©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Sep 16, 2024; 16(9): 509-518
Published online Sep 16, 2024. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v16.i9.509
Published online Sep 16, 2024. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v16.i9.509
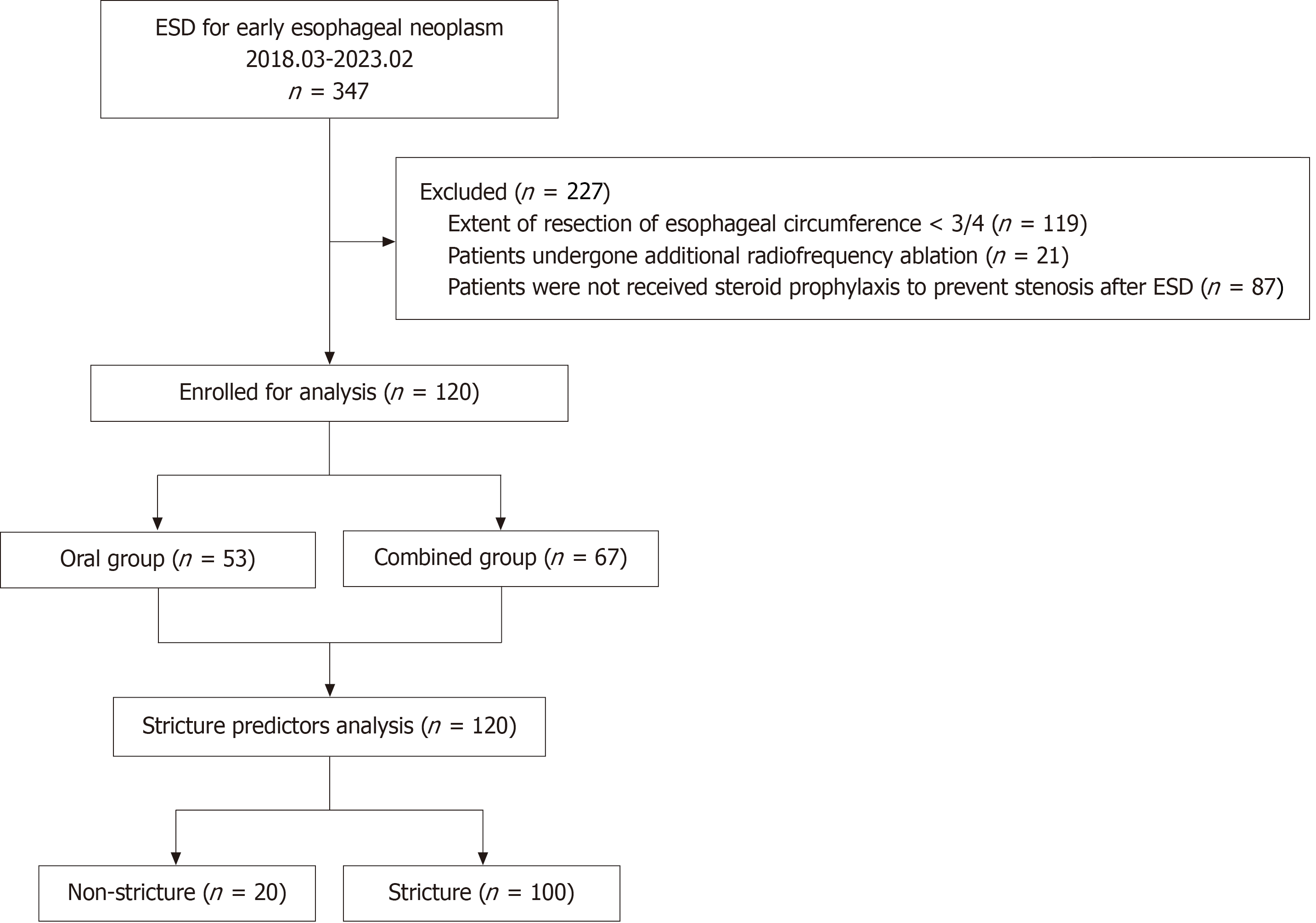
Figure 1 Flow diagram of the study.
ESD: Endoscopic submucosal dissection.
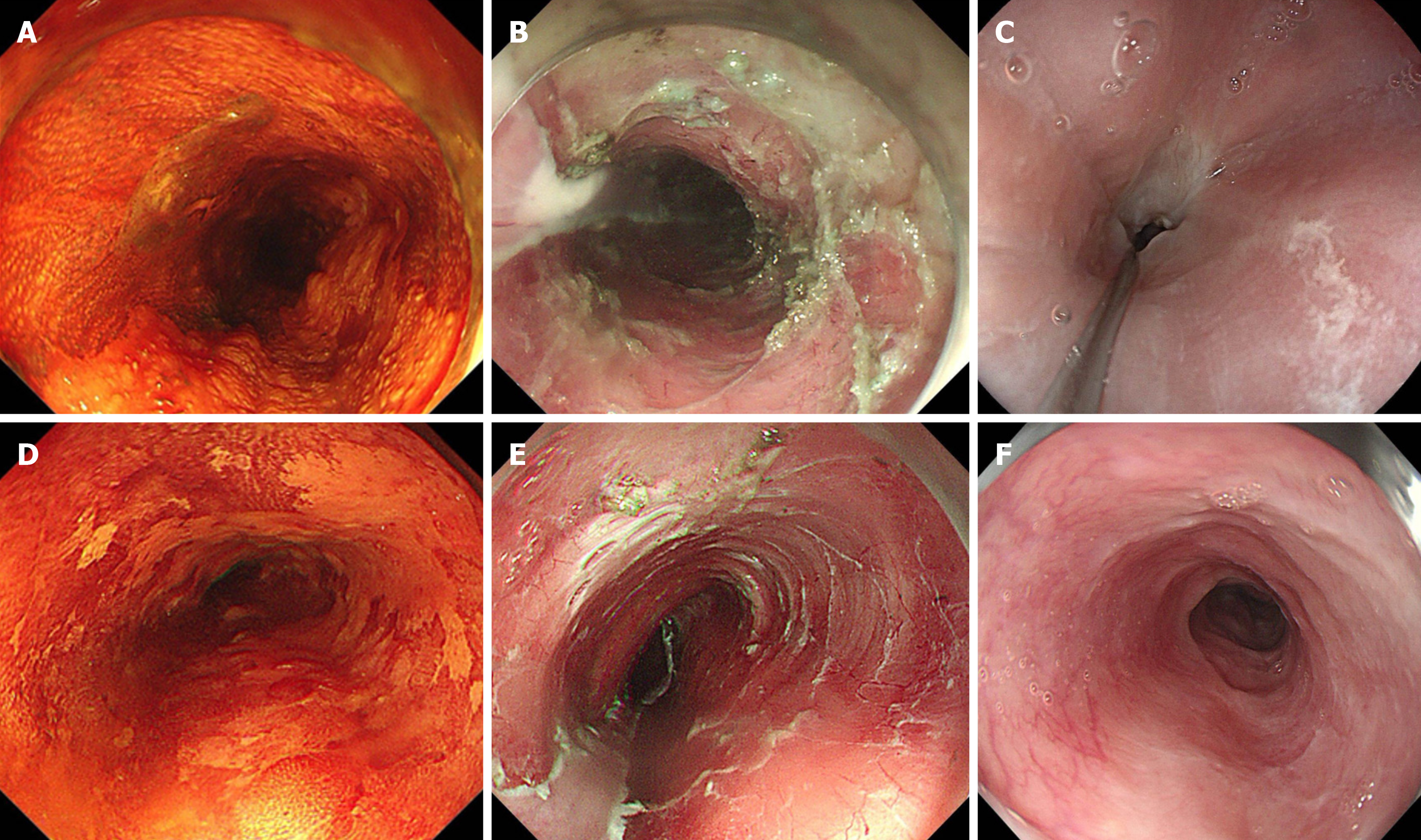
Figure 2 Endoscopic image.
A: Lugol’s chromoendoscopy showed lesion located at 18-24 cm of the incisors; B: The mucosal defect after endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) involved 4/5th of the esophageal circumference and the longitudinal length of defect was 65 mm. The patient took no prophylactic measures; C: Stricture developed after one month located at 20 cm of the incisors. The patient underwent a total of three exploratory strip dilatations after esophageal stricture; D: Lugol’s chromoendoscopy showed lesion located at 28-35 cm of the incisors; E: The mucosal defect after ESD involved 4/5th of the esophageal circumference and the longitudinal length of defect was 55 mm. This patient took prophylactic measures to prevent postoperative stenosis with local multipoint injections of triamcinolone acetonide and oral prednisone; F: No stricture developed after seven months. The standard diagnostic endoscope (9.8 mm in diameter) could pass through the ESD wound scar smoothly.
- Citation: Wang QX, Ding Y, Qian QL, Zhu YN, Shi RH. Predictors of stricture after endoscopic submucosal dissection of the esophagus and steroids application. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2024; 16(9): 509-518
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v16/i9/509.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v16.i9.509