©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Sep 27, 2025; 17(9): 109691
Published online Sep 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i9.109691
Published online Sep 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i9.109691
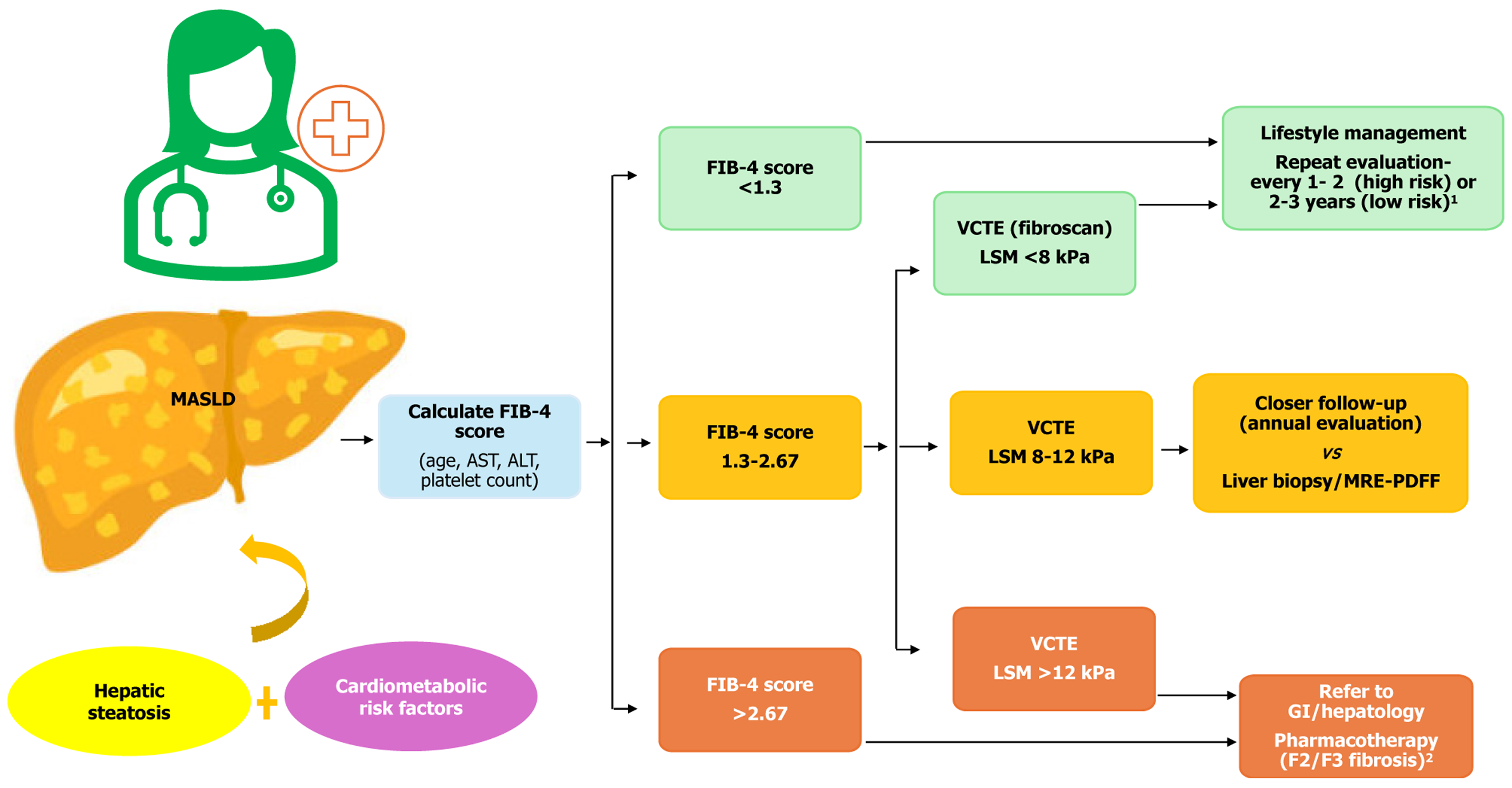
Figure 1 Noninvasive diagnosis of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.
1If the fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) score is < 1.3 or FibroScan liver stiffness measurement (LSM) is < 8 kPa, patients can be followed in the primary care setting and reassessed periodically. Patients without prediabetes/type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and 1 metabolic risk factor have a low risk for disease progression and can be reassessed every 2–3 years. Patients with pre
- Citation: Masood M, Thandassery RB. Noninvasive prediction of clinically significant portal hypertension in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease compared to other chronic liver diseases. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(9): 109691
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i9/109691.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i9.109691