©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Jan 16, 2026; 18(1): 111395
Published online Jan 16, 2026. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v18.i1.111395
Published online Jan 16, 2026. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v18.i1.111395
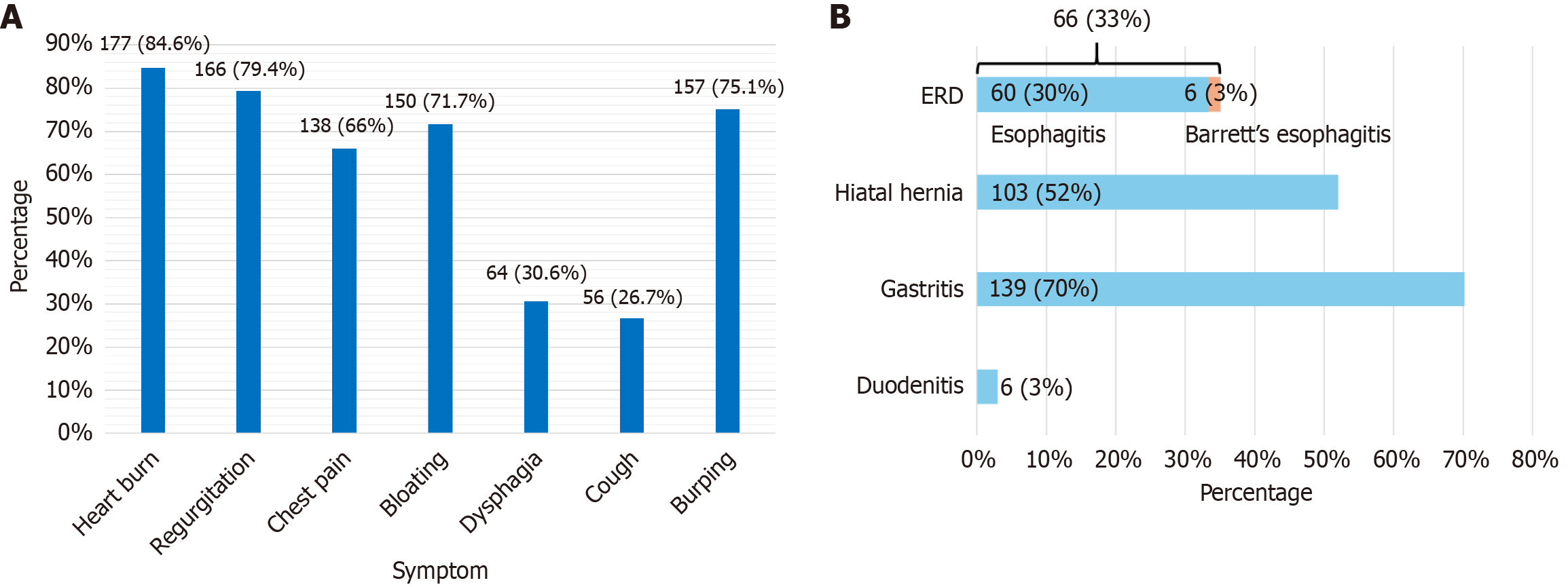
Figure 1 Distribution and categorization of subjects (n = 199).
A: Distribution of symptoms among subjects with gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms; B: Categorization of subjects with gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms according to upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. ERD: Erosive reflux disease.
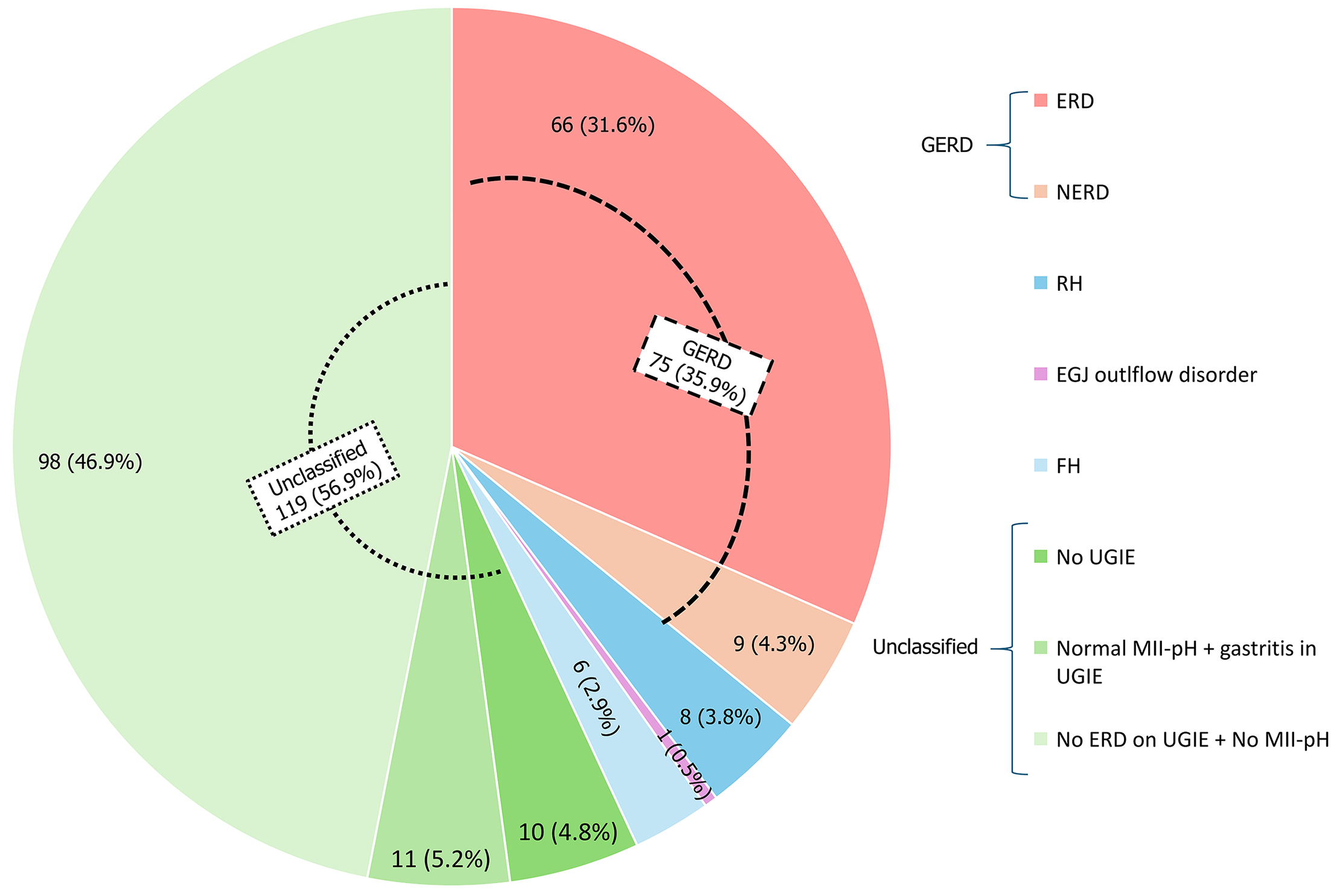
Figure 2 Categorization of subjects with gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms according to all available investigation results (n = 209).
GERD: Gastroesophageal reflux disease; ERD: Erosive reflux disease; NERD: Non-erosive reflux disease; RH: Reflux hypersensitivity; EGJ: Esophageal-gastric junction; FH: Functional heartburn; UGIE: Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy; MII-pH: Multichannel intraluminal impedance-pH monitoring.
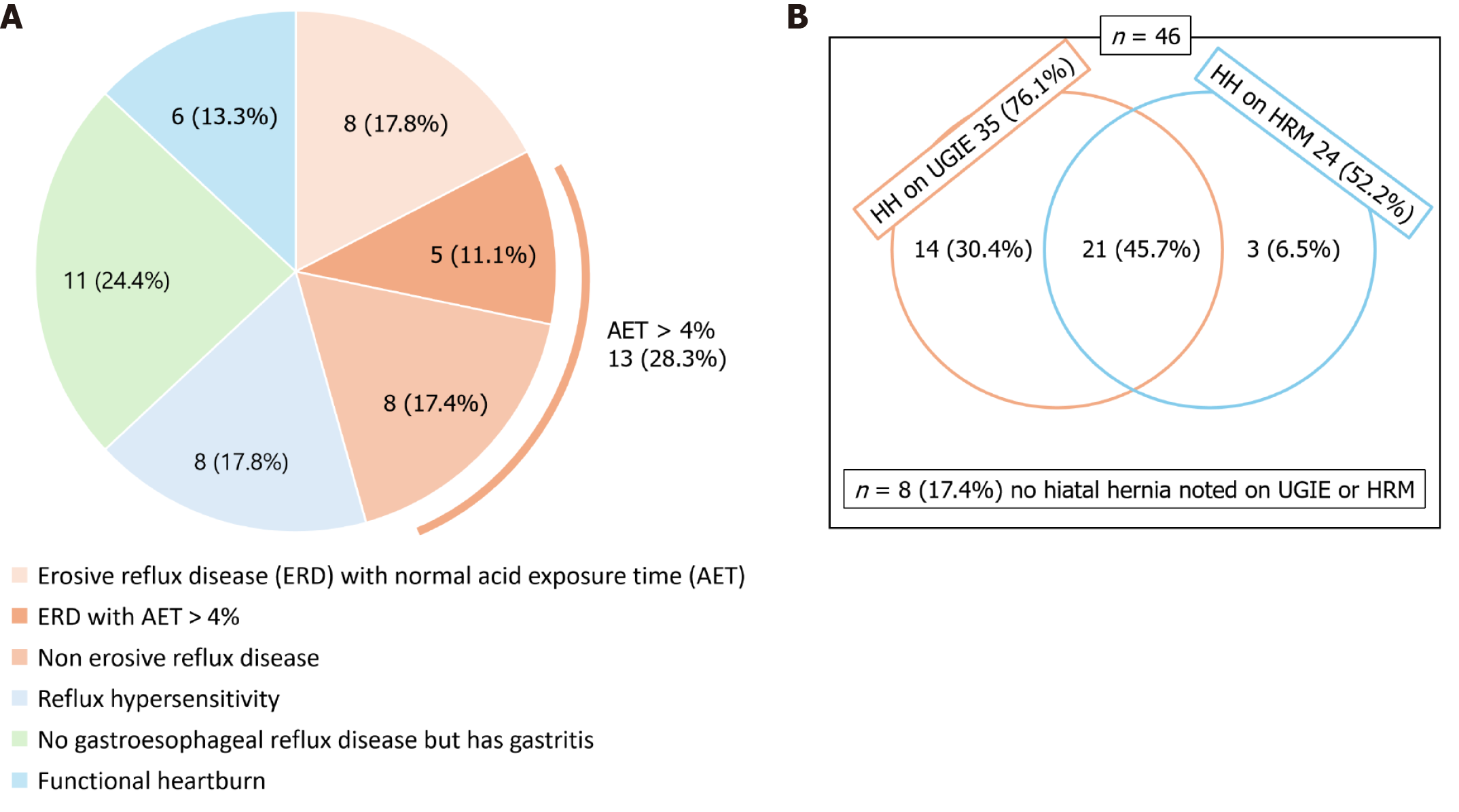
Figure 3 Information on subjects with gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms who underwent endoscopy, high-resolution manometry, and multichannel intraluminal impedance-pH monitoring (n = 46).
A: Categorization of subjects; B: Number and percentage of hiatal hernia detected by high-resolution manometry and upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. ERD: Erosive reflux disease; AET: Acid exposure times; HH: Hiatal hernia; UGIE: Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy; HRM: High-resolution manometry.
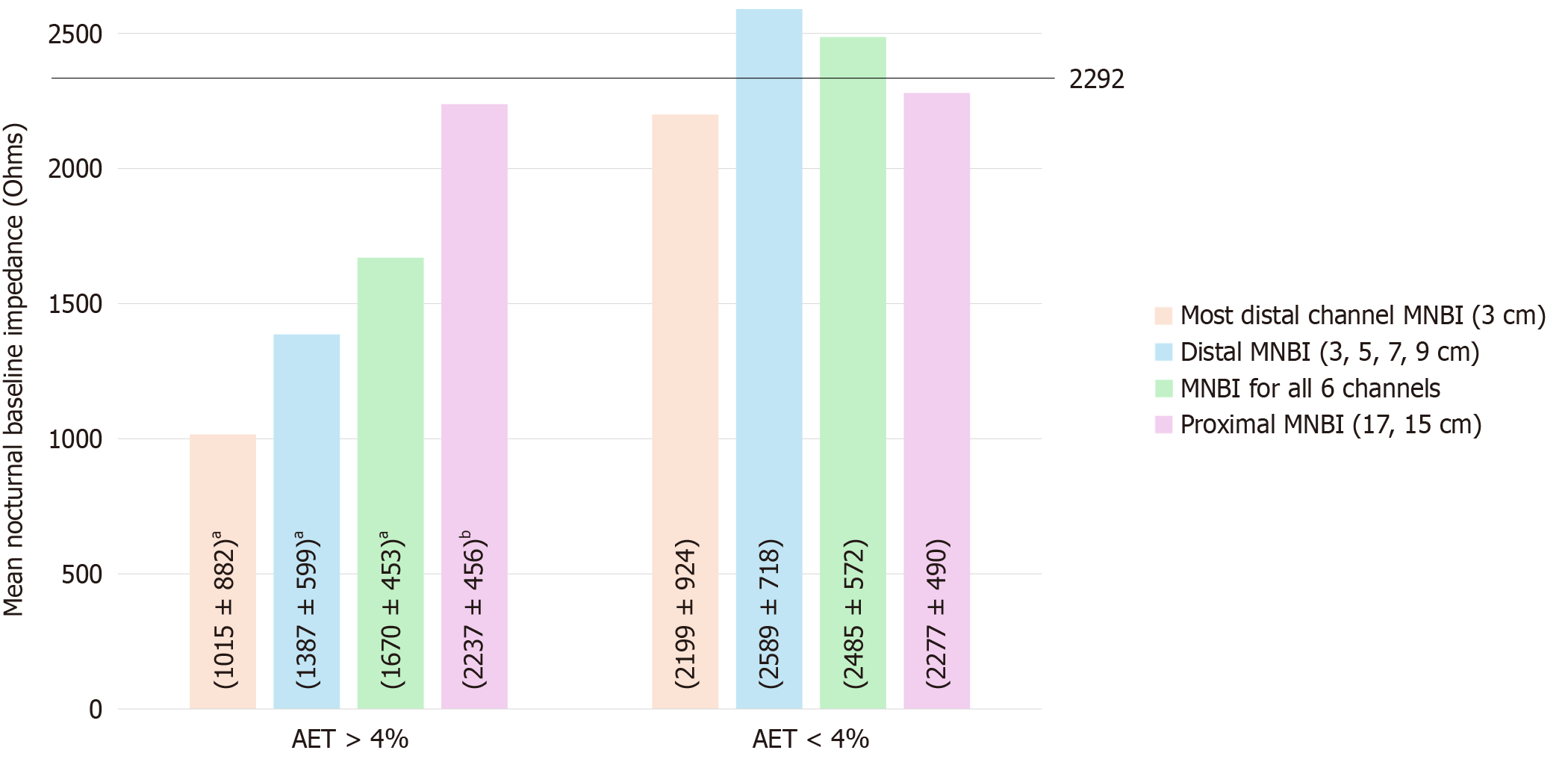
Figure 4 Mean nocturnal baseline impedance values in patients with acid exposure times > 4% and acid exposure times < 4%.
P values were obtained via Mann-Whitney U test. aP < 0.001, bP = 0.913. AET: Acid exposure time; MNBI: Mean nocturnal baseline impedance.
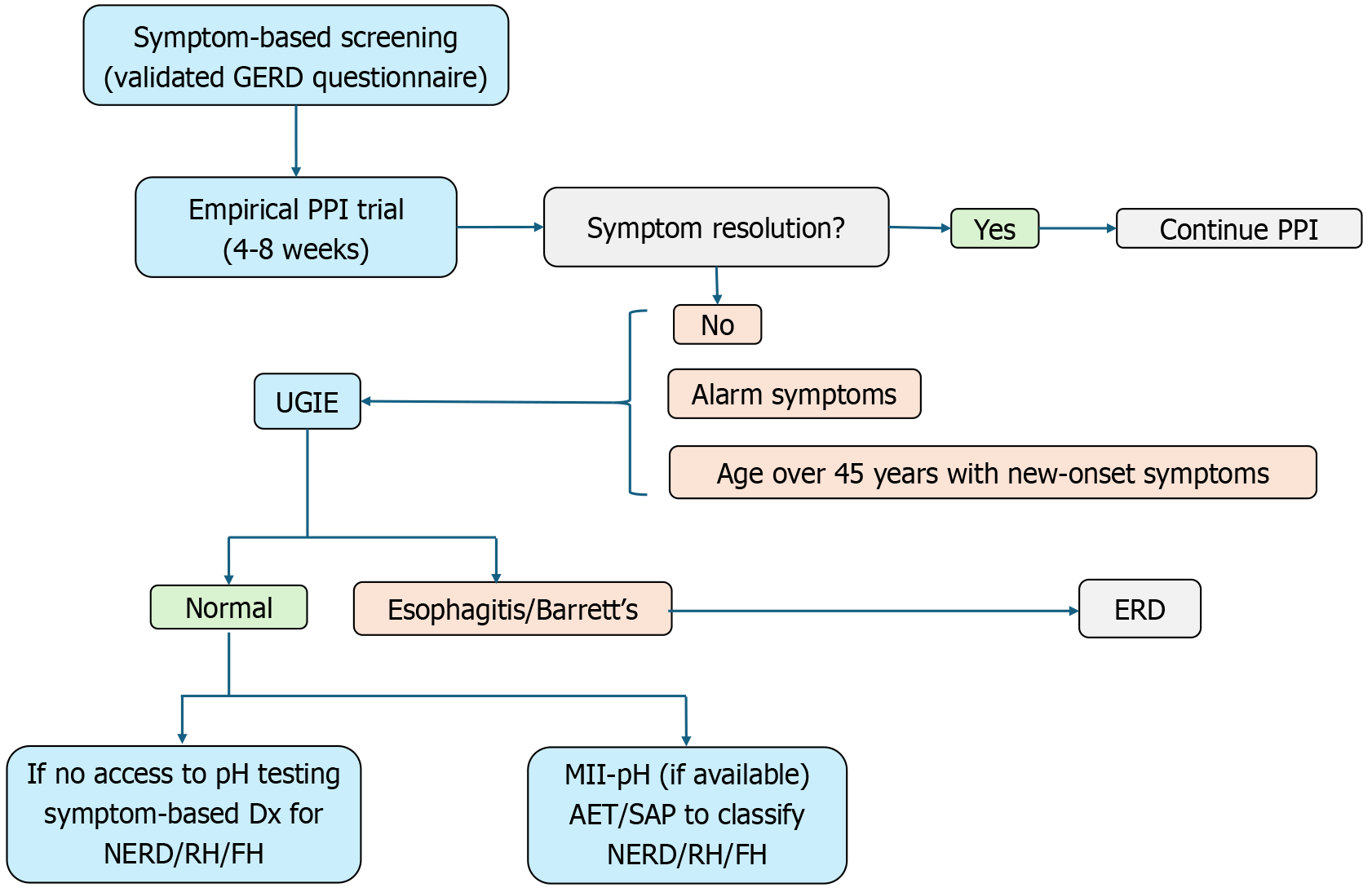
Figure 5 Clinical algorithm for gastroesophageal reflux disease diagnosis in resource-limited settings.
GERD: Gastroesophageal reflux disease; PPI: Proton pump inhibitor; UGIE: Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy; ERD: Erosive reflux disease; NERD: Non-erosive reflux disease; RH: Reflux hypersensitivity; FH: Functional heartburn; AET: Acid exposure times; SAP: Symptom association probability.
- Citation: Wickramasinghe N, Devanarayana NM. Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms: Correlating endoscopic findings with symptoms and pH-impedance results. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2026; 18(1): 111395
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v18/i1/111395.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v18.i1.111395