©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Hepatol. Aug 27, 2022; 14(8): 1550-1561
Published online Aug 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i8.1550
Published online Aug 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i8.1550
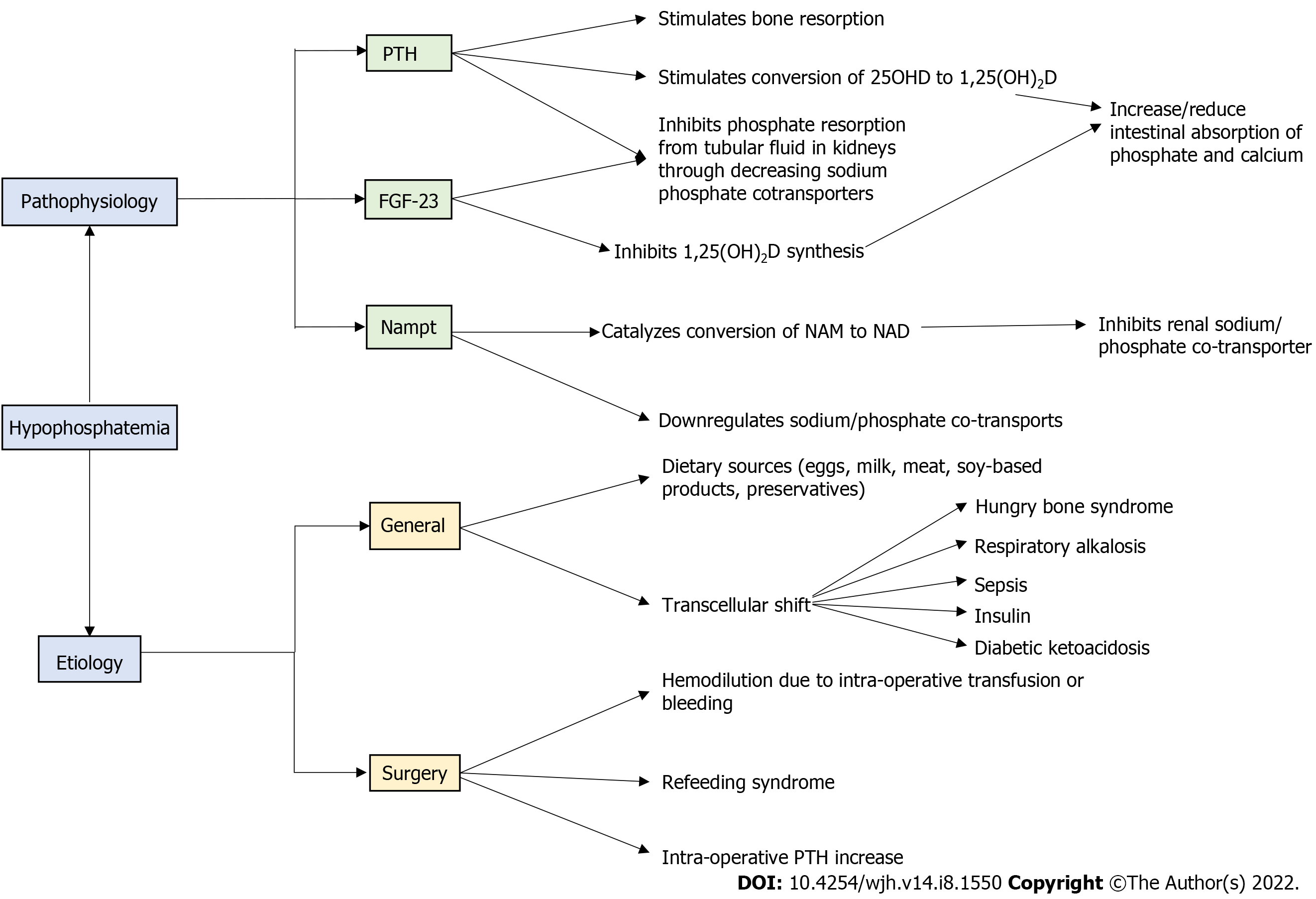
Figure 1 Pathophysiology and etiology outlining hypophosphatemia.
1,25(OH)2D: 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D; 25OHD: 25-hydroxyvitamin D; FGF-23: Fibroblast growth factor-23; NAD: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NAM: Nicotinamide; Nampt: Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase; PTH: Parathyroid hormone.
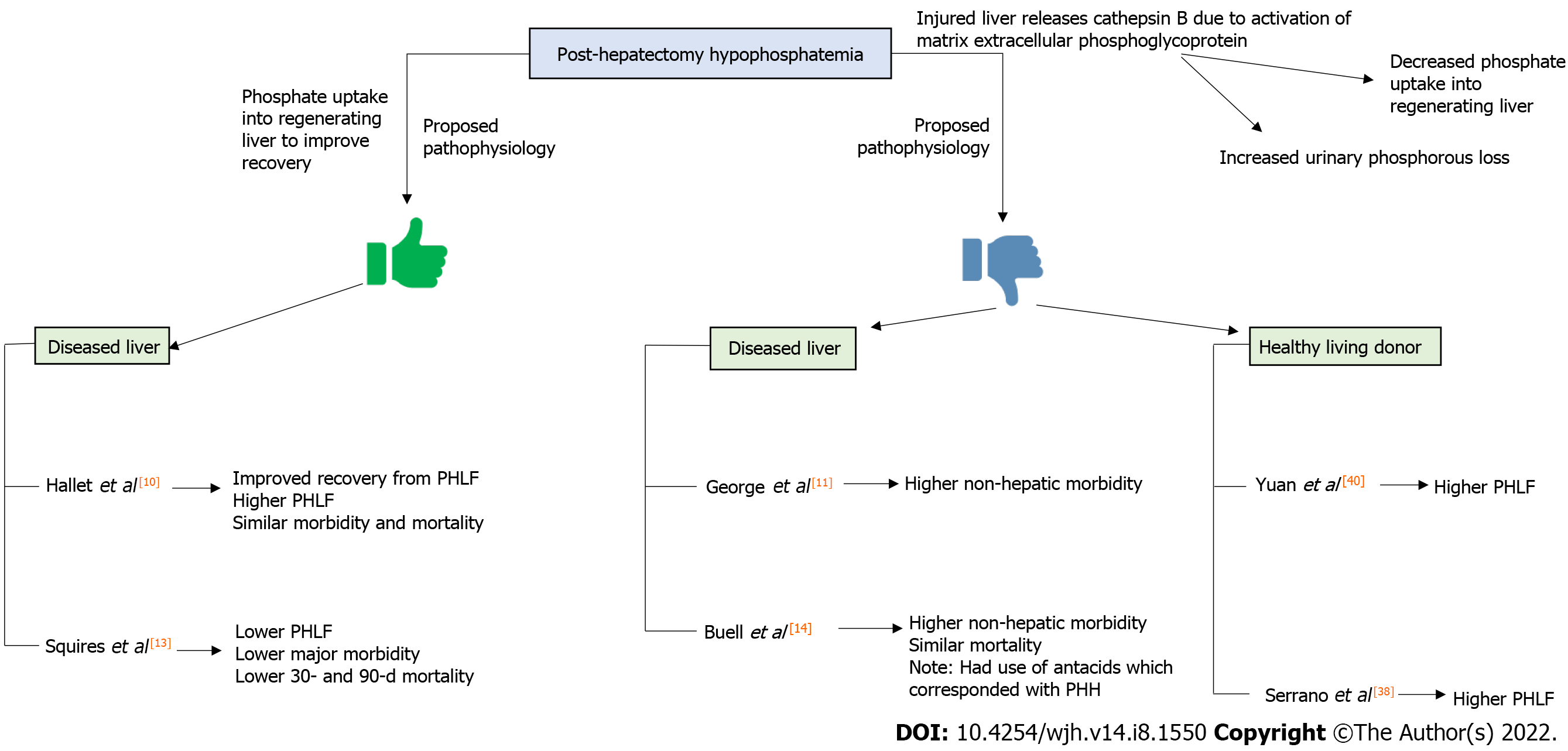
Figure 2 Schematic diagram summarizing the postulated pathophysiology of the impact of post-hepatectomy hypophosphatemia on post-operative outcomes, as well as summary of the advantages (green) and disadvantages (blue) of post-hepatectomy hypoph
- Citation: Chan KS, Mohan S, Shelat VG. Outcomes of patients with post-hepatectomy hypophosphatemia: A narrative review. World J Hepatol 2022; 14(8): 1550-1561
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v14/i8/1550.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v14.i8.1550