©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Aug 15, 2022; 14(8): 1388-1405
Published online Aug 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i8.1388
Published online Aug 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i8.1388
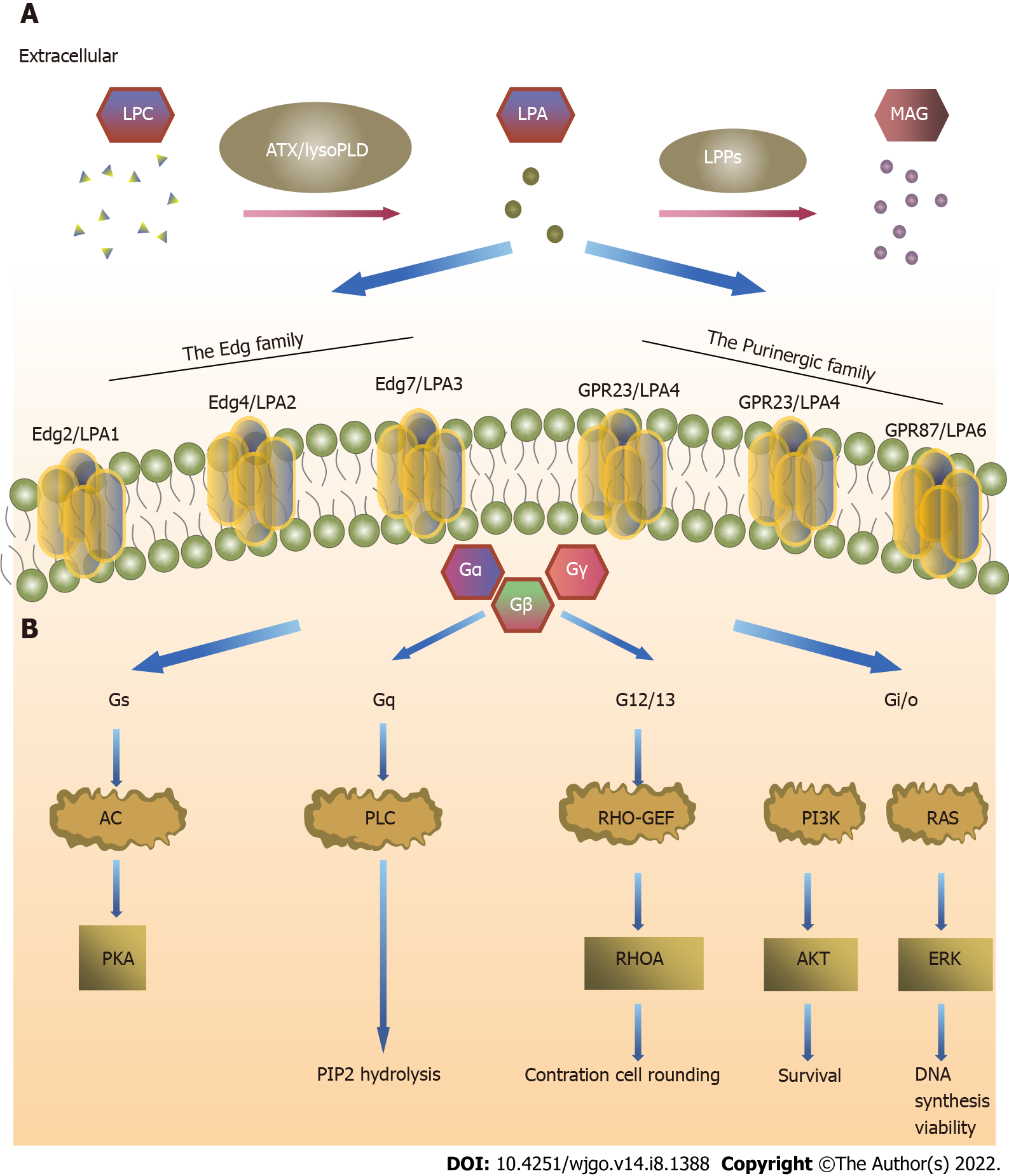
Figure 1 Autotaxin-lysophosphatidic acid axis plays a key role in the pathophysiology of tumor cells.
A: The anabolism and catabolism of tumor extracellular lysophosphatidic acid (LPA). Autotaxin/lysophospholipase D catalyzes the generation of LPA from lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC), and lipid phosphate phosphohydrolases promotes LPC hydrolysis; B: LPA activates multiple pathological processes in tumor cells by binding GPRs (lysophosphatidic acid receptors) to promote tumor occurrence and development. LPC: Lysophosphatidylcholine; LPA: Lysophosphatidic acid; ATX: Autotaxin; Edg: Endothelial cell differentiation gene; LPPs: Lipid phosphate phosphohydrolases; LysoPLD: Lysophospholipase D.
- Citation: Wang S, Chen J, Guo XZ. KAI1/CD82 gene and autotaxin-lysophosphatidic acid axis in gastrointestinal cancers. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022; 14(8): 1388-1405
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v14/i8/1388.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v14.i8.1388