©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Hepatol. Jan 27, 2026; 18(1): 113429
Published online Jan 27, 2026. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v18.i1.113429
Published online Jan 27, 2026. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v18.i1.113429
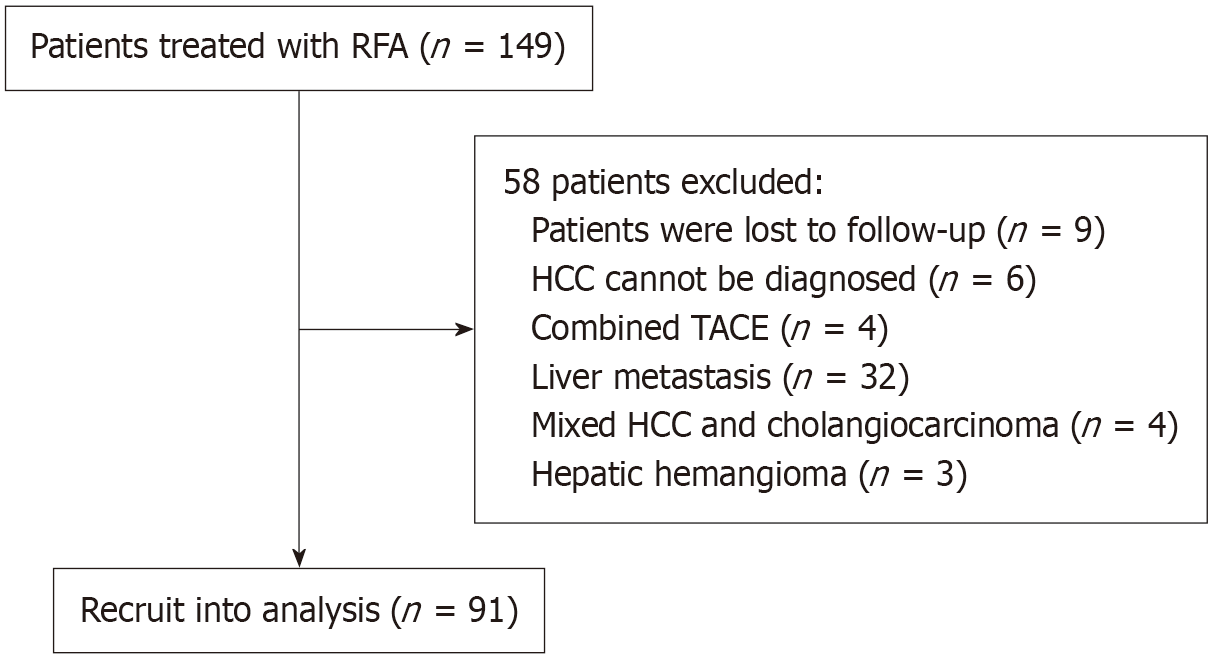
Figure 1 Flowchart of patient selection and enrollment with histopathologically confirmed hepatic malignancies undergoing radio
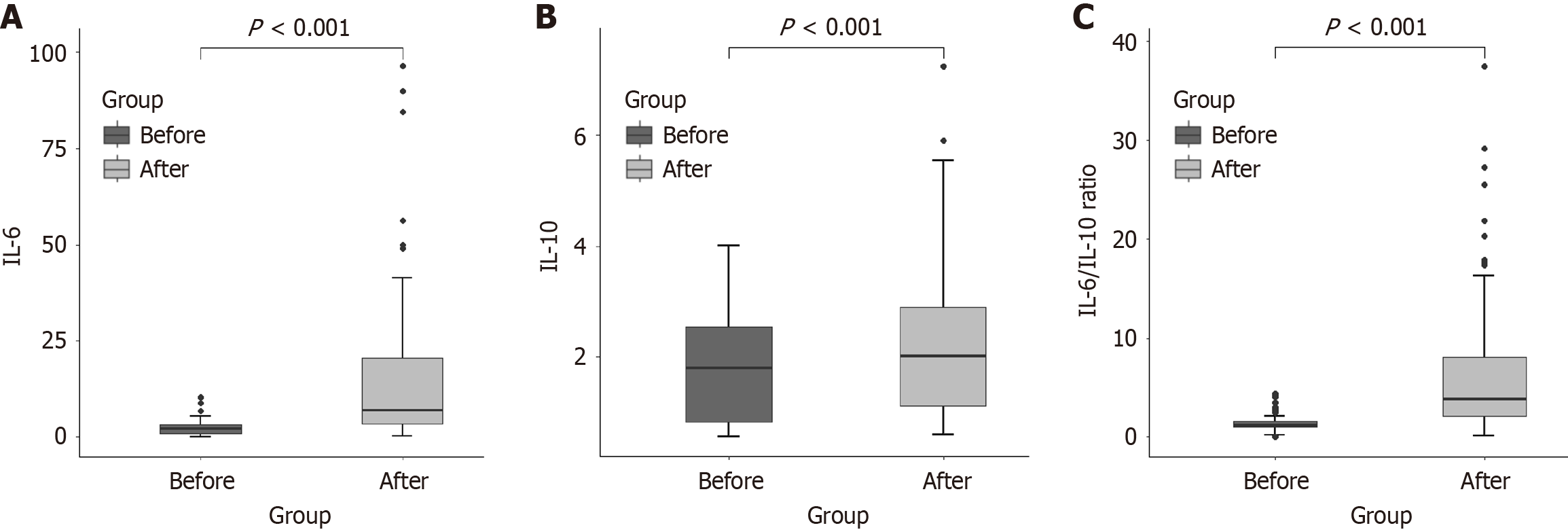
Figure 2 Temporal changes in serum interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 levels before and after radiofrequency ablation.
A: Serum interleukin (IL)-6 levels significantly increased after radiofrequency ablation (RFA), peaking early post-treatment; B: Serum IL-10 levels showed a moderate increase following RFA; C: IL-6/IL-10 ratio was markedly elevated throughout the post-RFA period. IL: Interleukin.
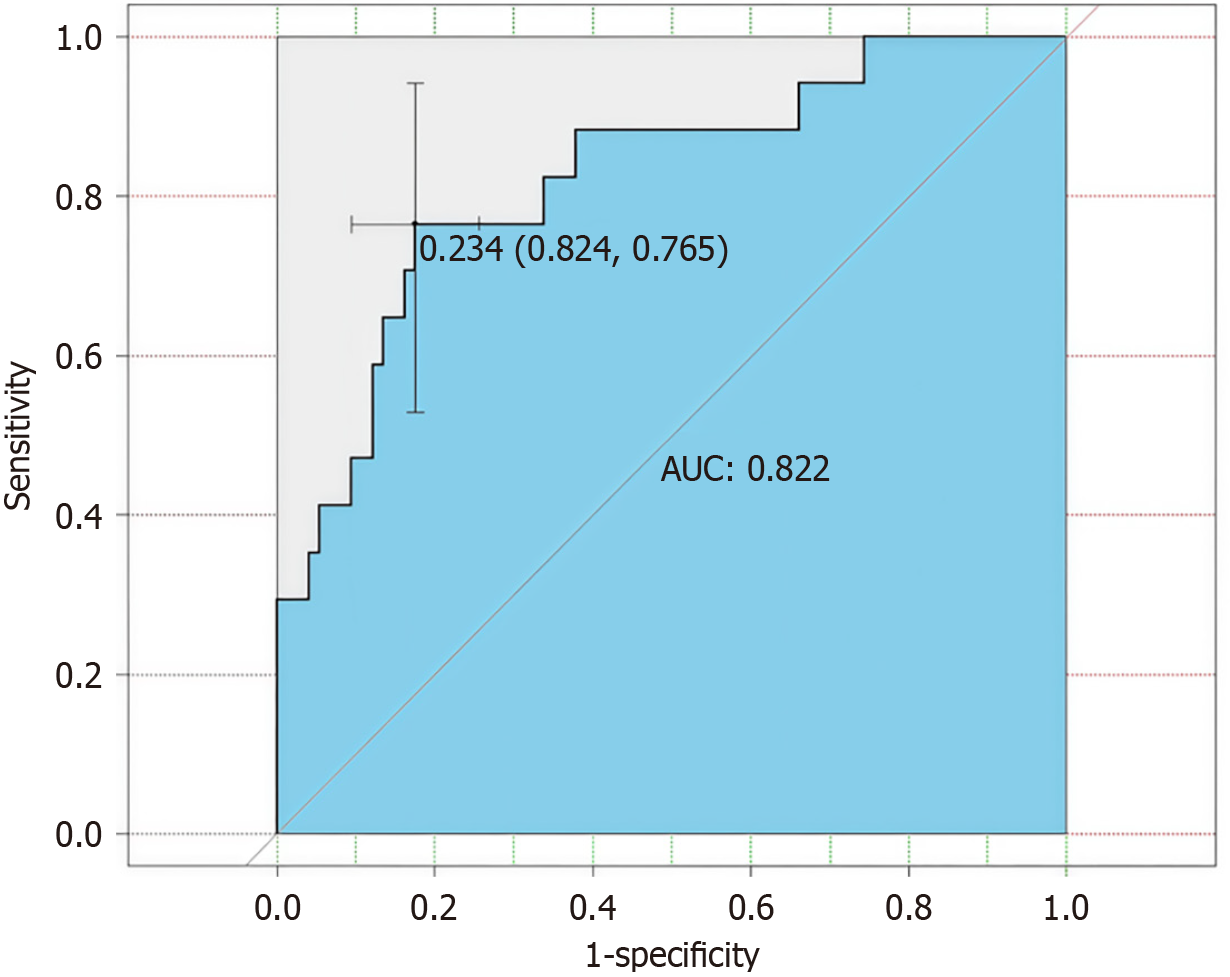
Figure 3 Receiver operating characteristic curve evaluating the predictive performance of the interleukin-6/interleukin-10 ratio for immune dysregulation following radiofrequency ablation.
AUC: Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve.
- Citation: Pang L, Tang D, Zhou WL, Bai X, Zhao HJ, Wang LQ, Cheng W, Wu BL. Interleukin-6/interleukin-10 ratio and immune dysregulation after radiofrequency ablation. World J Hepatol 2026; 18(1): 113429
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v18/i1/113429.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v18.i1.113429