©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Hepatol. Oct 8, 2015; 7(22): 2389-2395
Published online Oct 8, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i22.2389
Published online Oct 8, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i22.2389
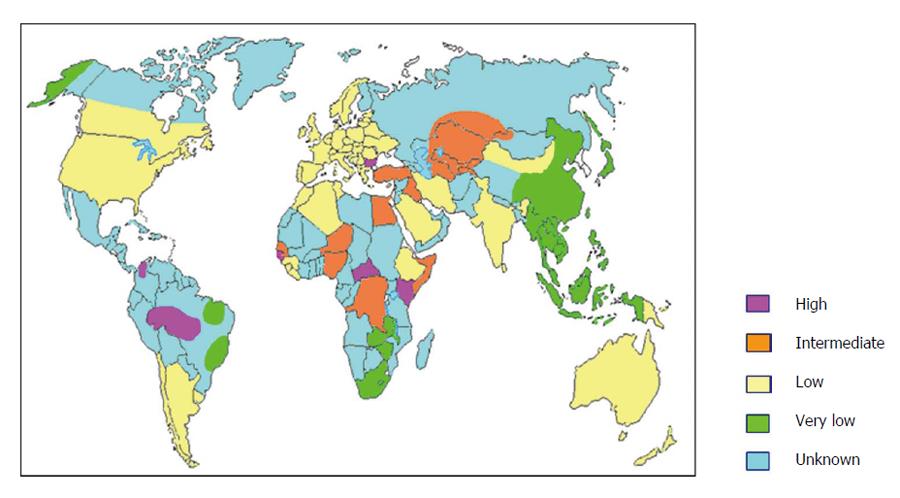
Figure 1 Estimated world epidemiology of hepatitis delta virus infection.
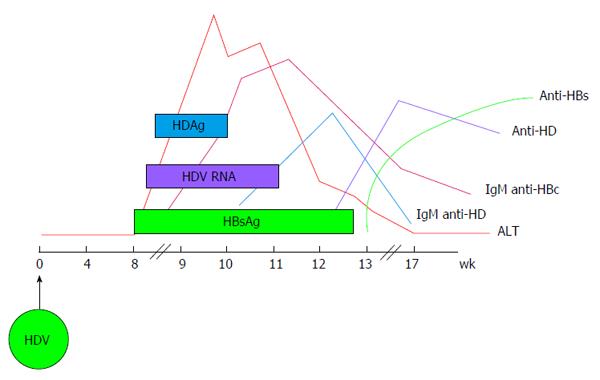
Figure 2 Typical serologic pattern of coinfection by hepatitis B virus and hepatitis delta virus.
The ALT peak is characterised by a double phase being the first due to HBV replication and the second to HDV replication. IgM anti-HDV appear quickly, followed by seroconversion to IgG anti-HD. HBV infection in this phase is revealed by the presence of IgM anti-HBc and HBV viremia. The self-limiting coinfection is transient and persistence of serum IgG anti-HD is the only marker of past HDV infection. HDV: Hepatitis delta virus; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen; ALT: Alanine aminotransferases.
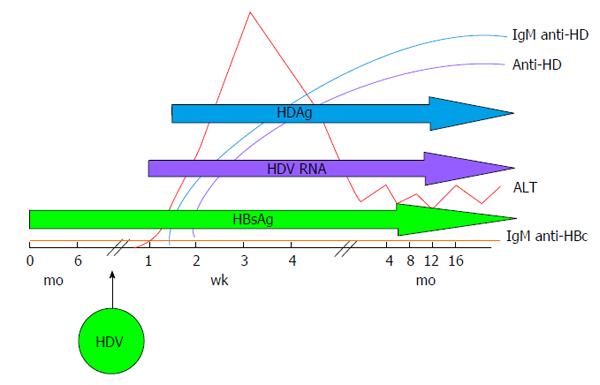
Figure 3 Typical serologic pattern of hepatitis delta virus superinfection: Severe acute hepatitis is characterised by alanine aminotransferases elevation that follows the peak of hepatitis delta virus viremia and is coincidental with IgM anti-HD rise.
Markers of HBV infection are usually inhibited. IgM anti-HBc and HBV DNA typically test negative. HDV: Hepatitis delta virus; HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen; ALT: Alanine aminotransferases.
- Citation: Romeo R, Perbellini R. Hepatitis delta virus: Making the point from virus isolation up to 2014. World J Hepatol 2015; 7(22): 2389-2395
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v7/i22/2389.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v7.i22.2389