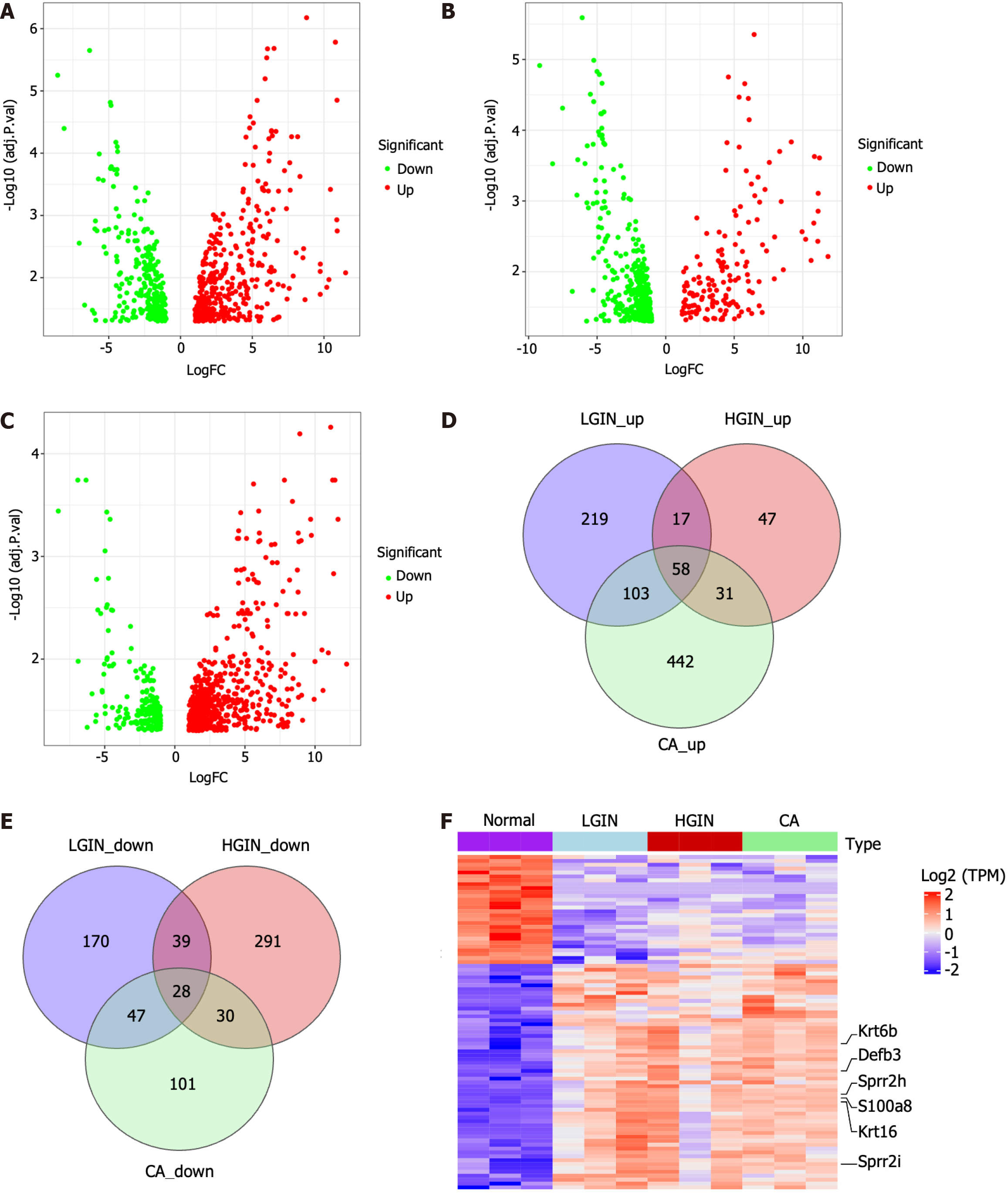
Figure 2 Differentially expressed gene analysis and identification of key genes in development of esophageal carcinogenesis.
A-C: The volcano plots show the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) for low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia, high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia, and carcinoma (CA) compared to the normal, respectively; D and E: Venn diagrams of up-regulated and down-regulated DEGs; F: Heatmap of the 86 key genes. LGIN: Low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia; HGIN: High-grade intraepithelial neoplasia; CA: Carcinoma; NOR: Normal; TPM: Transcript per Kilobase per Million mapped reads.
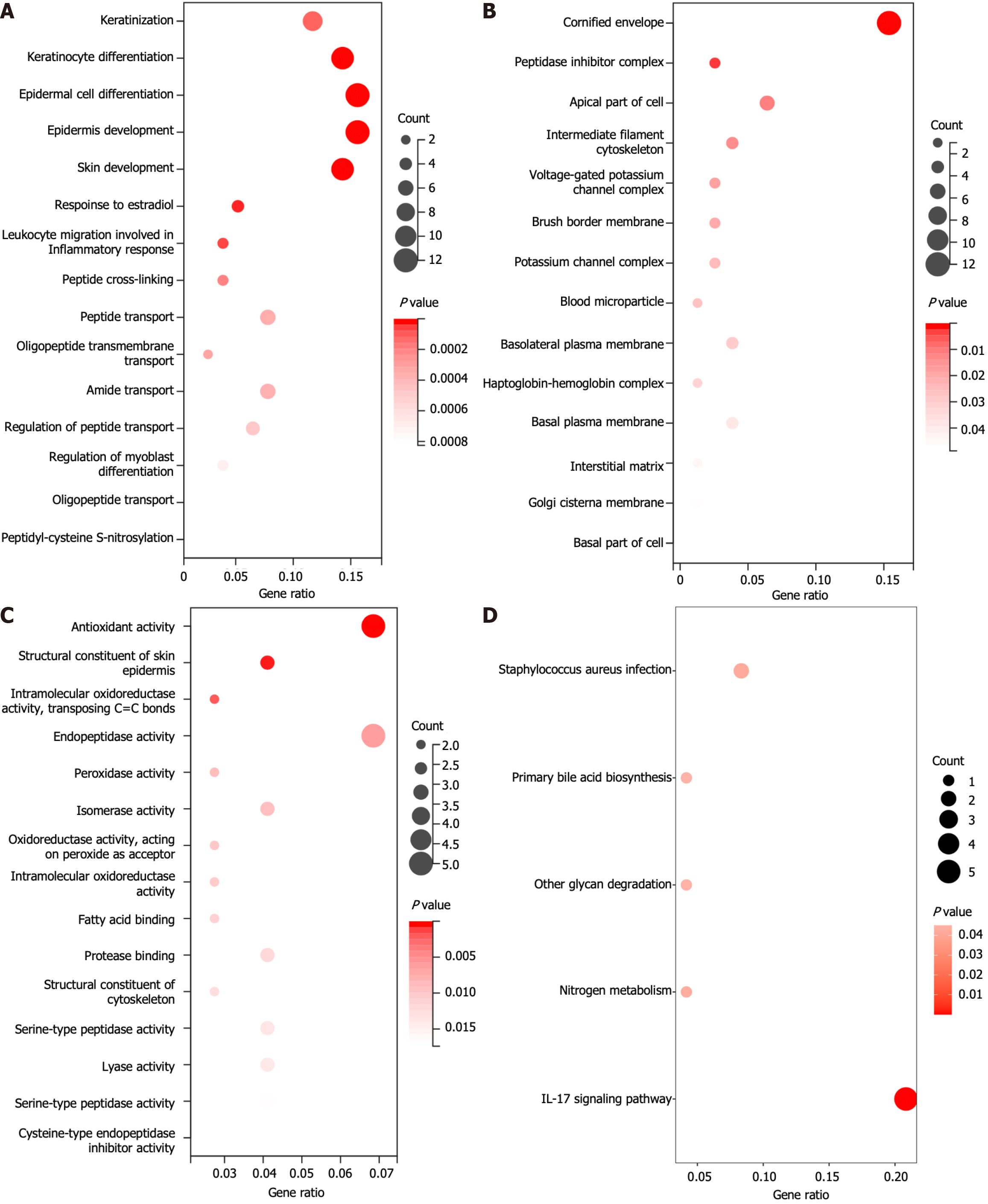
Figure 3 Functional enrichment analysis of key genes.
A: Biological process terms; B: Cellular component terms; C: Molecular function terms; D: Kyoto Genome Encyclopedia signaling pathway terms. IL: Interleukin.
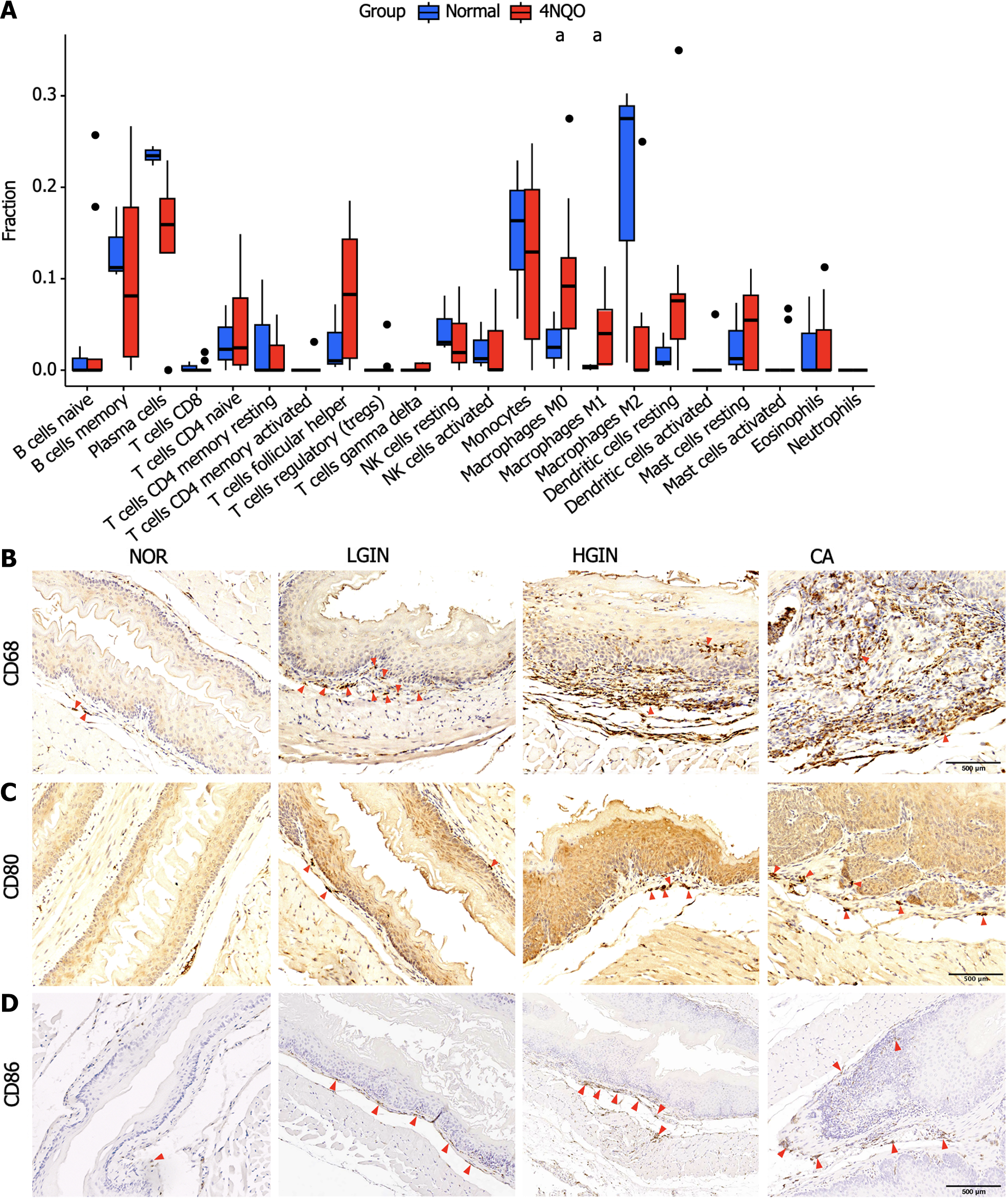
Figure 4 The immune infiltration pattern of the 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide group compared to the normal group.
A: Fraction of immune cell infiltration in 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide (4NQO) carcinogenic intervention and normal (NOR) groups based on CIBERSORT algorithm; B-D: Expression of M0 (CD68) and M1 (CD80 and CD86) macrophage markers in NOR and 4NQO groups including low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia, high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia, and carcinoma. aP < 0.05. LGIN: Low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia; HGIN: High-grade intraepithelial neoplasia; CA: Carcinoma; NK: Natural killer.
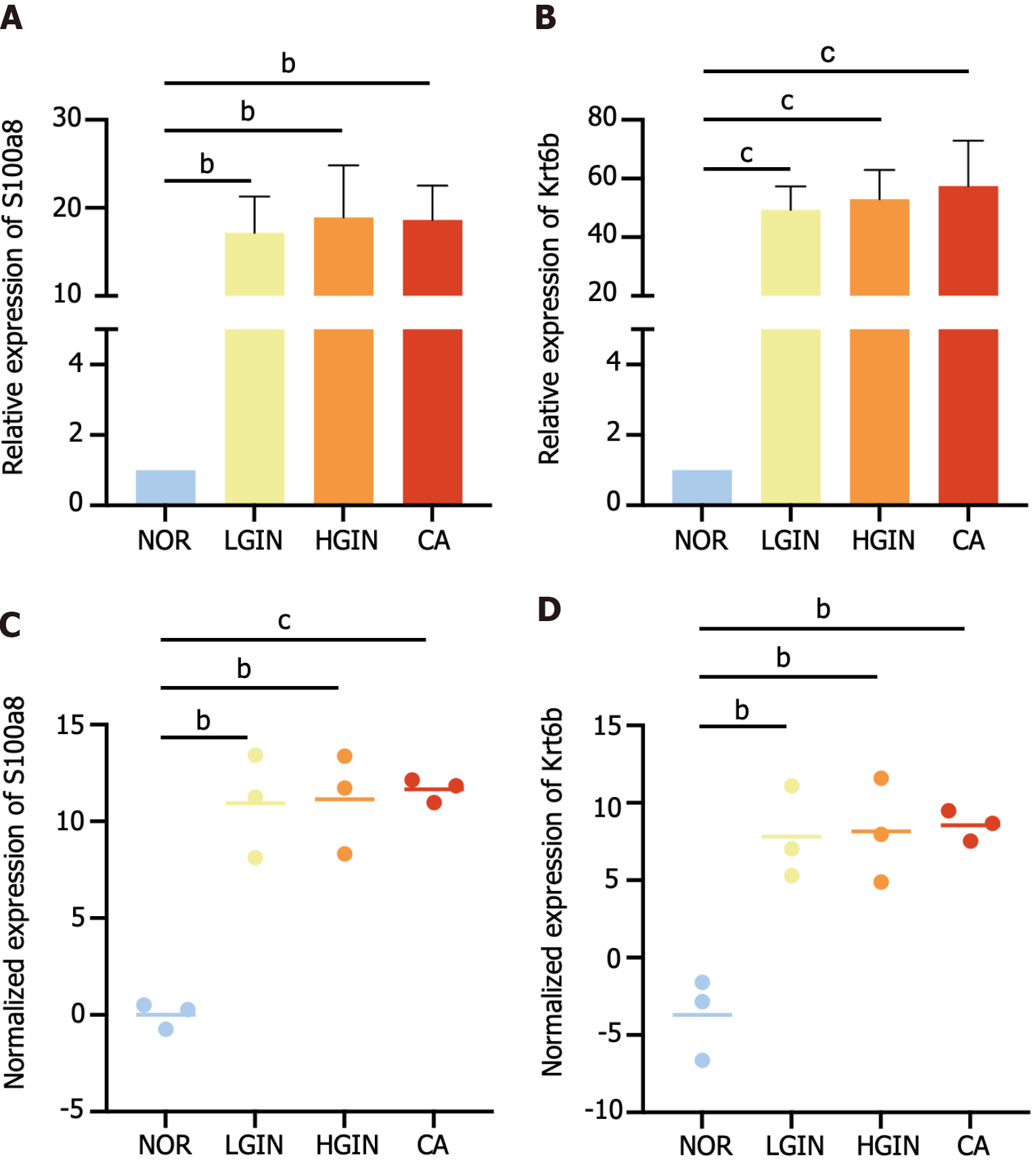
Figure 5 Expression of S100a8 and Krt6b at the transcriptional level.
A and B: Expression of S100a8 and Krt6b were validated by relative quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; C and D: Expression of S100a8 and Krt6b in transcriptome sequencing. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. Low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia; HGIN: High-grade intraepithelial neoplasia; CA: Carcinoma; NOR: Normal.
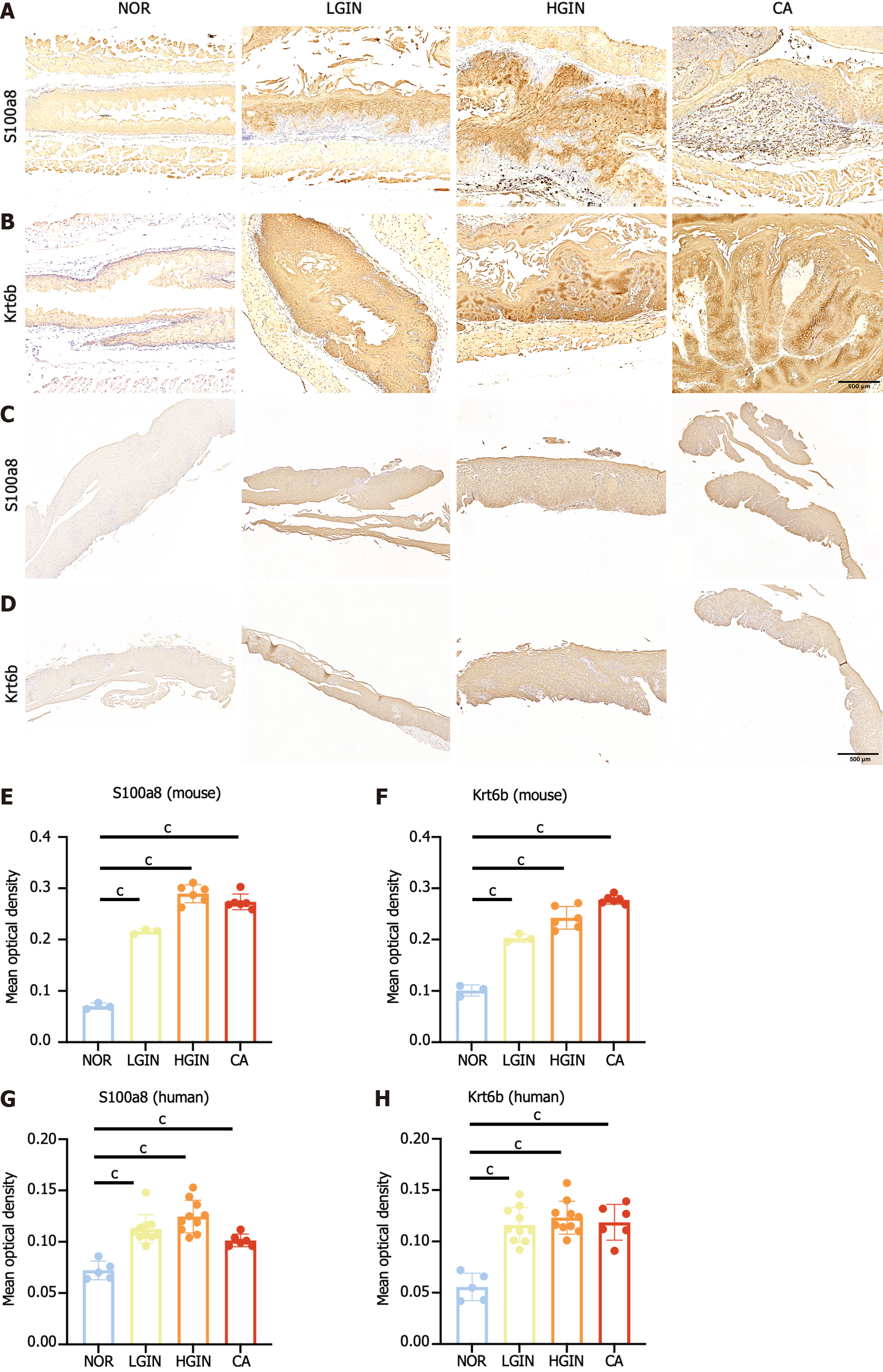
Figure 6 Validation of S100a8 and Krt6b.
A and B: Protein expression of S100a8 and Krt6b in mouse; C and D: Validation of the protein expression of S100a8 and Krt6b in human samples; E-H: Quantitative analysis of immunohistochemical results of s100a8 and krt6b in mouse and human samples. cP < 0.001. Low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia; HGIN: High-grade intraepithelial neoplasia; CA: Carcinoma; NOR: Normal.
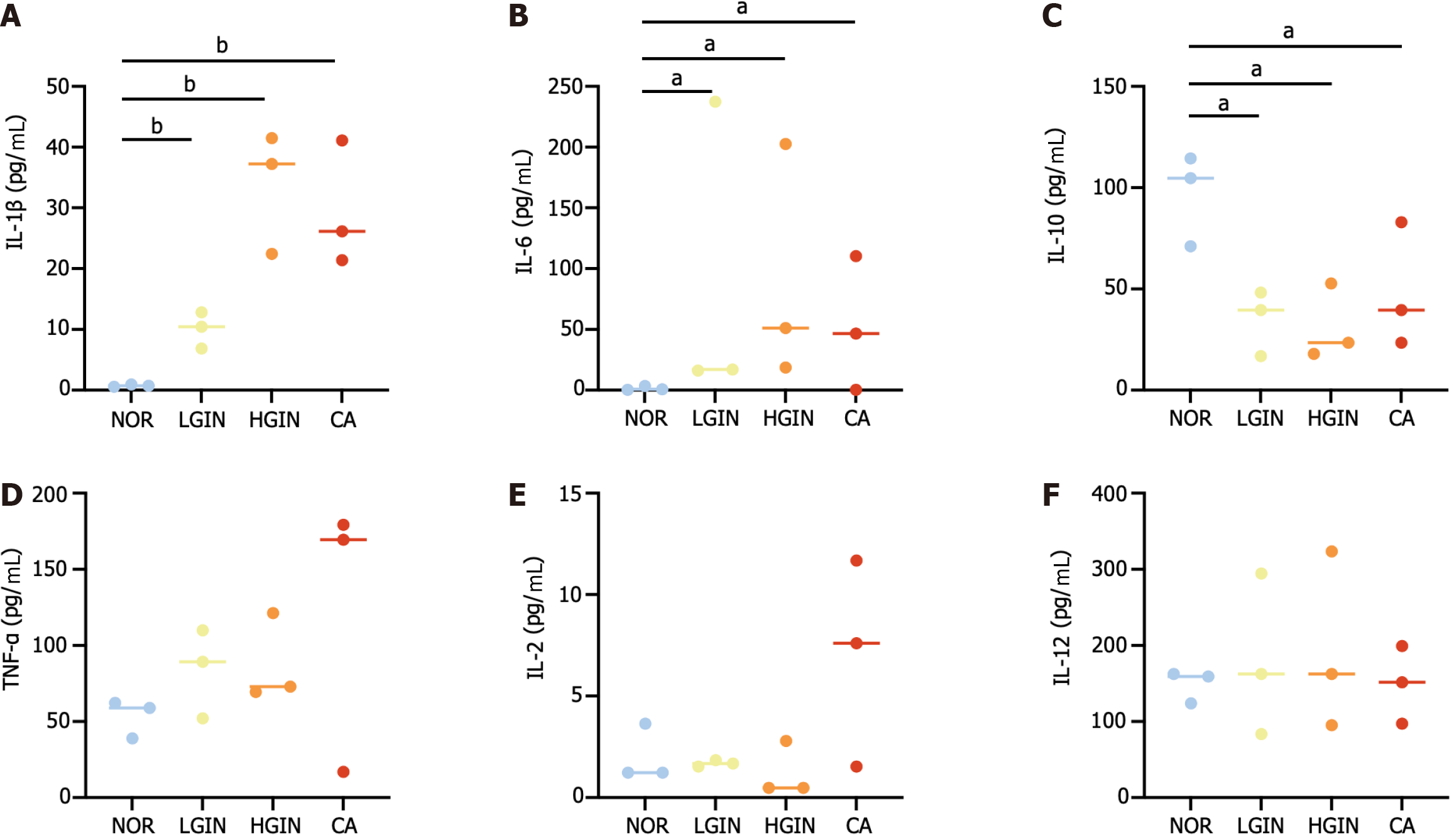
Figure 7 Expression of serum cytokines.
A-F: Expression of inflammation-associated cytokines including interleukin (IL)-1β, IL6, IL-10, tumor necrosis factor-α, IL-2, and IL-12. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. Low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia; HGIN: High-grade intraepithelial neoplasia; CA: Carcinoma; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor.
- Citation: Sun JR, Chen DM, Huang R, Wang RT, Jia LQ. Transcriptome sequencing reveals novel biomarkers and immune cell infiltration in esophageal tumorigenesis. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(4): 1500-1513
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i4/1500.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i4.1500