©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Hepatol. Feb 27, 2026; 18(2): 111962
Published online Feb 27, 2026. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v18.i2.111962
Published online Feb 27, 2026. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v18.i2.111962
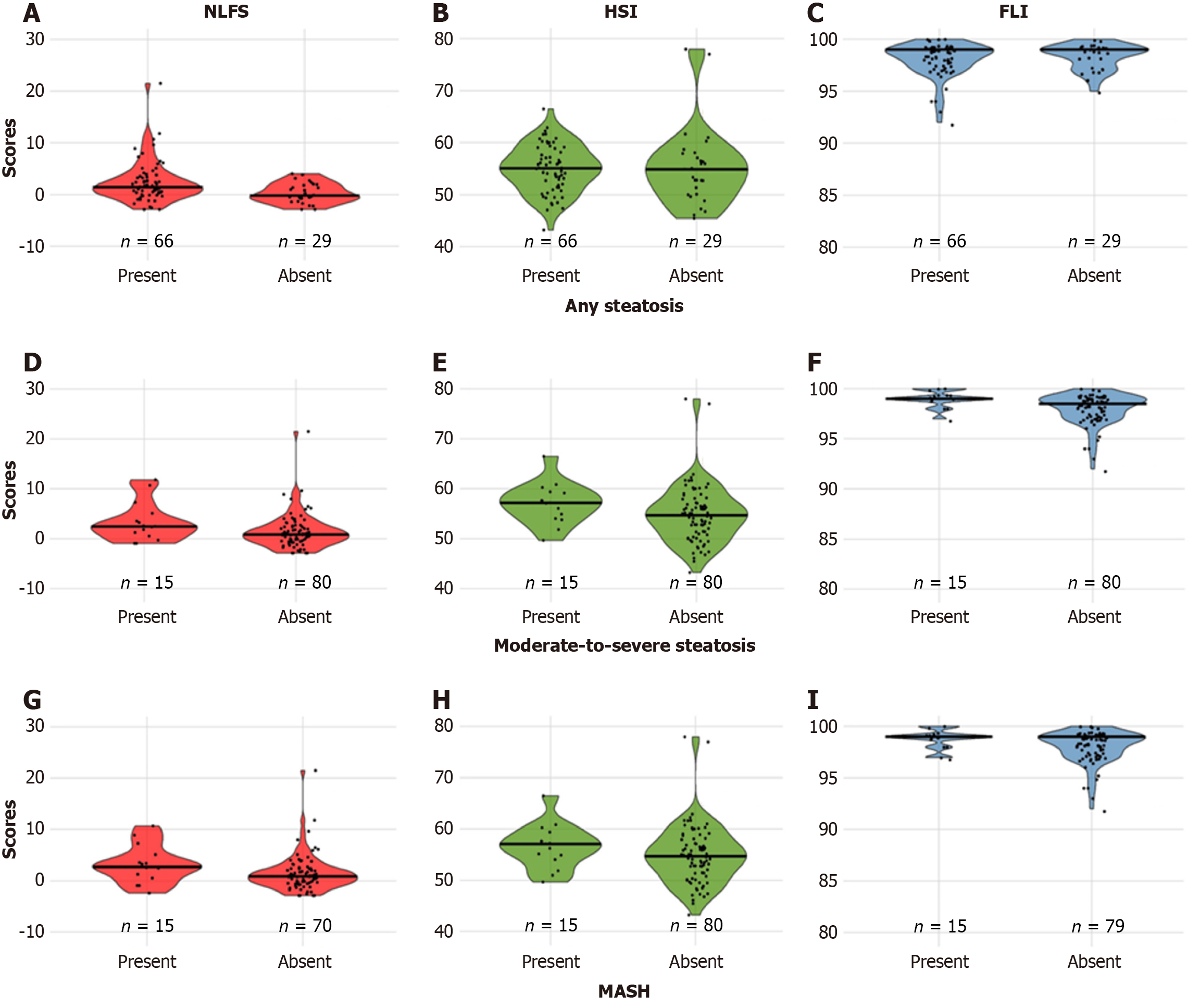
Figure 1 Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease liver fat score showed a statistically significant difference in the score distribution by any degree of steatosis.
All scores presented differences in the distributions by moderate-to-severe steatosis, but only the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease liver fat score (NLFS) and fatty liver index (FLI) were statistically significant. NLFS showed a statistically significant difference in the score distribution by metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH). Score distribution was compared by histopathology. A: Distribution of NLFS for any degree of steatosis; B: Distribution of hepatic steatosis index (HSI) for any degree of steatosis; C: Distribution of FLI for any degree of steatosis; D: Distribution of NLFS for moderate-to-severe steatosis; E: Distribution of HSI for moderate-to-severe steatosis; F: Distribution of FLI for moderate-to-severe steatosis; G: Distribution of NLFS for MASH; H: Distribution of HSI for MASH; I: Distribution of FLI for MASH. The horizontal bar represents the median value for each score. Statistics were performed by the Mann-Whitney U test. NLFS: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease liver fat score; HSI: Hepatic steatosis index; FLI: Fatty liver index; MASH: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis.
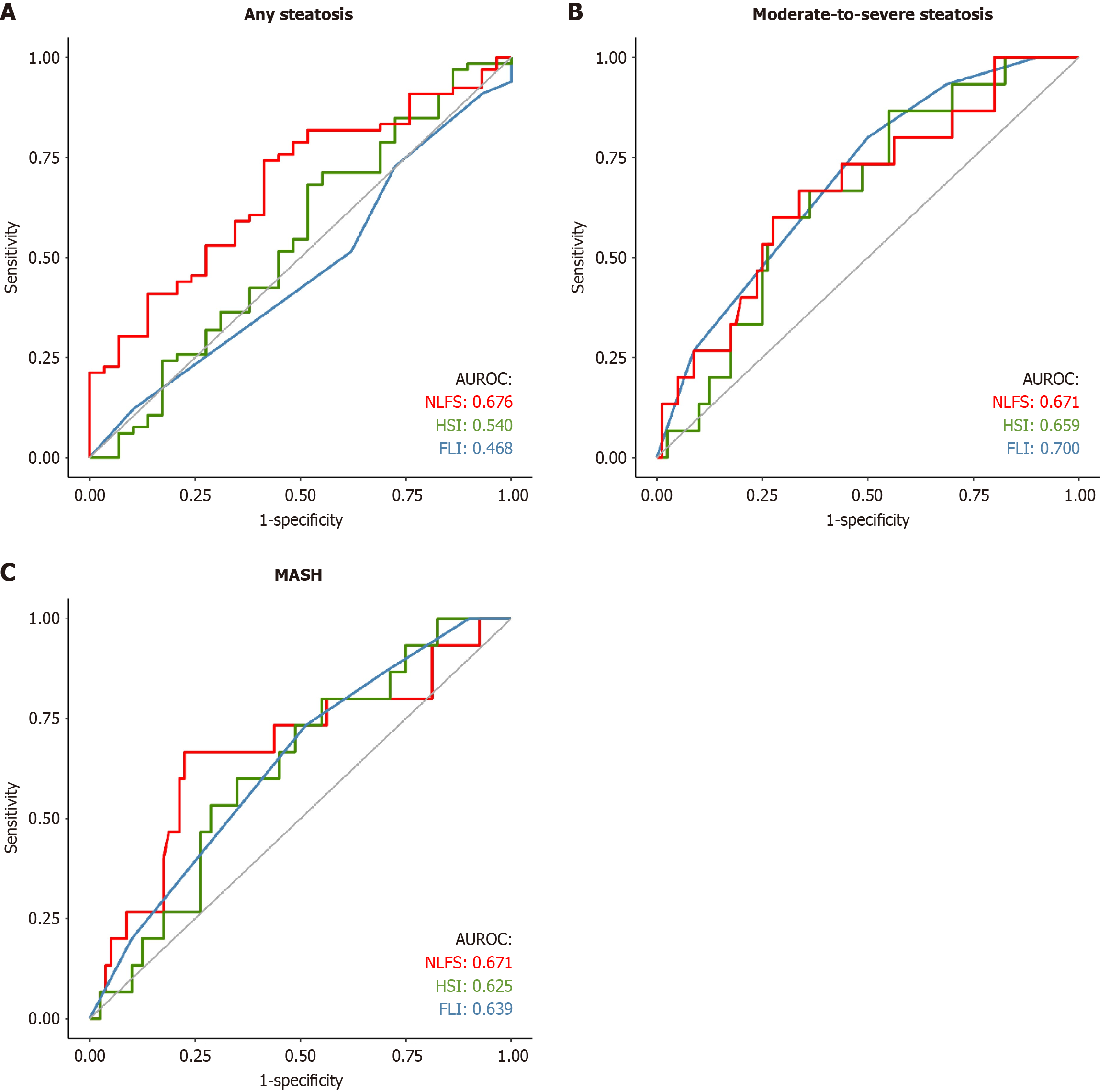
Figure 2 Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease liver fat score had the best performance among all scores in detecting any degree of steatosis and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis.
Performances of the three scores were similar in detecting moderate-to-severe steatosis, with the fatty liver index having a slight advantage. Each score was compared with biopsy-proven scores. A: Any degree of steatosis; B: Moderate-to-severe steatosis; C: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis. AUROC: Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; NLFS: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease liver fat score; HSI: Hepatic steatosis index; FLI: Fatty liver index; MASH: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis.
- Citation: Farina GS, Brambilla B, Pandolfo EM, Lazzaretti LKN, Kuiava SMS, Graciolli AM, Kriger VM, Fistarol CHDB, Sgarioni AC, Giovanardi HP, Tregnago AC, Riva F, Scholze CDS, Agostini DC, Dellamea B, Tamayo A, Cerqueira TL, Soldera J, Illigens BMW. Performance of three clinical scores for steatosis and steatohepatitis and their interaction with metabolic syndrome in obese individuals. World J Hepatol 2026; 18(2): 111962
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v18/i2/111962.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v18.i2.111962