©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Dec 27, 2025; 17(12): 113359
Published online Dec 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i12.113359
Published online Dec 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i12.113359
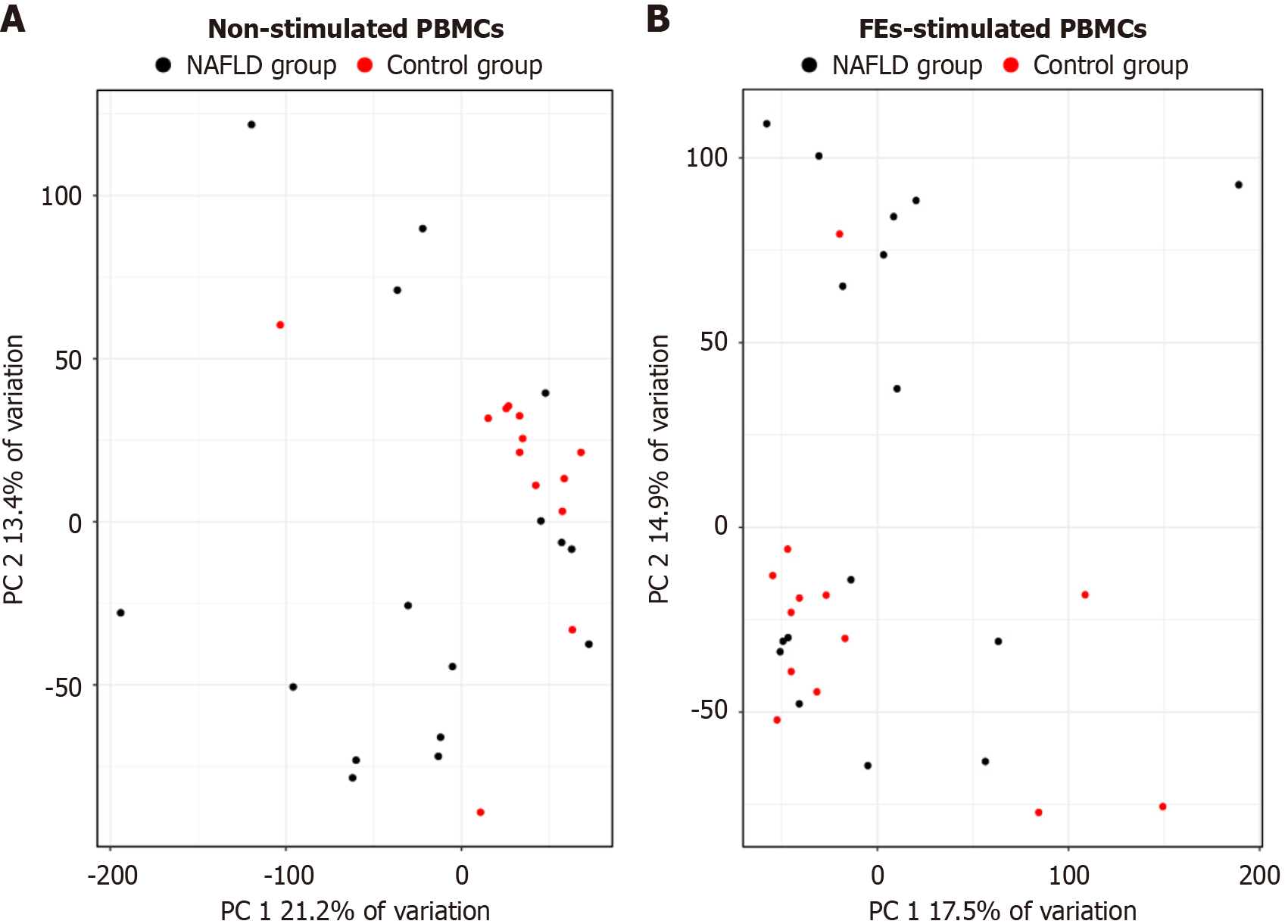
Figure 1 Principal component analysis comparing the transcriptome profiles of peripheral blood mononuclear cells isolated from patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients and controls.
A: Non-stimulated; B: Fecal extract-stimulated. PBMCs: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells; FEs: Fecal extracts; PC: Principal component; NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
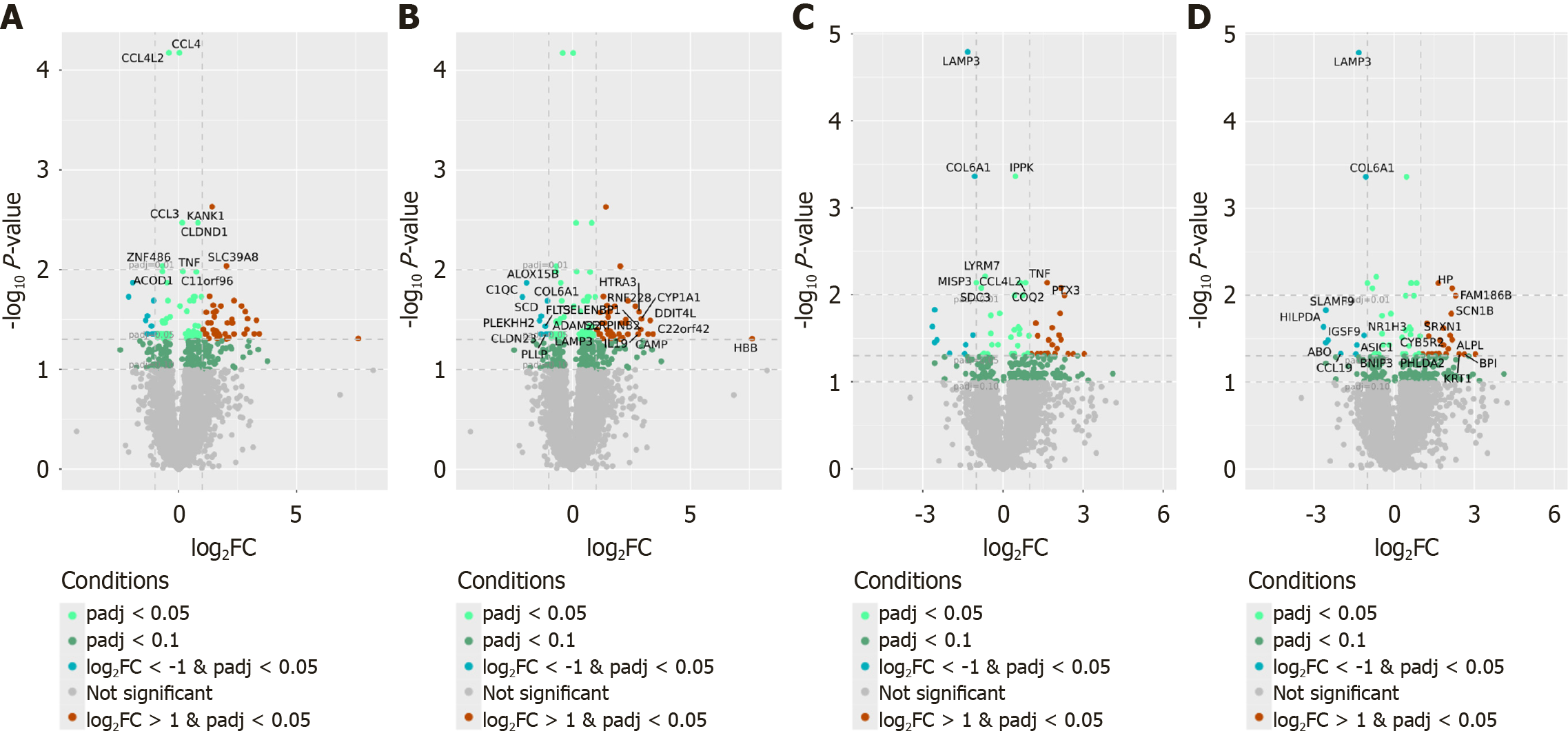
Figure 2 Volcano plots showing differentially expressed genes in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients compared to healthy controls.
A and B: Non-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). Genes highlighted based on statistical significance (lowest adjusted P-values) (A), genes highlighted based on fold change (top upregulated and downregulated genes) (B); C and D: Fecal extract-stimulated PBMCs. Genes highlighted based on statistical significance (lowest adjusted P-values) (C), genes highlighted based on fold change (top upregulated and downregulated genes) (D).
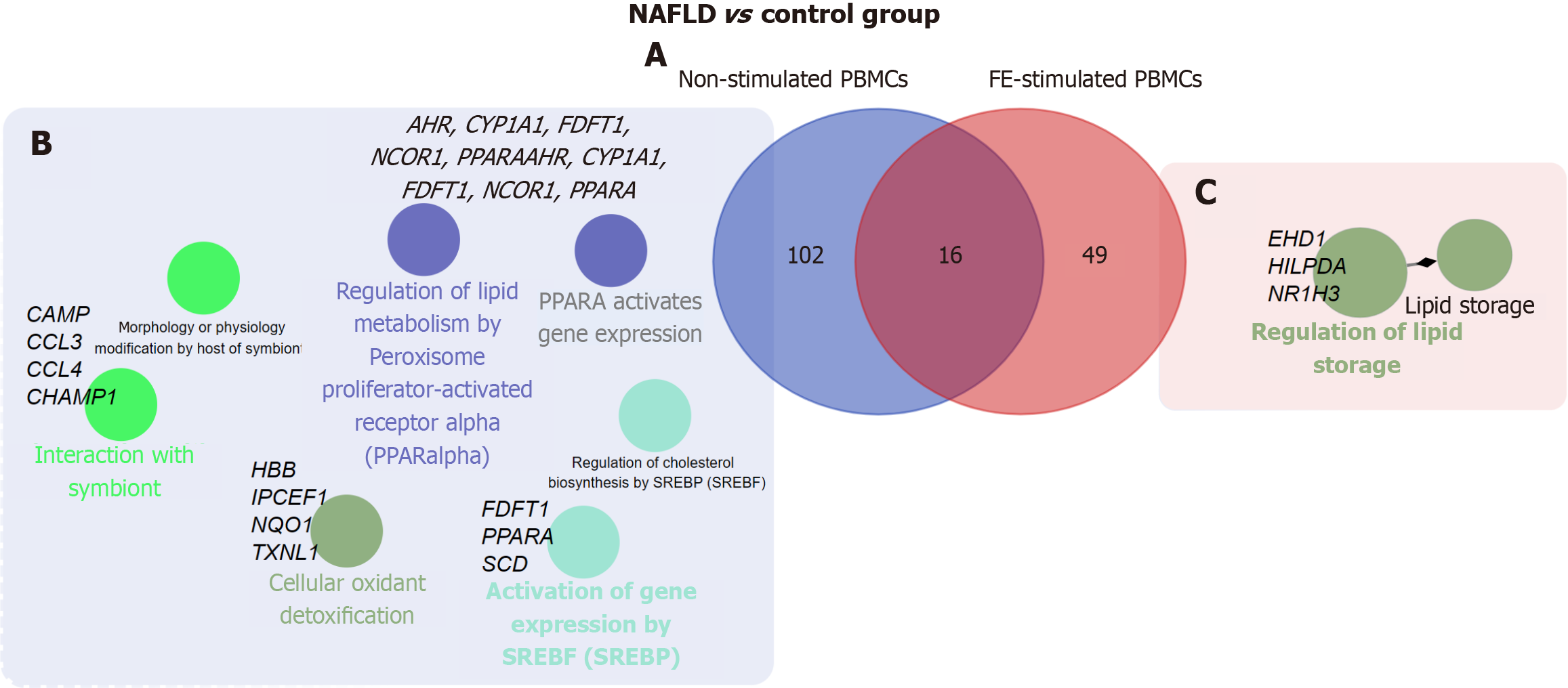
Figure 3 Analysis of differentially expressed genes and pathway enrichment characteristics in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (unstimulated/fecal extracts-stimulated) from patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and healthy controls.
A: Venn diagram of the unique and shared differentially expressed genes in the comparison of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients and controls using non-stimulated and fecal extracts-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells; B and C: Overrepresented pathways identified through Gene Ontology: Biological process and molecular function term categories as well as Reactome pathways for unique differentially expressed genes in the comparison of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients and controls using (B) non-stimulated and (C) fecal extracts-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Associated genes contributing to the most significantly enriched pathways are annotated next to the respective terms. The pathways shown correspond to those with the lowest corrected P-values (Benjamini-Hochberg adjustment). NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; PBMCs: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells; FE: Fecal extracts; PPAR: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha; SREBP: Sterol regulatory element-binding protein.
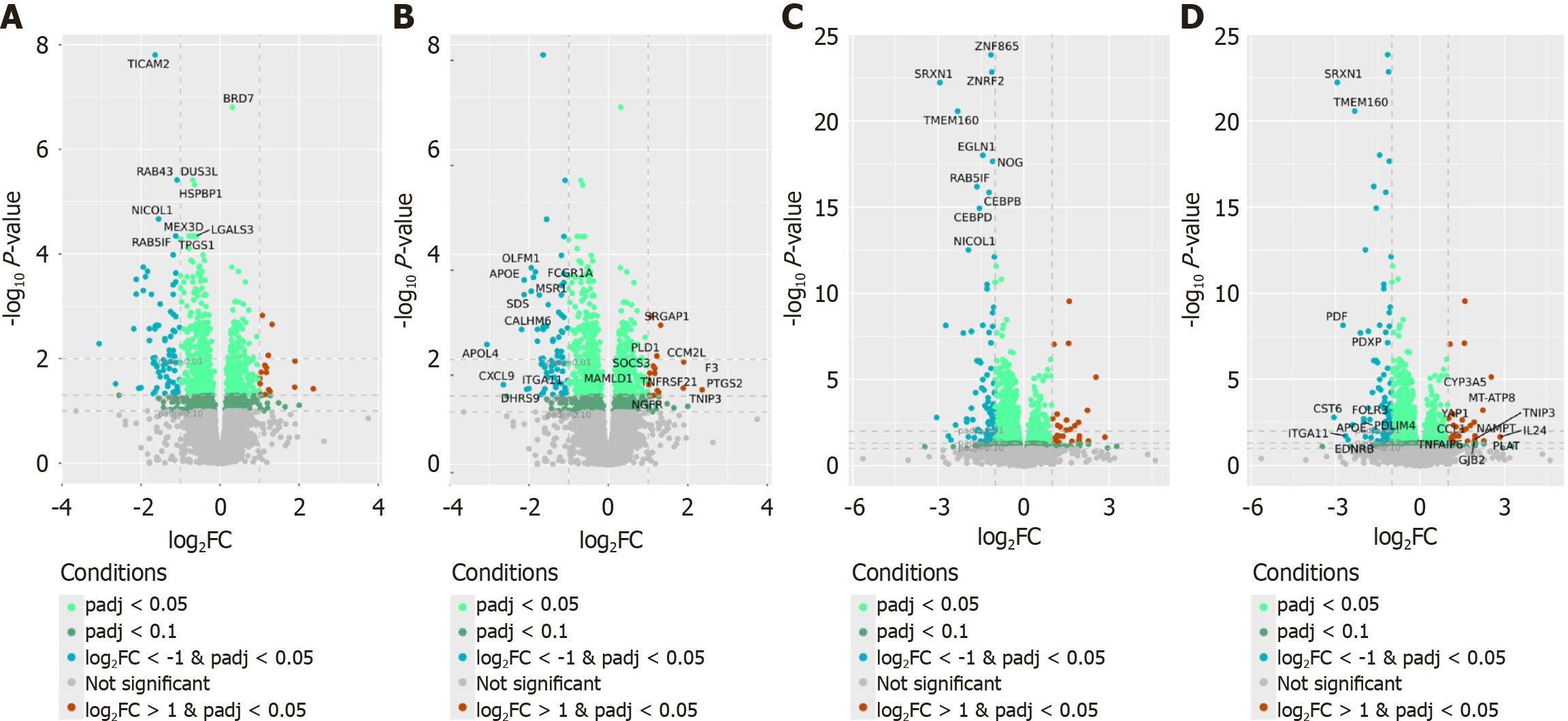
Figure 4 Volcano plots showing differentially expressed genes in the comparison of non-stimulated and fecal extracts-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells isolated from patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients and controls.
A and B: Patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Genes highlighted based on statistical significance (lowest adjusted P-values) (A), genes highlighted based on fold change (top upregulated and downregulated genes) (B); C and D: Control group. Genes highlighted based on statistical significance (lowest adjusted P-values) (C), fecal extracts-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells: Genes highlighted based on fold change (top upregulated and downregulated genes) (D).
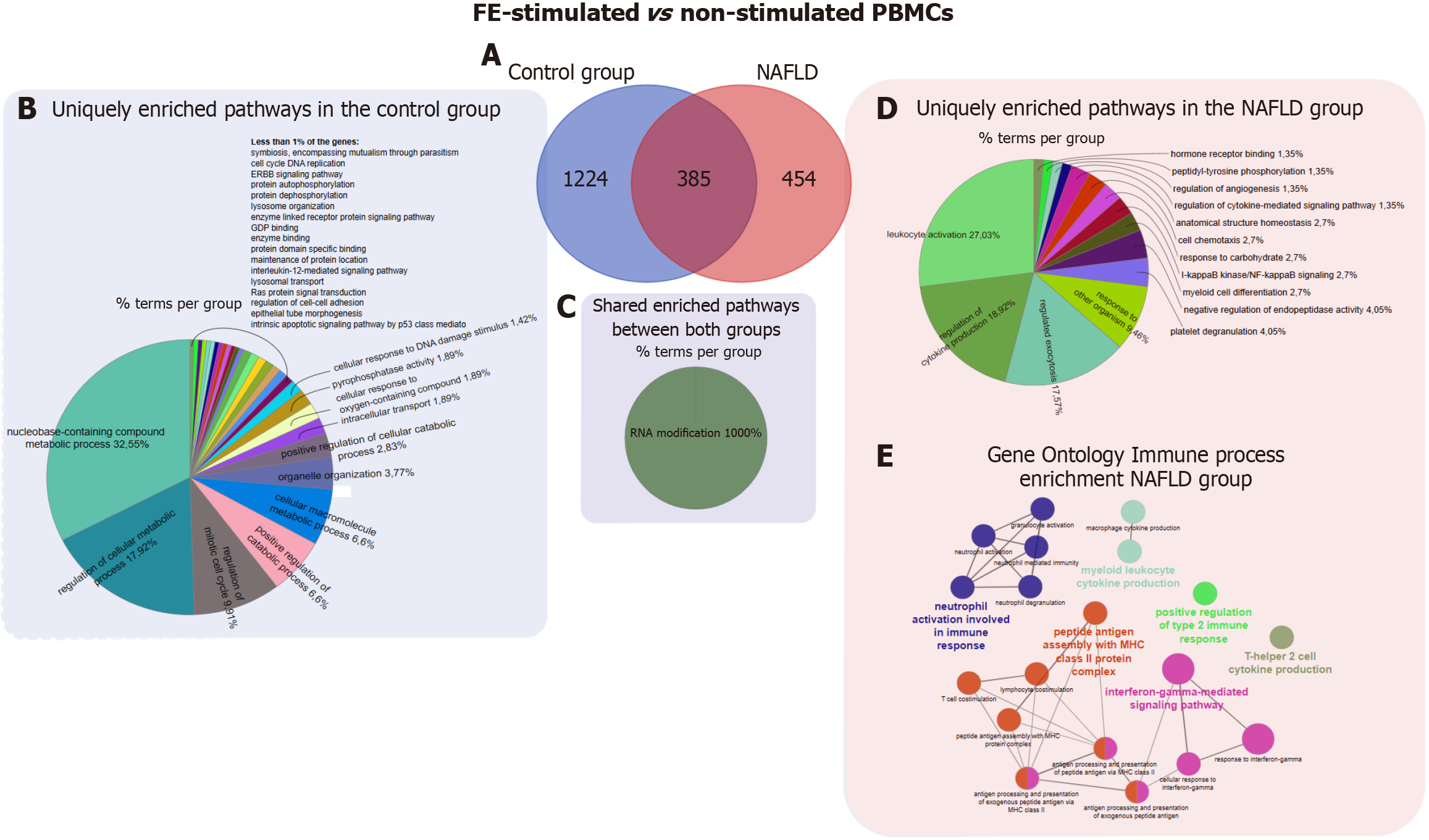
Figure 5 Differential expression genes and functional enrichment analysis of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and controls under fecal extract-stimulated/non-stimulated conditions.
A: Venn diagram of the unique and shared differentially expressed genes in the comparison of fecal extract-stimulated and non-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells isolated from patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients and controls; B-D: The top overrepresented pathways identified through ClueGO functional enrichment analysis (Gene Ontology (GO): Biological process GO and molecular function) of unique (B and C) and common (D) differentially expressed genes; E: The top overrepresented pathways identified through GO - immune system process functional enrichment analysis of unique genes in the comparison of fecal extract-stimulated and non-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells isolated from patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients. The percentage values shown in the pie chart represent the relative contribution of each process to the total set of enriched pathways, based on the distribution of differentially expressed genes. FE: Fecal extracts; PBMCs: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells; NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; ERBB: Family of proteins contains four receptor tyrosine kinases, structurally related to the epidermal growth factor receptor; GDP: Guanosine diphosphate.
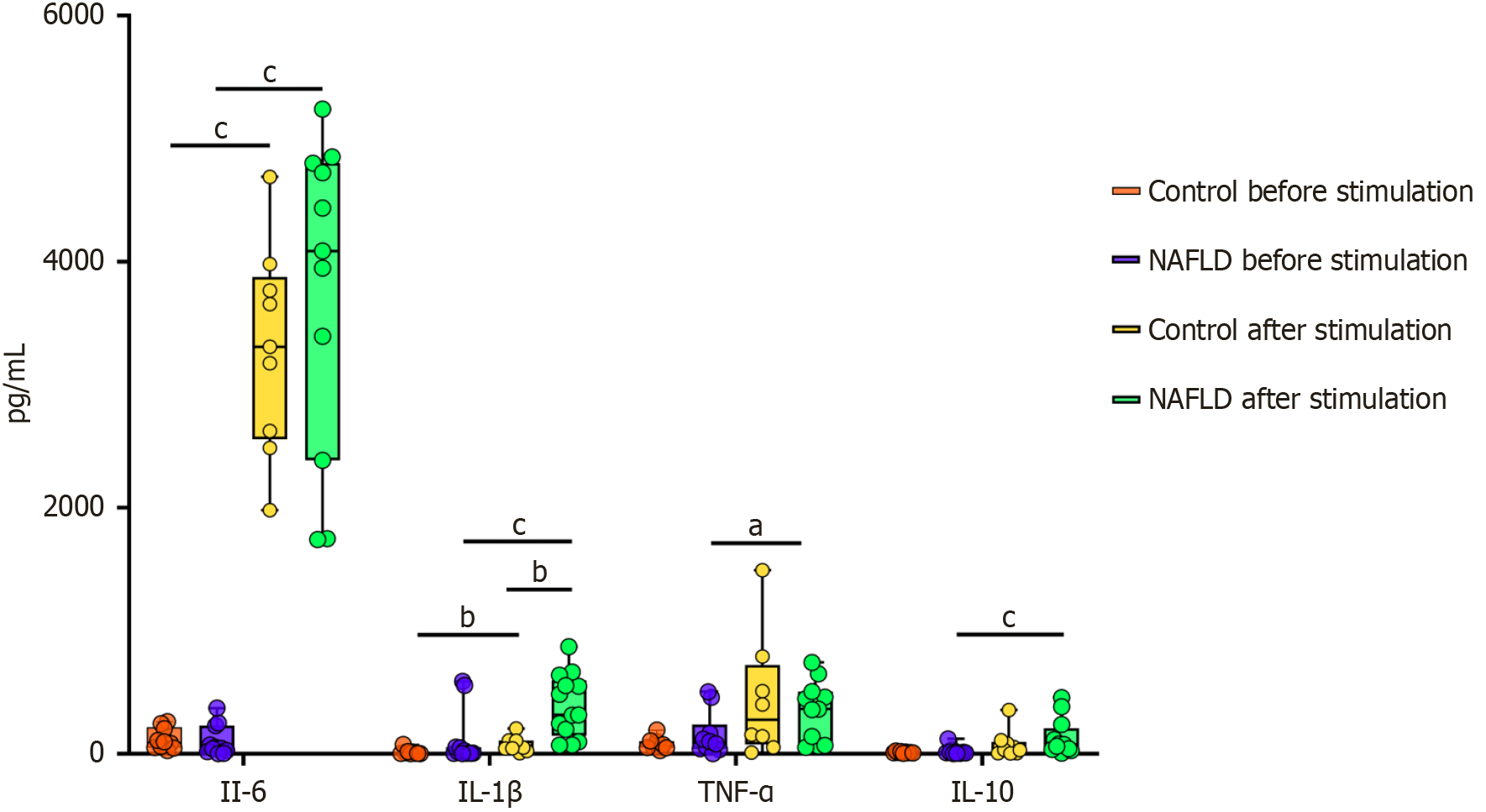
Figure 6 Cytokine production in peripheral blood mononuclear cells isolated from controls and patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients before and after fecal extract stimulation.
Individual data points are displayed alongside median and interquartile range to visualize the distribution and variability of cytokine production in each group. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Citation: Zeber-Lubecka N, Michalkiewicz J, Dabrowska M, Goryca K, Wierzbicka-Rucińska A, Jańczyk W, Jankowska I, Świąder-Leśniak A, Kubiszewska I, Ziemska-Legięcka J, Socha P, Ostrowski J. Transcriptome profiles of peripheral blood mononuclear cells differentiate male adolescents with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease from healthy peers. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(12): 113359
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i12/113359.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i12.113359