©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Dec 27, 2025; 17(12): 114084
Published online Dec 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i12.114084
Published online Dec 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i12.114084
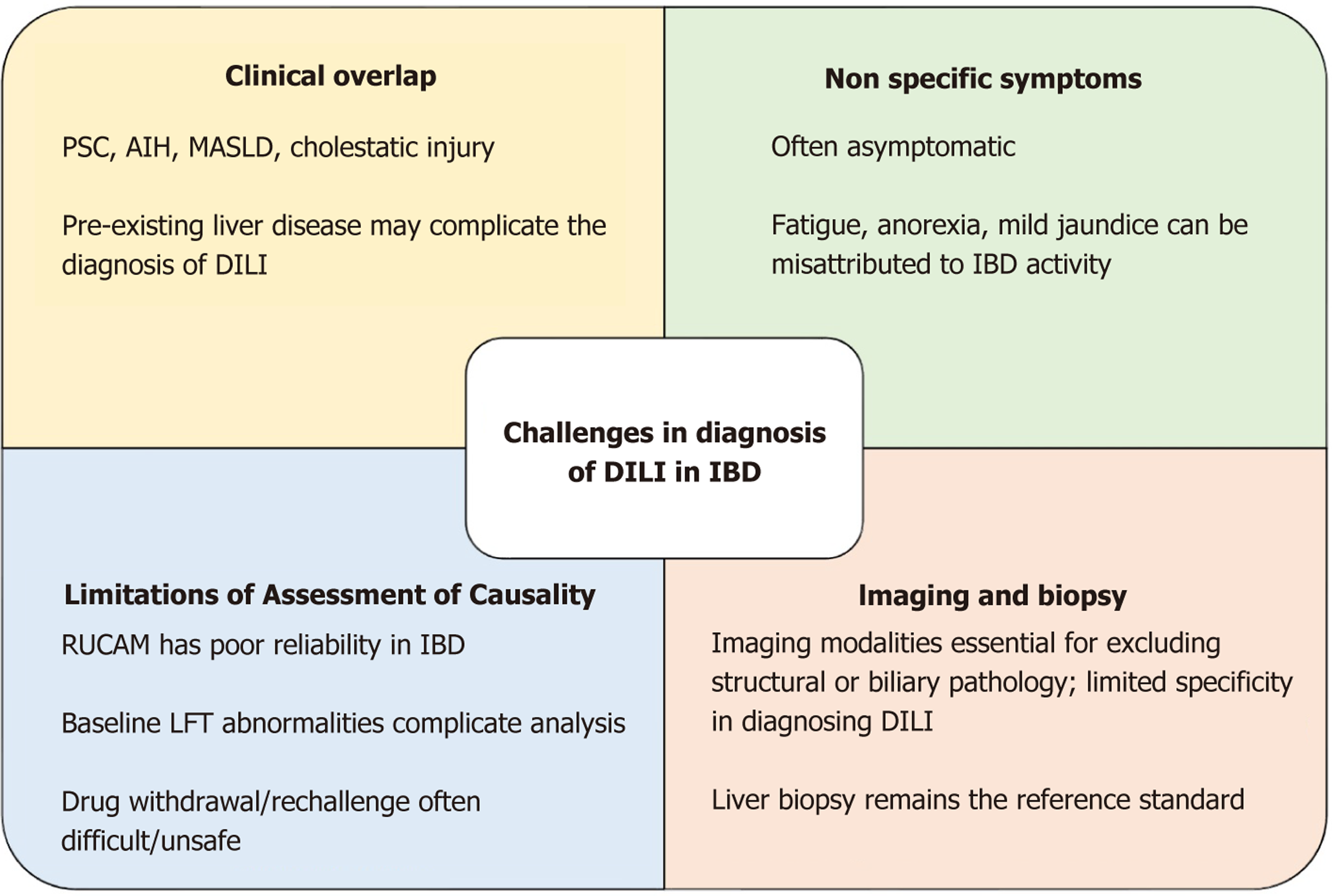
Figure 1 Challenges in the diagnosis of drug induced liver injury in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.
AIH: Autoimmune hepatitis; LFT: Liver function test; MASLD: Metabolic dysfunction associated steatotic liver disease; PSC: Primary sclerosing cholangitis; RUCAM: Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method; DILI: Drug induced liver injury; IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease.
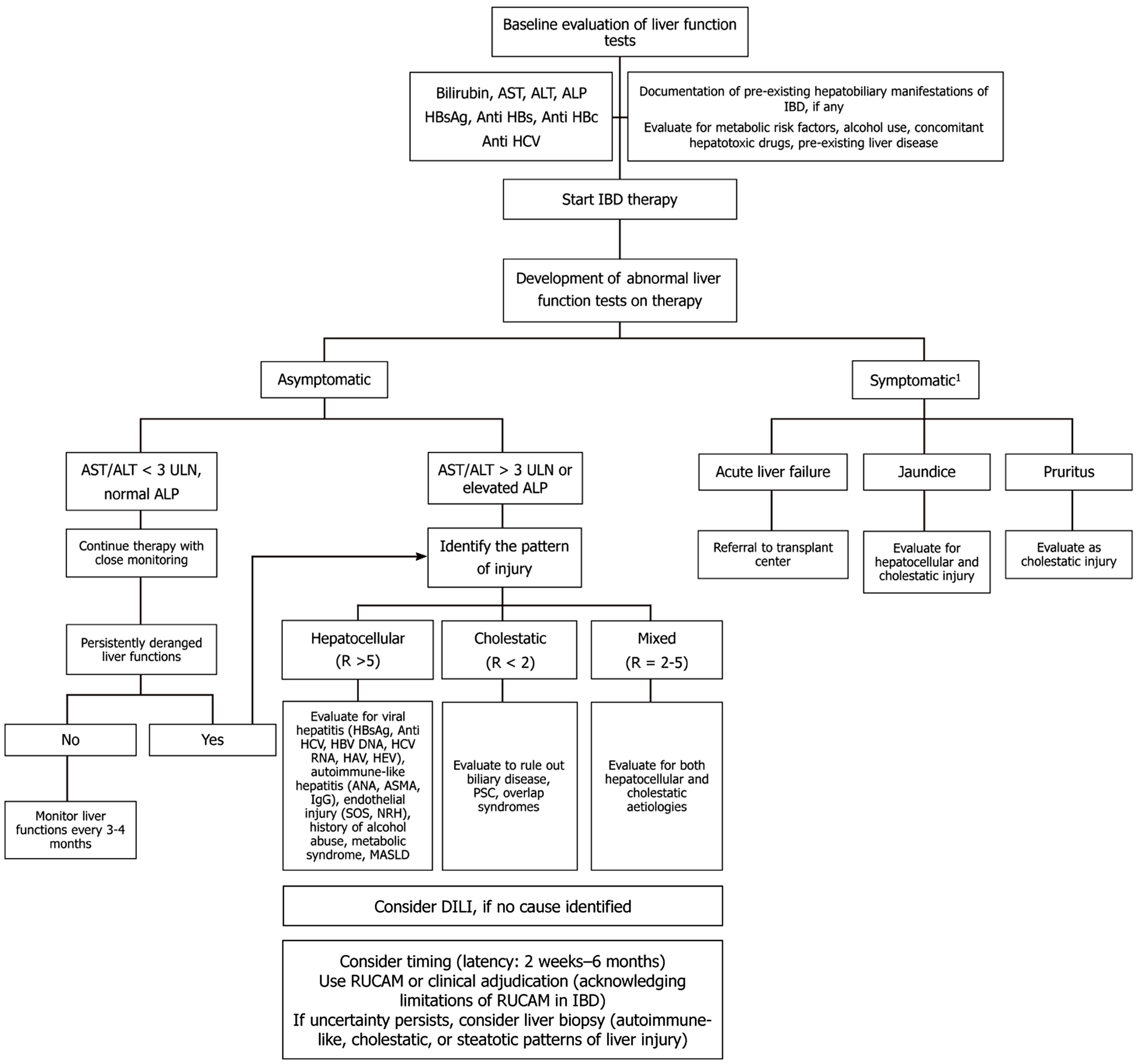
Figure 2 Approach to drug induced liver injury in a patient with inflammatory bowel disease.
1Patients with symptomatic disease have poor out
- Citation: Singh A, Bhardwaj A, Kaur H, Bawa A, Midha V, Sood A. Drug-induced liver injury in inflammatory bowel disease: Challenges in diagnosis and monitoring. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(12): 114084
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i12/114084.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i12.114084