©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jun 15, 2023; 15(6): 988-1004
Published online Jun 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i6.988
Published online Jun 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i6.988
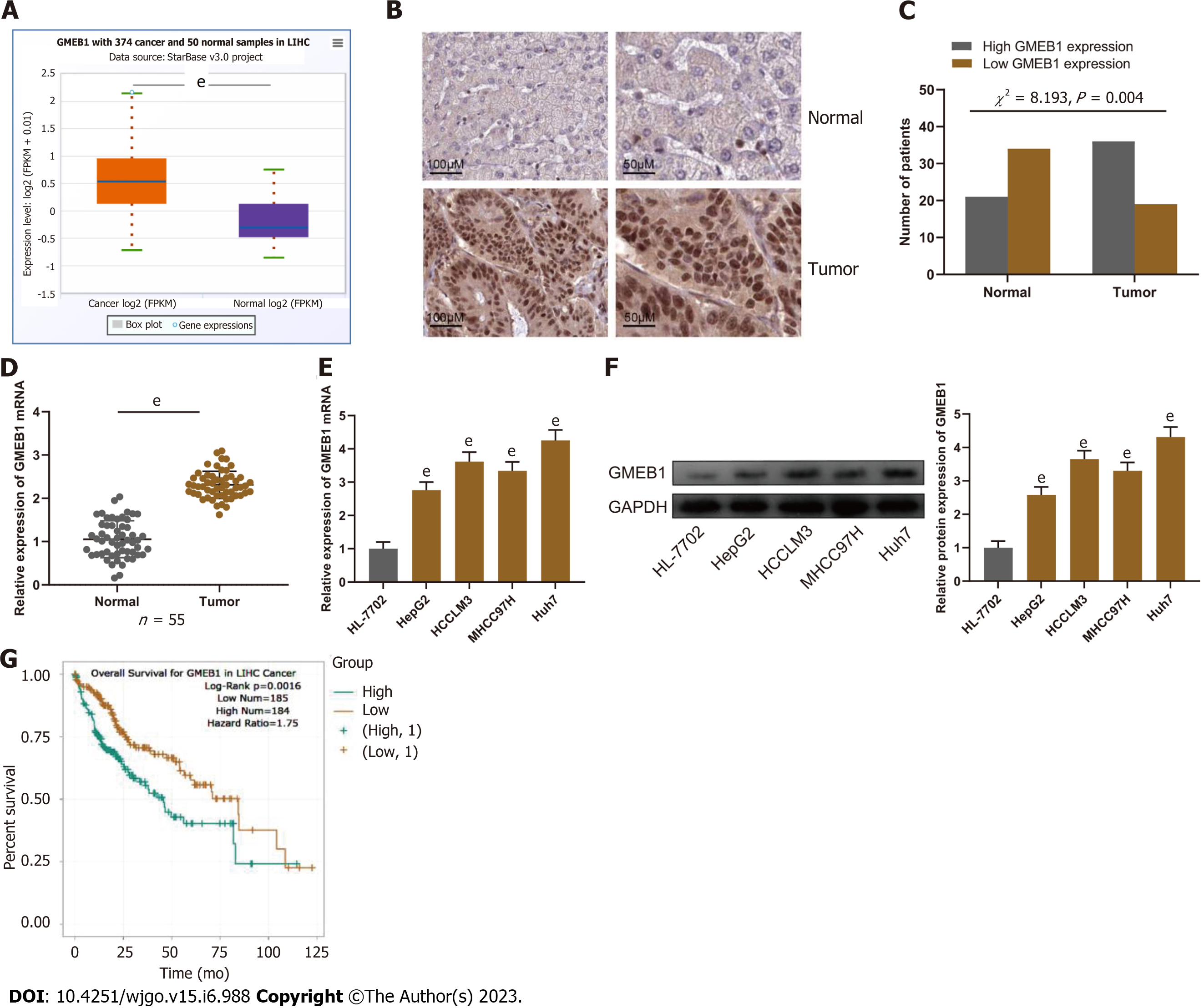
Figure 1 Glucocorticoid modulatory element-binding protein 1 is highly expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: StarBase database (http://starbase.sysu.edu.cn/) analysis of glucocorticoid modulatory element-binding protein 1 (GMEB1) expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues. B: Immunohistochemical assay was conducted to detect GMEB1 expression in HCC and para-cancerous tissues. C: IHC scores of GMEB1 expression in HCC and para-cancerous tissues. D and E: Detection by qRT-PCR of GMEB1 mRNA expression in HCC and para-cancer tissues, as well as in HCC cells (HepG2, HCCML3, MHCC97H and Huh7) and normal human hepatocytes (HL-7702). F: Detection by Western blot of GMEB1 protein expression in HCC cells and HL-7702 hepatocytes. G: The StarBase database analysis of the relationship between GMEB1 expression and HCC patients’ overall survival. eP < 0.001. GMEB1: Glucocorticoid modulatory element-binding protein 1; YAP1: Yes-associate protein 1.
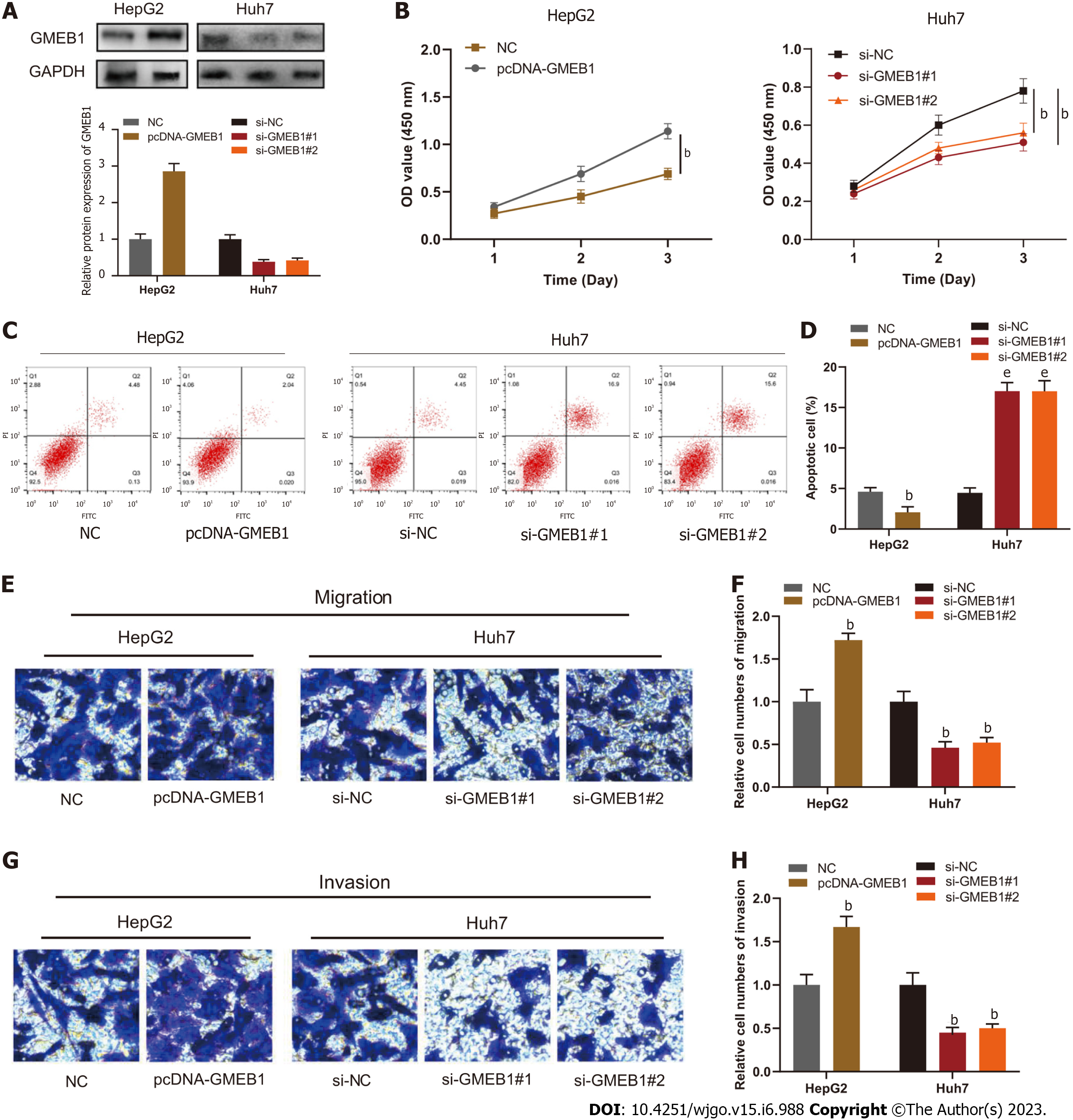
Figure 2 Biological functions of glucocorticoid modulatory element-binding protein 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: Western blotting was utilized to detect glucocorticoid modulatory element-binding protein 1 (GMEB1) expression in HepG2 cells transfected with GMEB1 overexpression plasmids and Huh7 cells transfected with si-GMEB1#1 and si-GMEB1#2; B: Evaluation of cell proliferation by the CCK-8 method; C and D: Detection of cell apoptosis via flow cytometry. E and F: Transwell assays were carried out to detect cell migration; G and H: Transwell assays were carried out to detect cell invasion. bP < 0.01; and eP < 0.001. GMEB1: Glucocorticoid modulatory element-binding protein 1; YAP1: Yes-associate protein 1.
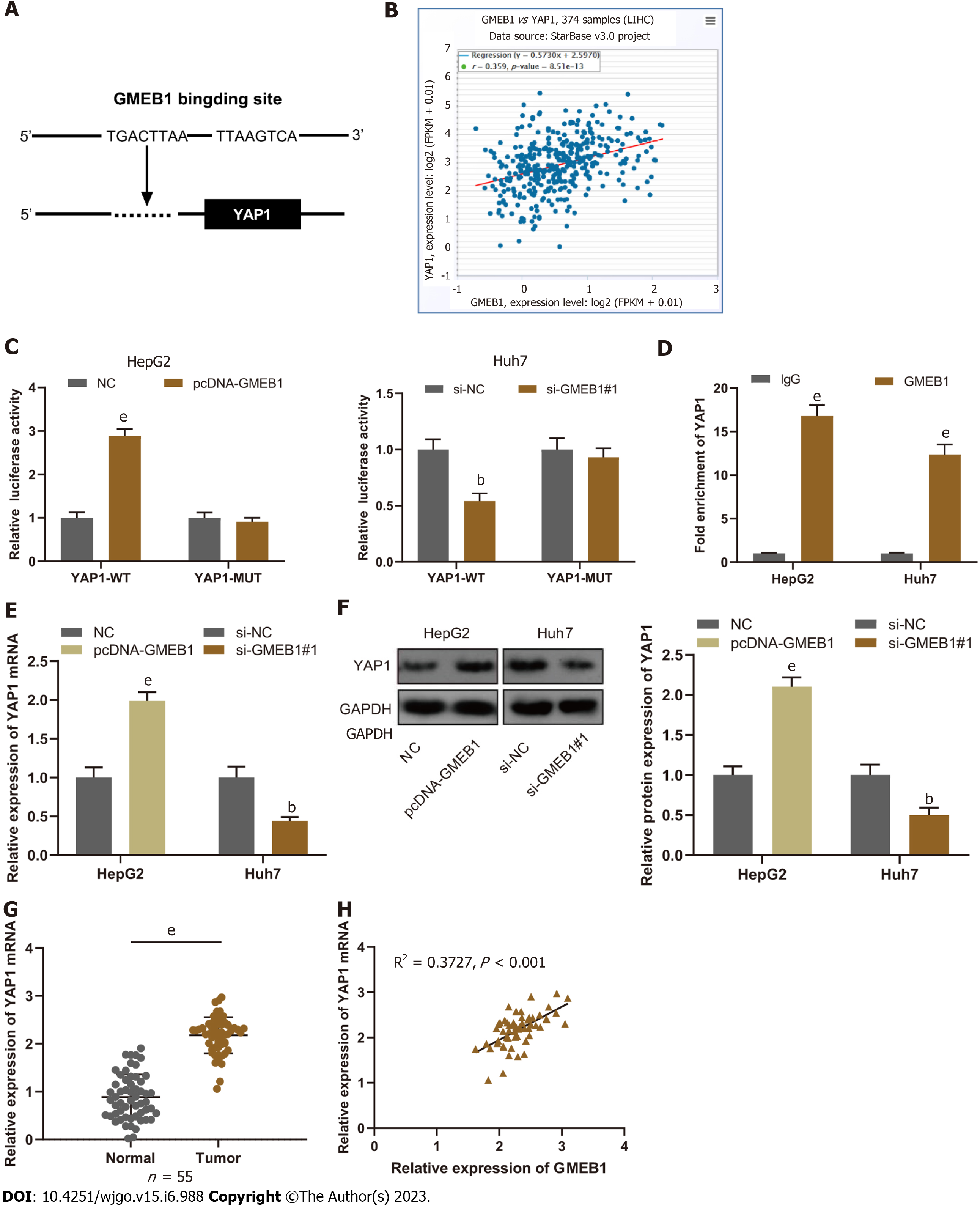
Figure 3 Glucocorticoid modulatory element-binding protein 1 targets and binds to Yes-associate protein 1.
A: The JASPR database (http://jaspar.genereg.net/) was employed to predict the binding site of glucocorticoid modulatory element-binding protein 1 (GMEB1) and Yes-associate protein 1 (YAP1) promoter region. B: The StarBase database was employed to analyze the correlation between GMEB1 and YAP1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues. C: Verification by dual-luciferase reporter gene assay of the binding relationship between GMEB1 and YAP1 promoter sequence. D: Detection via ChIP-qPCR assay of the binding of GMEB1 to the YAP1 promoter region. E and F: qRT-PCR and Western blotting were conducted to detect the effects of GMEB1 overexpression or knockdown on YAP1 mRNA and protein expression in HepG2 and Huh7 cells. G: Detection of YAP1 mRNA expression in HCC and para-tumorous tissues by qRT-PCR. H: Pearson correlation analysis of the correlation between GMEB1 mRNA and YAP1 mRNA expression in 55 cases of HCC tissues. bP < 0.01; and eP < 0.001. GMEB1: Glucocorticoid modulatory element-binding protein 1; YAP1: Yes-associate protein 1.
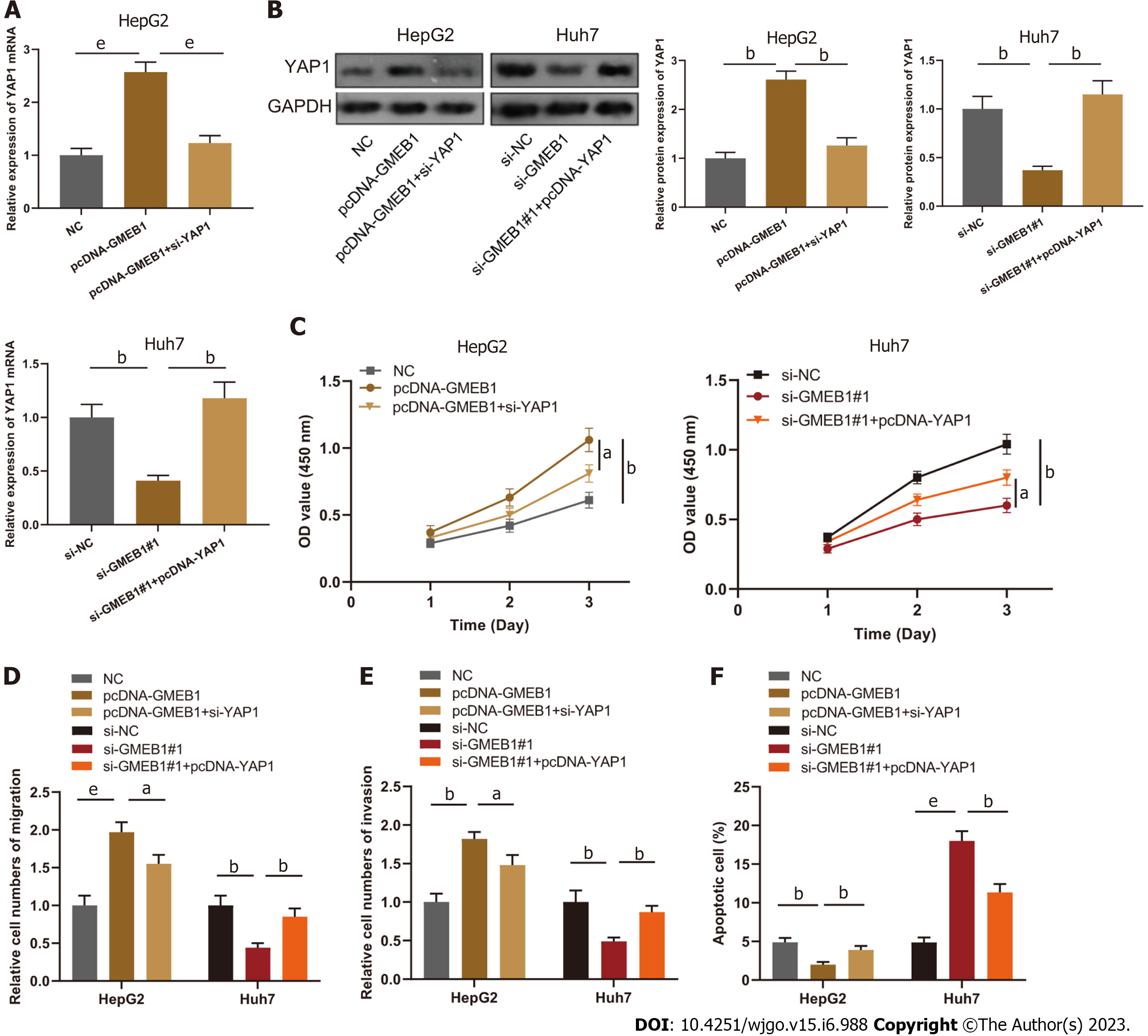
Figure 4 Effects of the interaction between glucocorticoid modulatory element-binding protein 1 and Yes-associate protein 1 on the biological functions of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
A and B: qRT-PCR and Western blot were utilized to detect YAP1 mRNA and protein expression in HepG2 cells transfected with NC, pcDNA-GMEB1, pcDNA-GMEB1+si-YAP1 and Huh7 cells transfected with si-NC, si-GMEB1#1, si-GMEB1#1+pcDNA-YAP1. C: Evaluation of HepG2 and Huh7 cell proliferation after transfection through the CCK-8 method. D and E: Transwell assays were conducted to detect HepG2 and Huh7 cell migration and invasion after transfection. F: Detection of HepG2 and Huh7 cell apoptosis after transfection via flow cytometry. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; and eP < 0.001. GMEB1: Glucocorticoid modulatory element-binding protein 1; YAP1: Yes-associate protein 1.
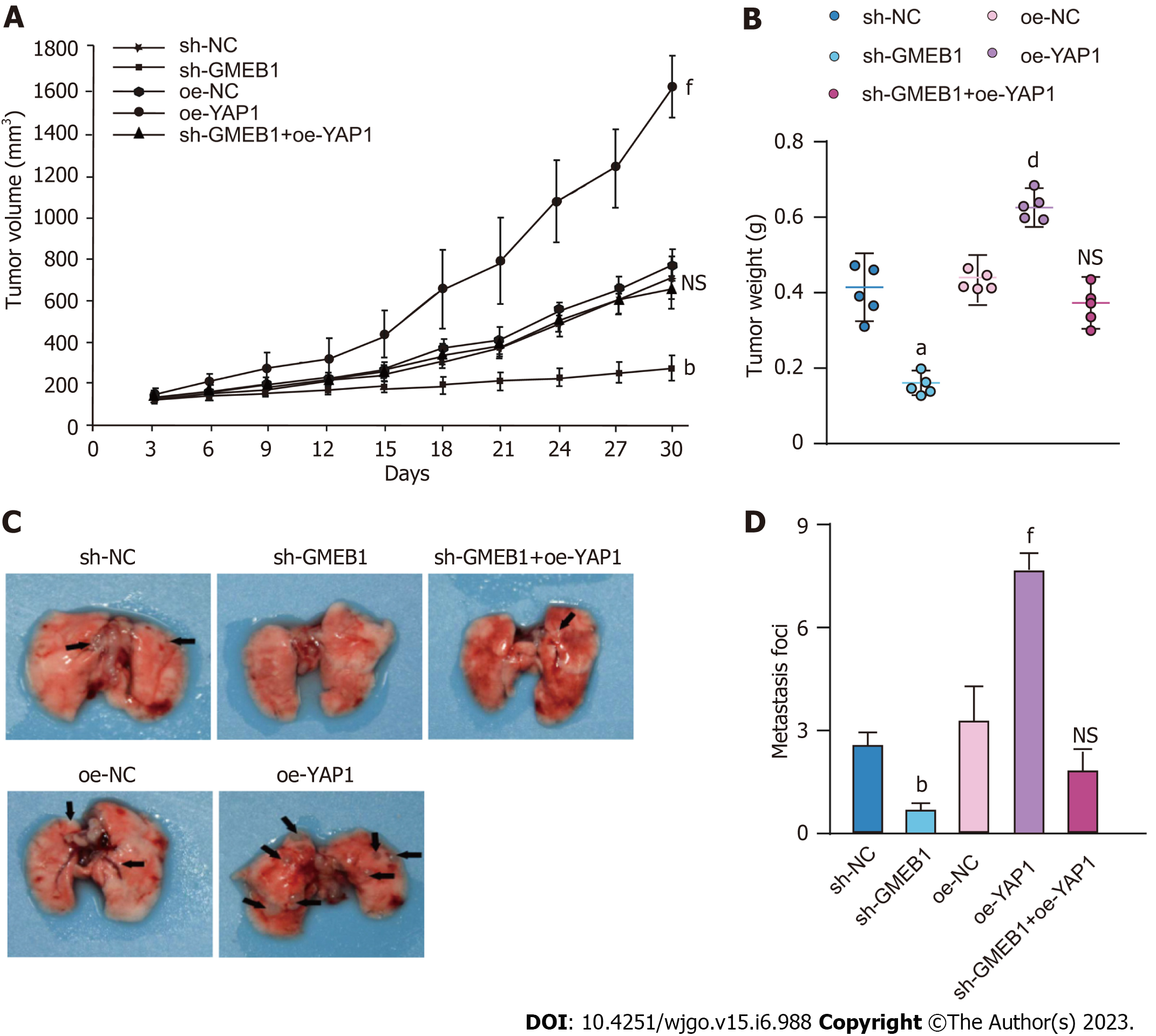
Figure 5 Effects of the interaction between glucocorticoid modulatory element-binding protein 1 and Yes-associate protein 1 on the biological functions of hepatocellular carcinoma CDX mice models.
A and B: HepG2 CDX mice model. Sh-NC, sh-GMEB1, oe-NC, oe-YAP1, sh-GMEB1+oe-YAP1 cells were injected subcutaneously into the right axilla of mice (n = 5/group) and tumor size was measured every 3 d. Tumor volume was calculated using the formula: V = (L x W2)/2. 30 days post injection, mice were sacrificed and tumors were peeled and weighted. C and D: HepG2 metastasis mice model. Sh-NC, sh-GMEB1, oe-NC, oe-YAP1, sh-GMEB1+oe-YAP1 cells were injected into nude mice (n = 5/group) via tail vein, respectively. Mice were sacrificed 60 d after injection, and number of metastatic foci on the lungs of each group were photographed and counted. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, and eP < 0.001 vs sh-NC group; dP < 0.01 and fP < 0.001 vs oe-NC group. NS: Not significant. GMEB1: Glucocorticoid modulatory element-binding protein 1; YAP1: Yes-associate protein 1.
- Citation: Chen C, Lin HG, Yao Z, Jiang YL, Yu HJ, Fang J, Li WN. Transcription factor glucocorticoid modulatory element-binding protein 1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by activating Yes-associate protein 1. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2023; 15(6): 988-1004
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v15/i6/988.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v15.i6.988