©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Apr 15, 2019; 11(4): 322-334
Published online Apr 15, 2019. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v11.i4.322
Published online Apr 15, 2019. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v11.i4.322
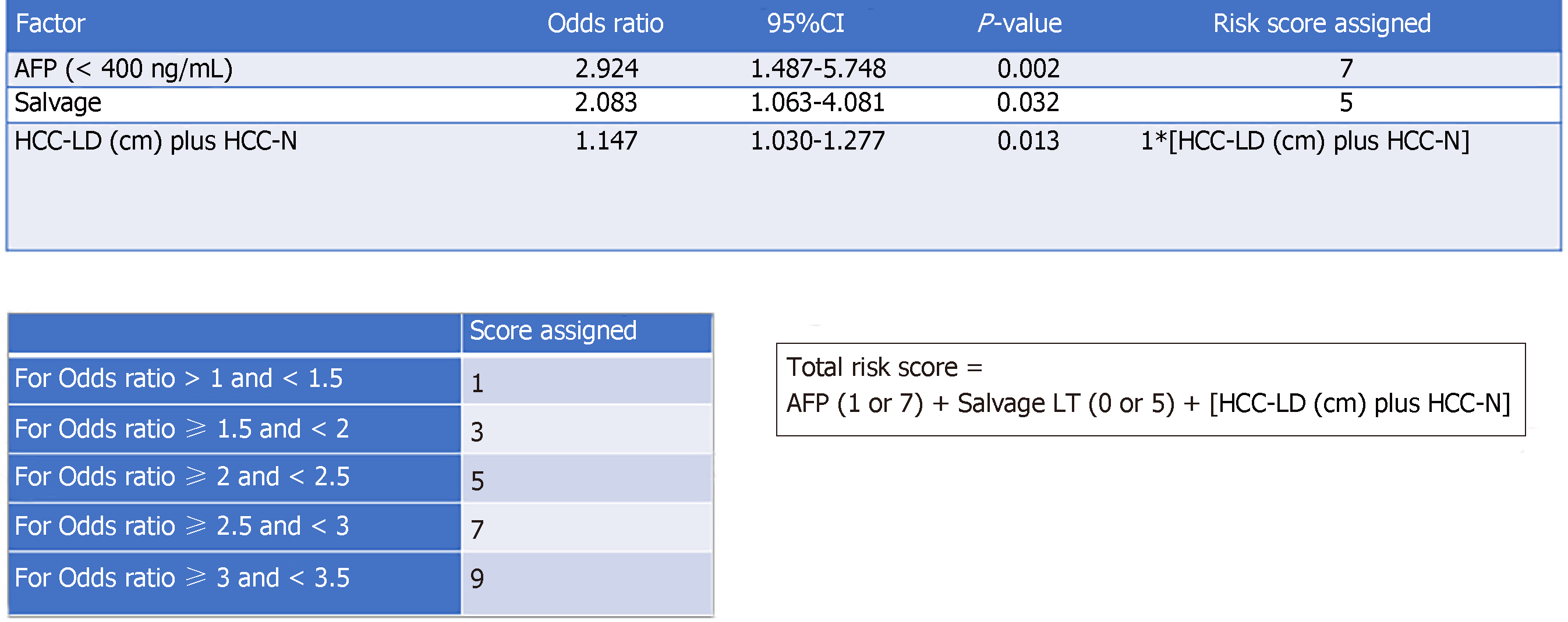
Figure 1 Method of total risk score development.
AFP: Alpha fetoprotein; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; CI: Confidence interval.
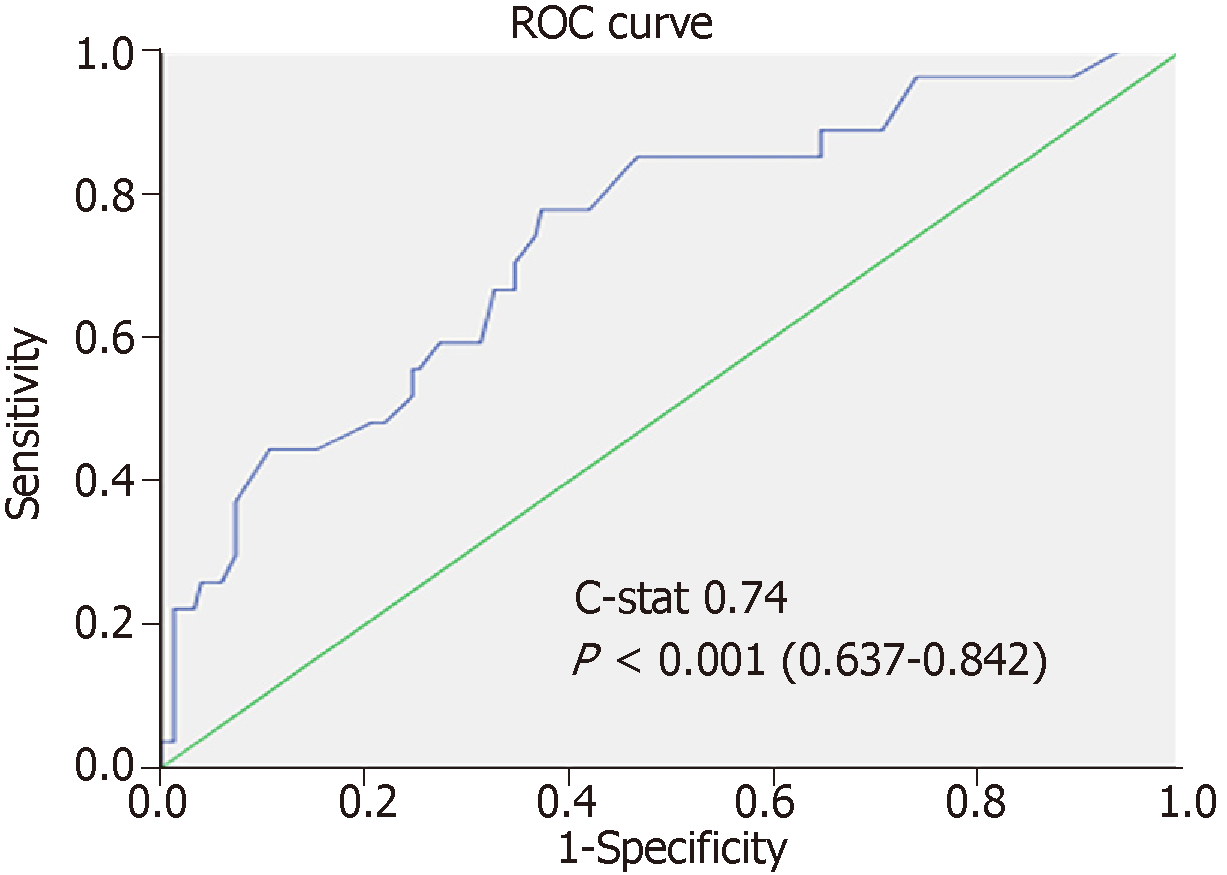
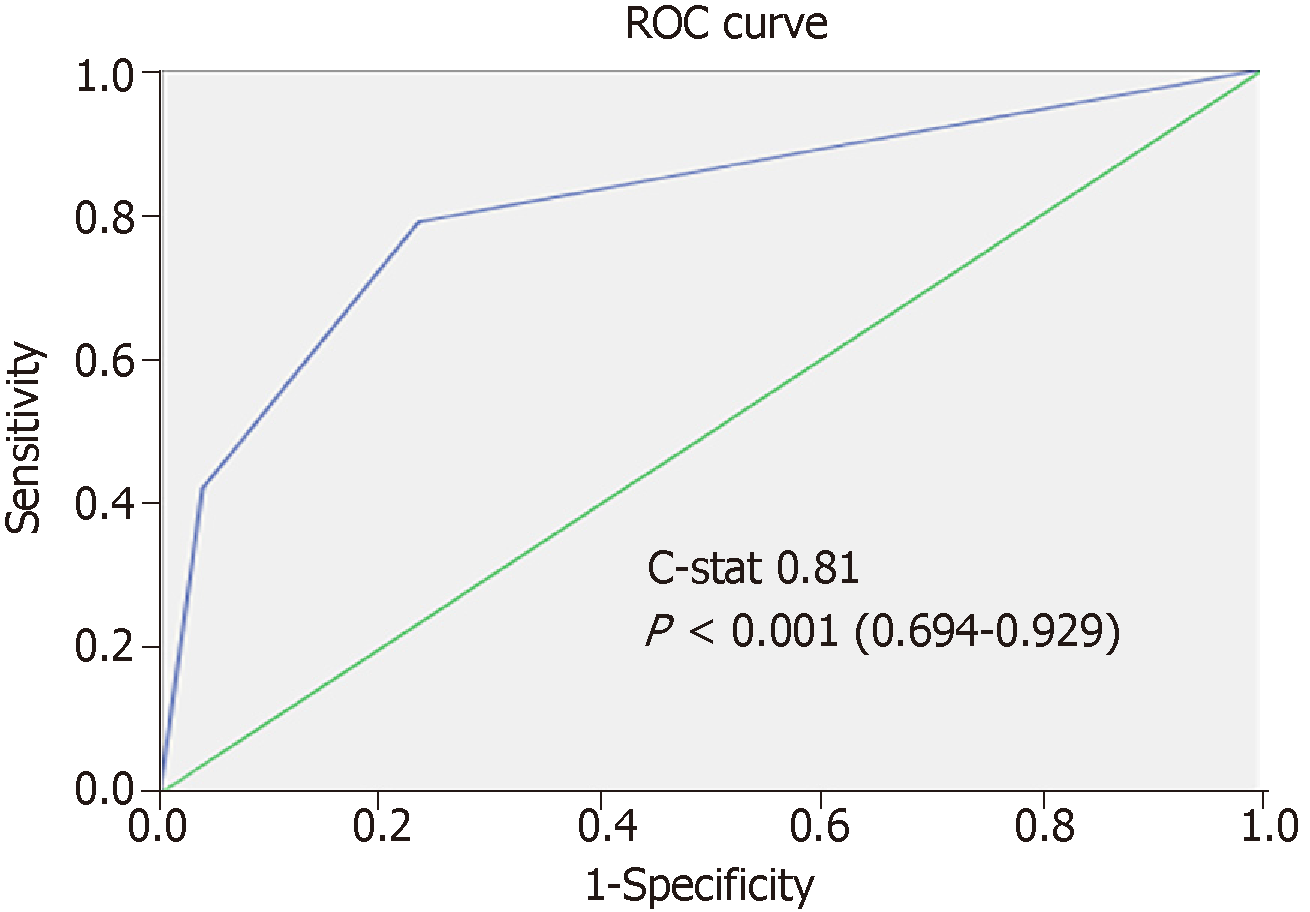
Figure 2 ROC curve for scoring system in the training set.
ROC: Receiver-operating characteristic.
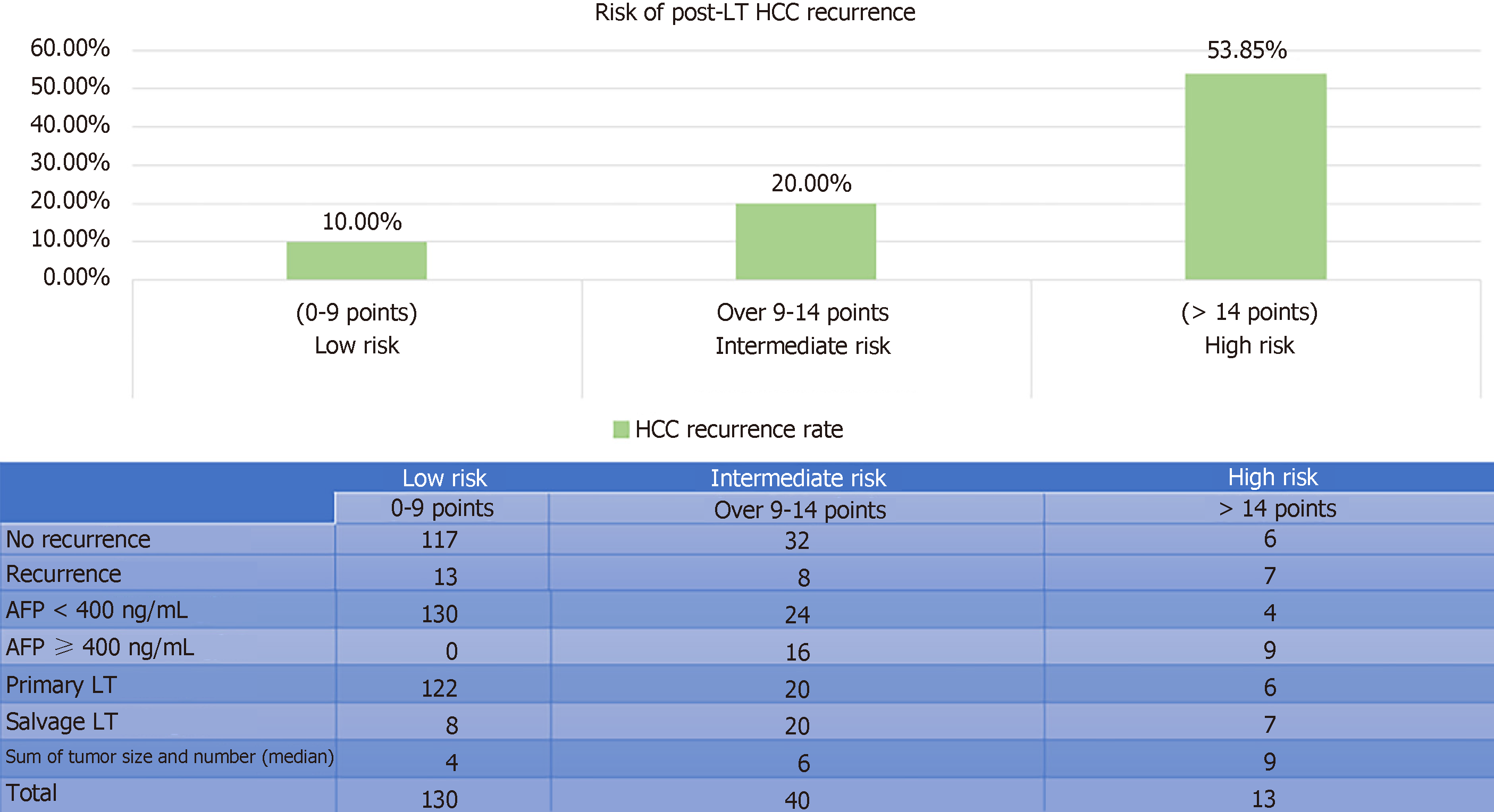
Figure 3 Risk stratification model in the training set.
AFP: Alpha fetoprotein; LT: Liver transplantation; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
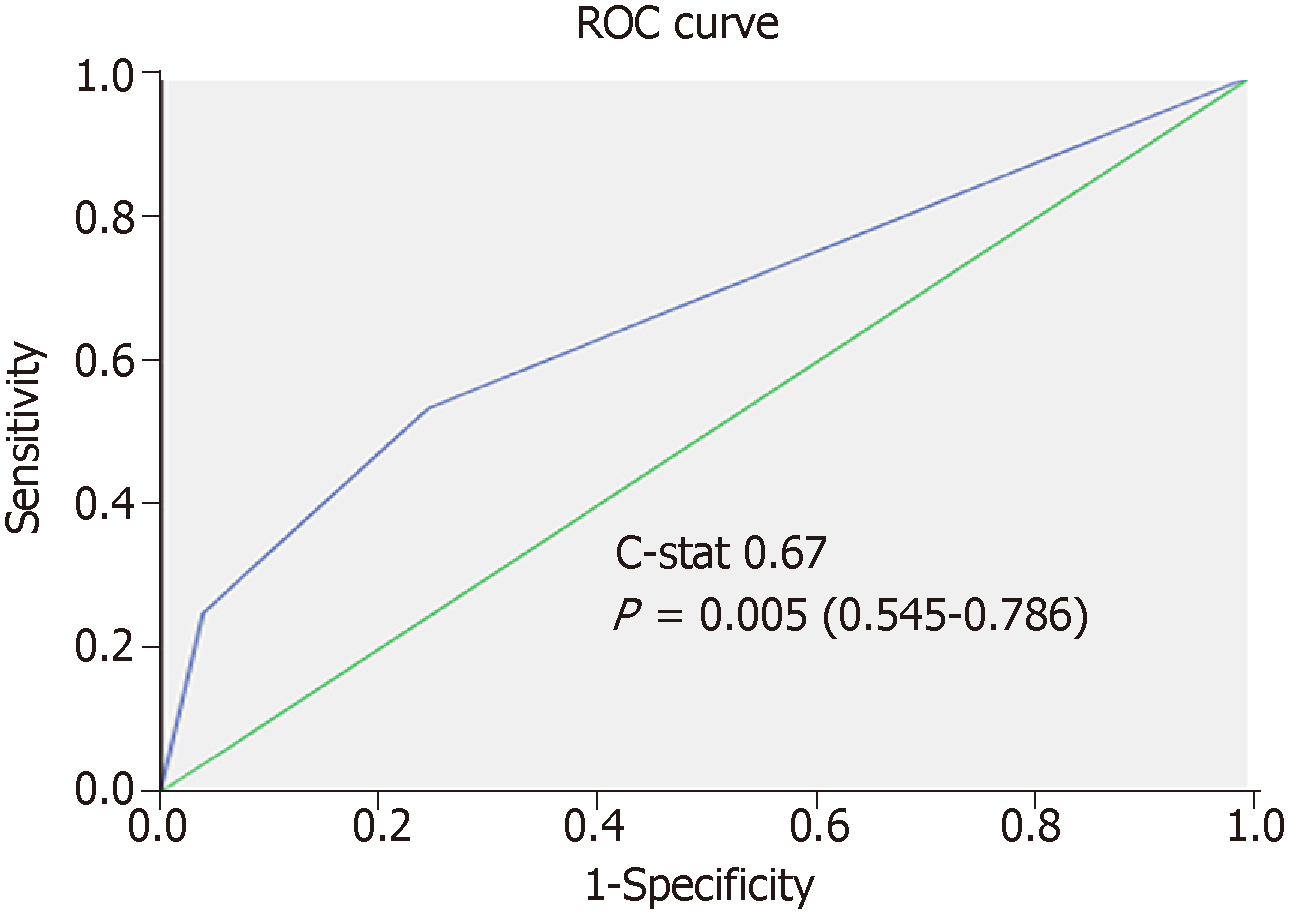
Figure 4 Performance of risk stratification model in relation to recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma in the training set.
ROC: Receiver-operating characteristic.
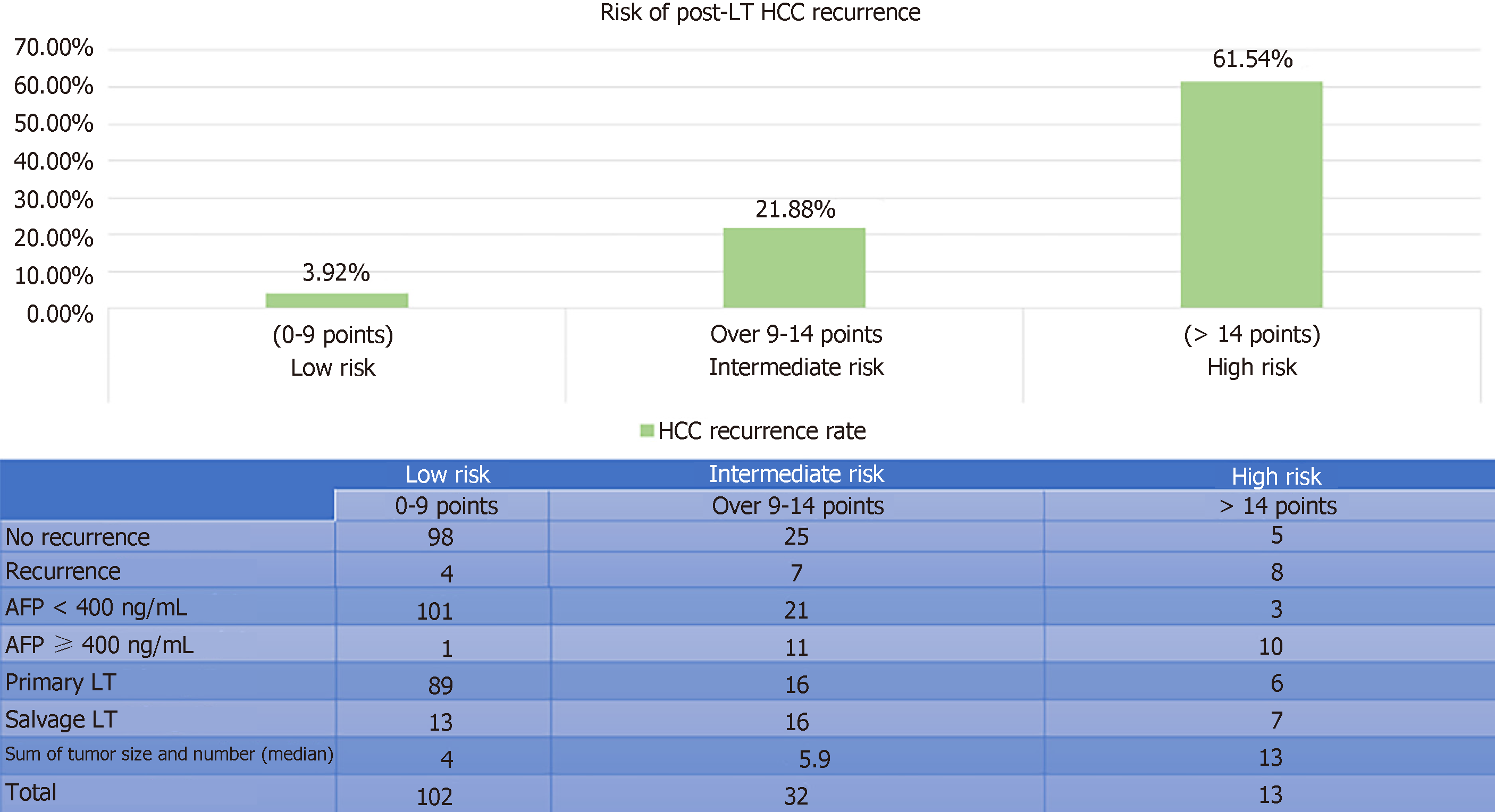
Figure 5 Risk stratification models with corresponding hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence rates in the training set.
AFP: Alpha fetoprotein; ROC: Receiver-operating characteristic.
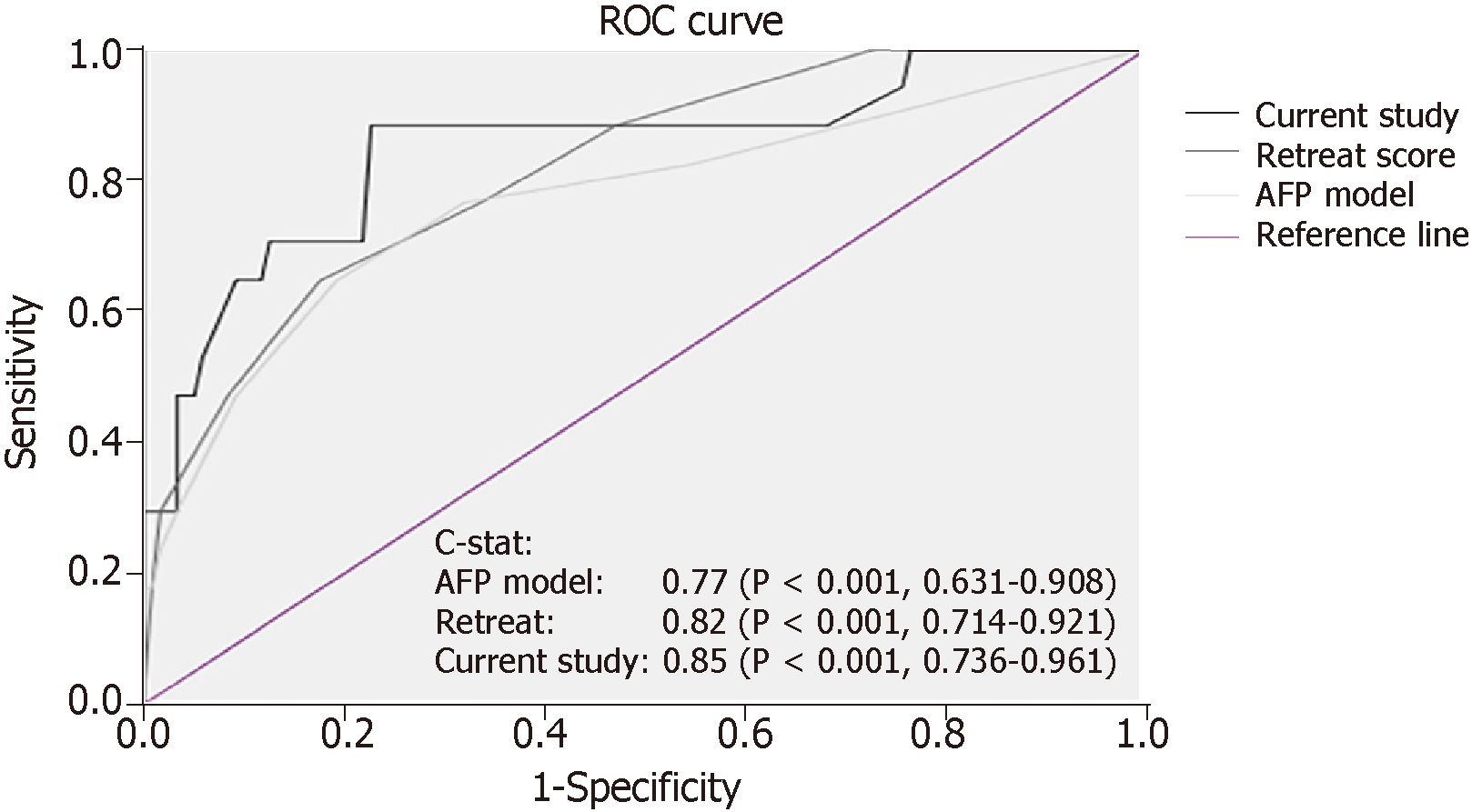
Figure 6 Comparison of the areas under ROC curve between the current scoring system, the alpha fetoprotein model, and the RETREAT score in the validation set.
AFP: Alpha fetoprotein; LT: Liver transplantation; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; ROC: Receiver-operating characteristic; RETREAT: Risk estimation of tumor recurrence after transplant.
Figure 7 Risk stratification model with corresponding hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence rates in the validation set.
ROC: Receiver-operating characteristic.
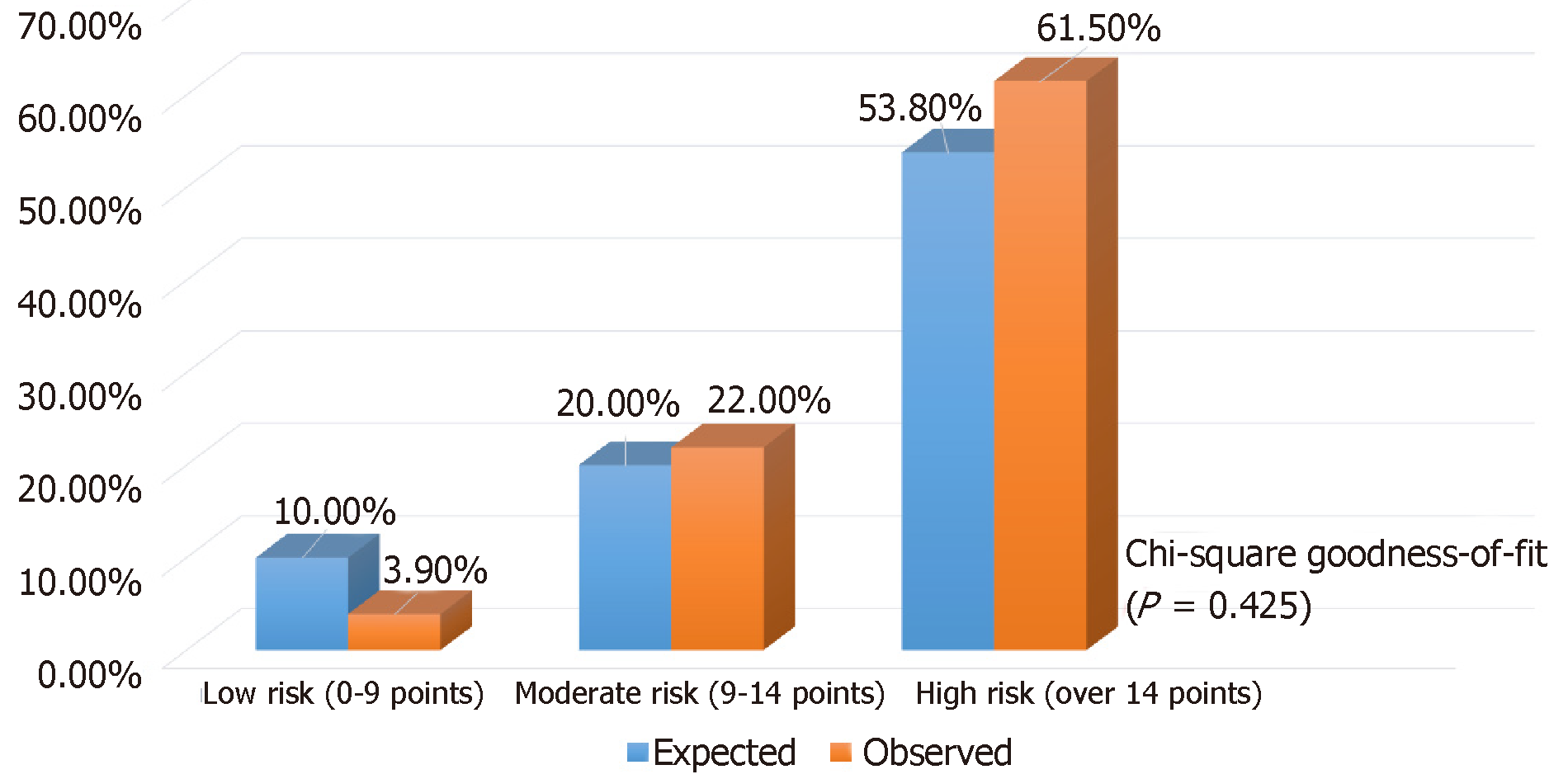
Figure 8 Diagram showing discrepancy between the expected and observed hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence rates.
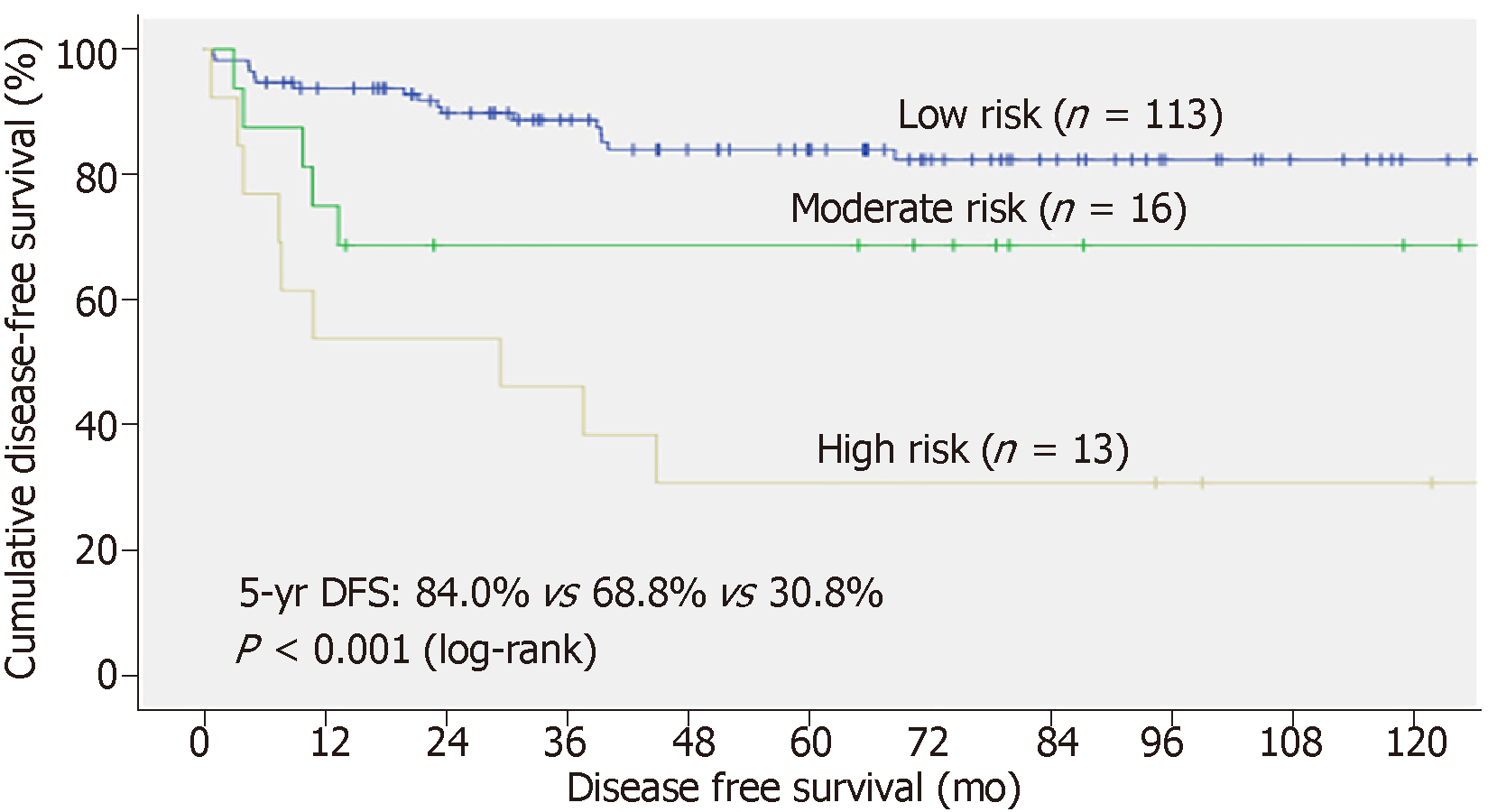
Figure 9 Disease-free survival of patients in different risk strata.
DFS: Disease-free survival.
- Citation: Ma KW, She WH, Chan ACY, Cheung TT, Fung JYY, Dai WC, Lo CM, Chok KSH. Validated model for prediction of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation in Asian population. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2019; 11(4): 322-334
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v11/i4/322.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v11.i4.322