Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Sep 27, 2025; 17(9): 109429
Published online Sep 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i9.109429
Published online Sep 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i9.109429
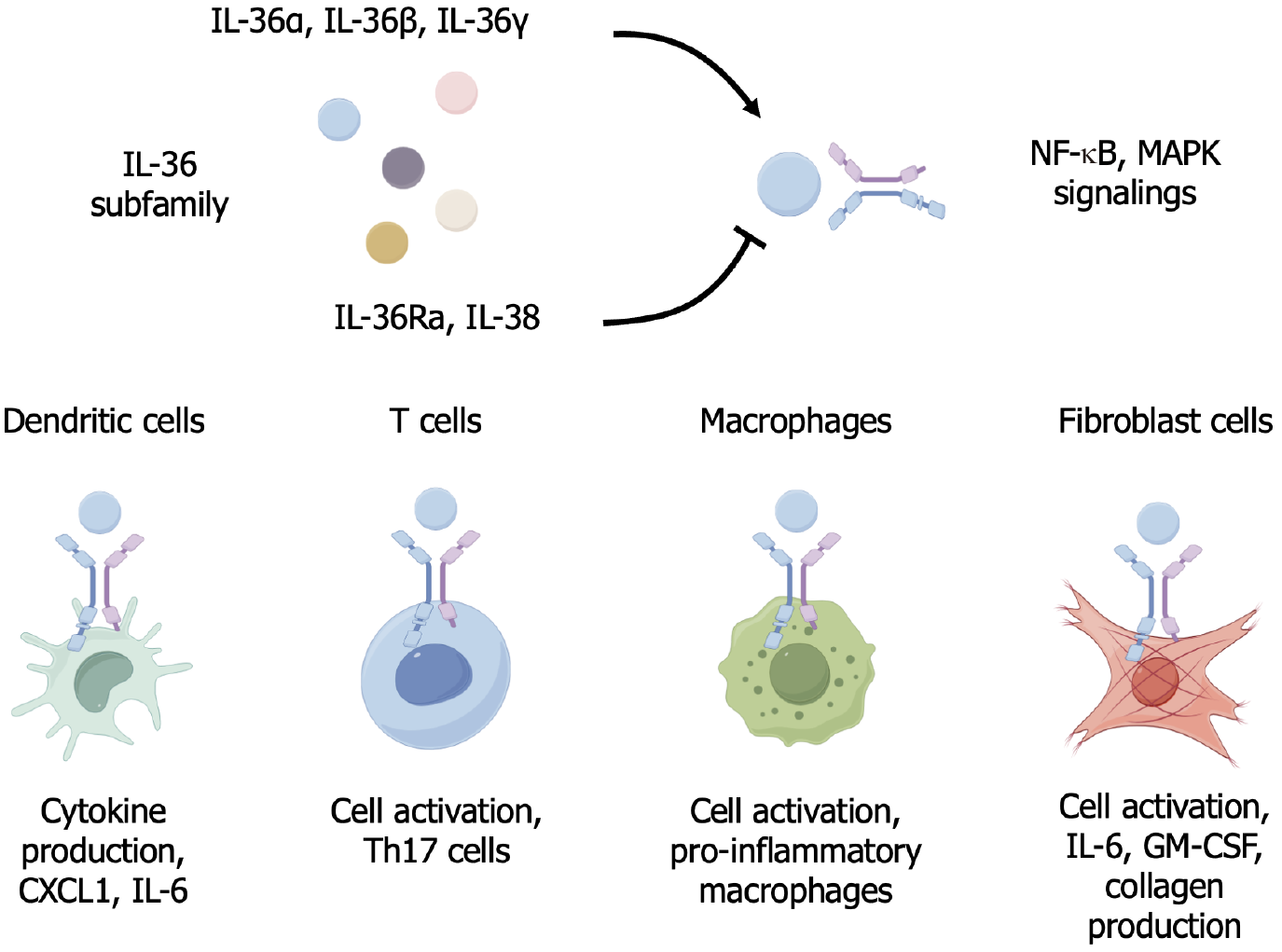
Figure 1 The role of interleukin-36 in liver disease.
In the context of liver diseases, interleukin-36 cytokines may activate a variety of immune and nonimmune cells in the liver, including dendritic cells, macrophages, T cells, and fibroblasts. IL: Interleukin; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; CXCL1: C-X-C motif ligand 1; Th 17 cells: T helper type 17 cells; GM-CSF: Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IL-36Ra: Interleukin-36 receptor antagonist.
- Citation: Xiong ZK, Gu SM, Zheng YY. Interleukin-36 subfamily cytokines in liver diseases. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(9): 109429
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i9/109429.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i9.109429