Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Hepatol. Dec 18, 2016; 8(35): 1569-1575
Published online Dec 18, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i35.1569
Published online Dec 18, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i35.1569
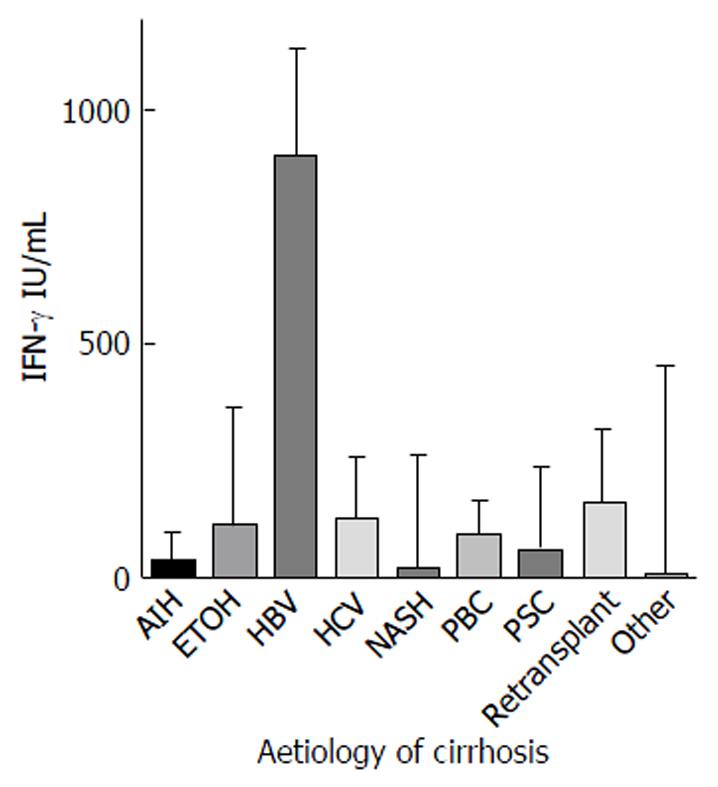
Figure 1 Median QuantiFERON (± IQR) by aetiology of liver disease.
IFN-γ: Interferon-γ; AIH: Autoimmune hepatitis; ETOH: Alcohol; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; NASH: Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis; PBC: Primary biliary cirrhosis; PSC: Primary sclerosing cholangitis.
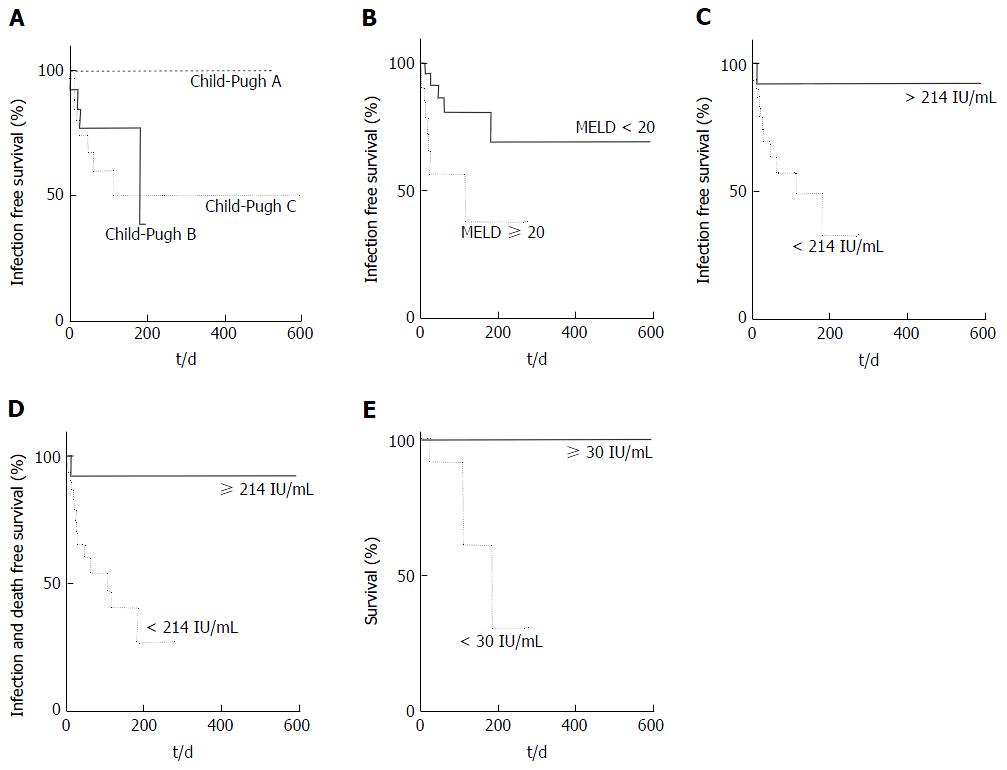
Figure 2 Pretransplant survival based on very low QuantiFERON.
A: Infection free survival by Child-Pugh; B: Infection free survival by MELD; C: Infection free survival by QFM; D: Infection and mortality free survival by QFM; E: Pretransplant survival based on very low QFM. QFM: QuantiFERON-Monitor; MELD: Model for end stage liver disease.
- Citation: Sood S, Yu L, Visvanathan K, Angus PW, Gow PJ, Testro AG. Immune function biomarker QuantiFERON-monitor is associated with infection risk in cirrhotic patients. World J Hepatol 2016; 8(35): 1569-1575
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v8/i35/1569.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v8.i35.1569