©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Hepatol. Feb 18, 2017; 9(5): 252-262
Published online Feb 18, 2017. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v9.i5.252
Published online Feb 18, 2017. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v9.i5.252
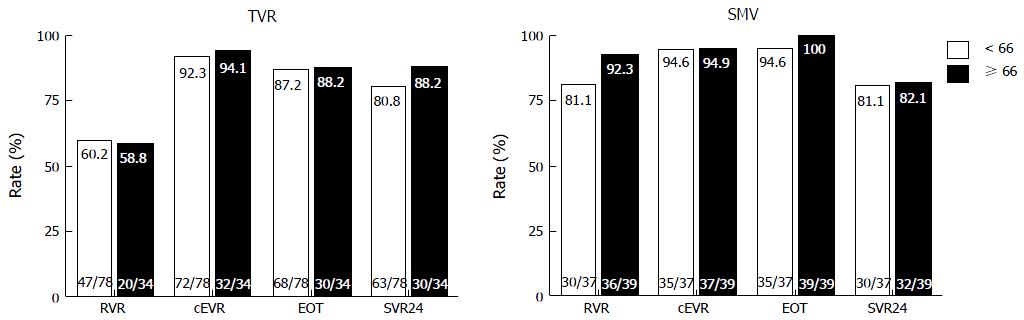
Figure 1 Rates of virological responses to telaprevir and simeprevir by age.
Percentages indicate the proportion of patients with undetectable serum hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA levels. Patient numbers are shown in parenthesis. TVR: Telaprevir; SMV: Simeprevir; RVR: Rapid virological response; cEVR: Complete early virological response; EOT: End of treatment response; SVR24: Sustained virological response defined as undetectable serum HCV RNA at 24 wk after the end of treatment.
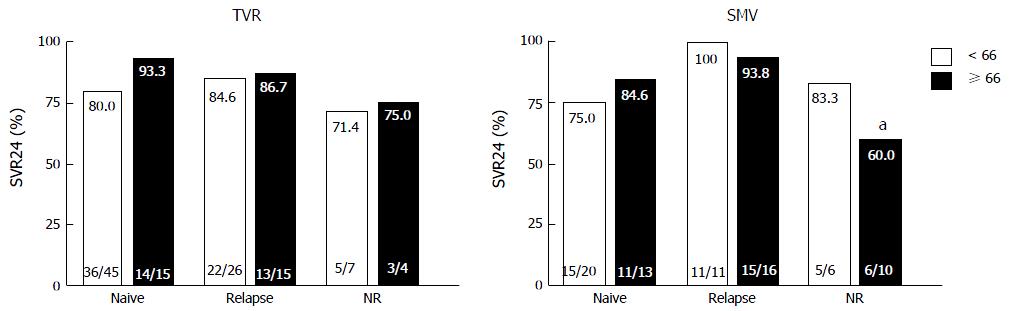
Figure 2 Rates of sustained virological response to telaprevir and simeprevir by prior treatment responses.
Percentages indicate the proportion of patients with undetectable serum hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA levels at 24 wk after the end of treatment. Patient numbers are shown in parenthesis. aP = 0.033 (compared to relapsers in the older patients). NR: Non-responders; TVR: Telaprevir; SMV: Simeprevir; SVR24: Sustained virological response defined as undetectable serum HCV RNA at 24 wk after the end of treatment.
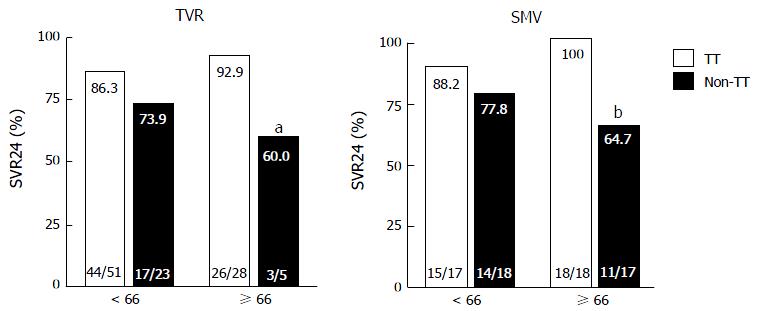
Figure 3 Rates of sustained virological response to telaprevir and simeprevir by interleukin 28B single-nucleotide polymorphism.
Percentages indicate the proportion of patients with undetectable serum hepatitis C virus RNA levels at 24 wk after the end of treatment. Patient numbers are shown in parenthesis. TT, interleukin 28B (IL28B) (rs8099917) TT-genotype; non-TT, IL28B TG/GG-genotypes aP = 0.038 (compared to older patients with the IL28B TT-genotype). bP = 0.005 (compared to older patients with the IL28B TT-genotype). TVR: Telaprevir; SMV: Simeprevir; SVR24: Sustained virological response defined as undetectable serum HCV RNA at 24 wk after the end of treatment.
- Citation: Yamagiwa S, Ishikawa T, Waguri N, Sugitani S, Wakabayashi H, Ohkoshi S, Tsukishiro T, Takahashi T, Watanabe T, Terai S. Efficacy and safety of telaprevir- and simeprevir-based triple therapies for older patients with chronic hepatitis C. World J Hepatol 2017; 9(5): 252-262
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v9/i5/252.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v9.i5.252